
Which of the following complexes is optically inactive?
(a)- $[RhCl(CO)(PP{{h}_{3}})(N{{H}_{3}})]$
(b)- ${{[Fe{{({{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}})}_{3}}]}^{3-}}$
(c)- $[Fe{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]$
(d)- $[Pd{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]$
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Optically inactive means the compound doesn’t rotate the plane of polarized light, so in the coordination complexes only the octahedral complexes are optically active but the square planar complexes are not optically active.
Complete step by step solution:
If the mirror images of the coordination complexes are non-superimposable mirror images of each other then the compounds are observed to be optically active. An optically active compound means the compound has the ability to rotate the plane of polarized light into one direction. The molecules that can form non-superimposable mirror images are called chiral compounds and this phenomenon is known as chirality. Among the octahedral complexes and square planar complexes, only the octahedral complexes are able to rotate the plane of polarized light.
Octahedral complexes are those in which the central metal atoms are joined to the ligands through six bonds and square planar complexes are those complexes in which the central metal atom is joined to the ligands through four bonds.
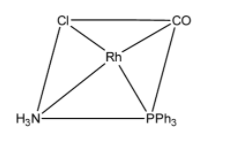
So in $[RhCl(CO)(PP{{h}_{3}})(N{{H}_{3}})]$, there are four ligands and it is a square planar complex. Hence it will be optically inactive.
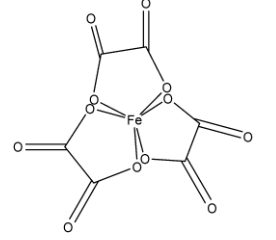
In ${{[Fe{{({{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}})}_{3}}]}^{3-}}$, there are three ligands and each ligand is attached to the central atom by two atoms so it is octahedral complexes. It is optically active.
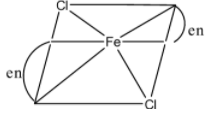
In $[Fe{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]$, there are four ligands, the two en ligand has four attachments to the iron atom so it is octahedral complex. It is optically active.
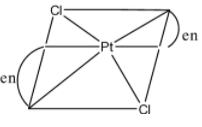
In $[Pd{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]$, there are four ligands, the two en ligand has four attachments to the iron atom so it is octahedral complex. It is optically active.
So the correct answer is an option (a)- $[RhCl(CO)(PP{{h}_{3}})(N{{H}_{3}})]$.
Note: en in the above complexes represent the ethylenediamine and it is a bidentate ligand i.e., there are two donor atoms in en which can attach to the central metal atom. $({{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}})$ is the oxalate ion and it is also a bidentate ligand.
Complete step by step solution:
If the mirror images of the coordination complexes are non-superimposable mirror images of each other then the compounds are observed to be optically active. An optically active compound means the compound has the ability to rotate the plane of polarized light into one direction. The molecules that can form non-superimposable mirror images are called chiral compounds and this phenomenon is known as chirality. Among the octahedral complexes and square planar complexes, only the octahedral complexes are able to rotate the plane of polarized light.
Octahedral complexes are those in which the central metal atoms are joined to the ligands through six bonds and square planar complexes are those complexes in which the central metal atom is joined to the ligands through four bonds.
So in $[RhCl(CO)(PP{{h}_{3}})(N{{H}_{3}})]$, there are four ligands and it is a square planar complex. Hence it will be optically inactive.

In ${{[Fe{{({{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}})}_{3}}]}^{3-}}$, there are three ligands and each ligand is attached to the central atom by two atoms so it is octahedral complexes. It is optically active.

In $[Fe{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]$, there are four ligands, the two en ligand has four attachments to the iron atom so it is octahedral complex. It is optically active.

In $[Pd{{(en)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}]$, there are four ligands, the two en ligand has four attachments to the iron atom so it is octahedral complex. It is optically active.

So the correct answer is an option (a)- $[RhCl(CO)(PP{{h}_{3}})(N{{H}_{3}})]$.
Note: en in the above complexes represent the ethylenediamine and it is a bidentate ligand i.e., there are two donor atoms in en which can attach to the central metal atom. $({{C}_{2}}{{O}_{4}})$ is the oxalate ion and it is also a bidentate ligand.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




