
Which of the following best describe the diagram of a molecular orbital?
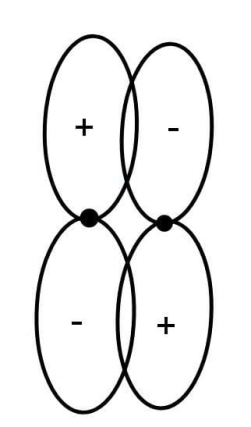
A.A bonding \[\pi \] orbital
B.A non-bonding orbital
C.An antibonding \[\sigma \] orbital
D.An antibonding \[\pi \] orbitals

Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:For this we must know the concept bonding of orbitals and shapes of orbitals. P orbital’s forms \[\pi \] bonds along sidewise interaction and in opposite phase constructive interference occurs.
Complete step by step answer:
There are different shapes of different orbitals. s orbital has spherical shapes and p orbital has two lobes and is termed as dumbbell shape and d orbital has double dumbbell shape and so on.
In the given figure we have been given two p orbital bonds to each other. As we can see each orbital has two lobes. They are overlapping with each other and show the formation of covalent bonds.
The formation of bonds in a chemical compound or bond also depends on in which phase the orbitals are combining. The plus and minus signs on the lobe does not indicate the charge but represents the phase. The physical significance of phase comes in existence when the orbital interacts. If the two orbits combine in the same phase then the electron density increases and constructive interference occurs. But if the orbitals combine in different phases than the net electron density decreases and destructive interference occurs. When constructive interference occurs the bonding molecular orbitals are formed and when they do destructive interference then antibonding molecular orbital forms.
Also p orbital can form either sigma bond or pi bond. If it interacts linearly i.e. only one lobe interaction is there then sigma bond forms and when sideways or lateral interaction occurs i.e. both the lobes interact then pi bond forms.
Since from the above diagram we can see that both the lobes are interacting, it means a \[\pi \] bond must have been formed. And since a positive lobe of one p orbital interacts with a negative lobe of another p orbital, an antibonding orbital must have been formed.
Hence option D is correct.
Note:
According to MOT, molecular orbital theory, whenever two orbital of nearly same energy mixes then two new orbital forms one with the lower energy which is called BMO, bonding molecular orbital and one with higher energy termed as ABMO, antibonding molecular orbital. This concept is completely opposite of hybridization in which orbitals of different energy mixes to produce orbitals of nearly the same energy.
Complete step by step answer:
There are different shapes of different orbitals. s orbital has spherical shapes and p orbital has two lobes and is termed as dumbbell shape and d orbital has double dumbbell shape and so on.
In the given figure we have been given two p orbital bonds to each other. As we can see each orbital has two lobes. They are overlapping with each other and show the formation of covalent bonds.
The formation of bonds in a chemical compound or bond also depends on in which phase the orbitals are combining. The plus and minus signs on the lobe does not indicate the charge but represents the phase. The physical significance of phase comes in existence when the orbital interacts. If the two orbits combine in the same phase then the electron density increases and constructive interference occurs. But if the orbitals combine in different phases than the net electron density decreases and destructive interference occurs. When constructive interference occurs the bonding molecular orbitals are formed and when they do destructive interference then antibonding molecular orbital forms.
Also p orbital can form either sigma bond or pi bond. If it interacts linearly i.e. only one lobe interaction is there then sigma bond forms and when sideways or lateral interaction occurs i.e. both the lobes interact then pi bond forms.
Since from the above diagram we can see that both the lobes are interacting, it means a \[\pi \] bond must have been formed. And since a positive lobe of one p orbital interacts with a negative lobe of another p orbital, an antibonding orbital must have been formed.
Hence option D is correct.
Note:
According to MOT, molecular orbital theory, whenever two orbital of nearly same energy mixes then two new orbital forms one with the lower energy which is called BMO, bonding molecular orbital and one with higher energy termed as ABMO, antibonding molecular orbital. This concept is completely opposite of hybridization in which orbitals of different energy mixes to produce orbitals of nearly the same energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




