
Which monosaccharide forms cellulose?
A. Beta D Glucose
B. Alpha D Galactose
C. Beta D Fructose
D. Alpha D Fructose
Answer
486.9k+ views
Hint: Carbohydrates are an important part of our diet; natural sources of carbohydrates include grains, fruits, and vegetables. Carbohydrates supply energy to the body, particularly glucose, a simple sugar found in starch and found in a variety of everyday foods. Carbohydrates play a variety of roles in humans, animals, and plants.
Complete answer:
Glucose is made up of two isomers of the aldohexose sugars, one of which (D-glucose) is physiologically active. L-glucose, the mirror counterpart of D-glucose, cannot be utilised by cells. The open-chain form of glucose (either 'D-' or 'L-') is in equilibrium in solutions with many cyclic isomers, each of which contains a ring of carbons closed by one oxygen atom.
There are two types of D-glucose: alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-glucose. Only the direction in which the -H and -OH groups point to carbon 1 differs. Starch is generated when alpha-glucose molecules are chemically bonded to create a polymer. When beta-glucose molecules are linked together to create a polymer, the result is cellulose.
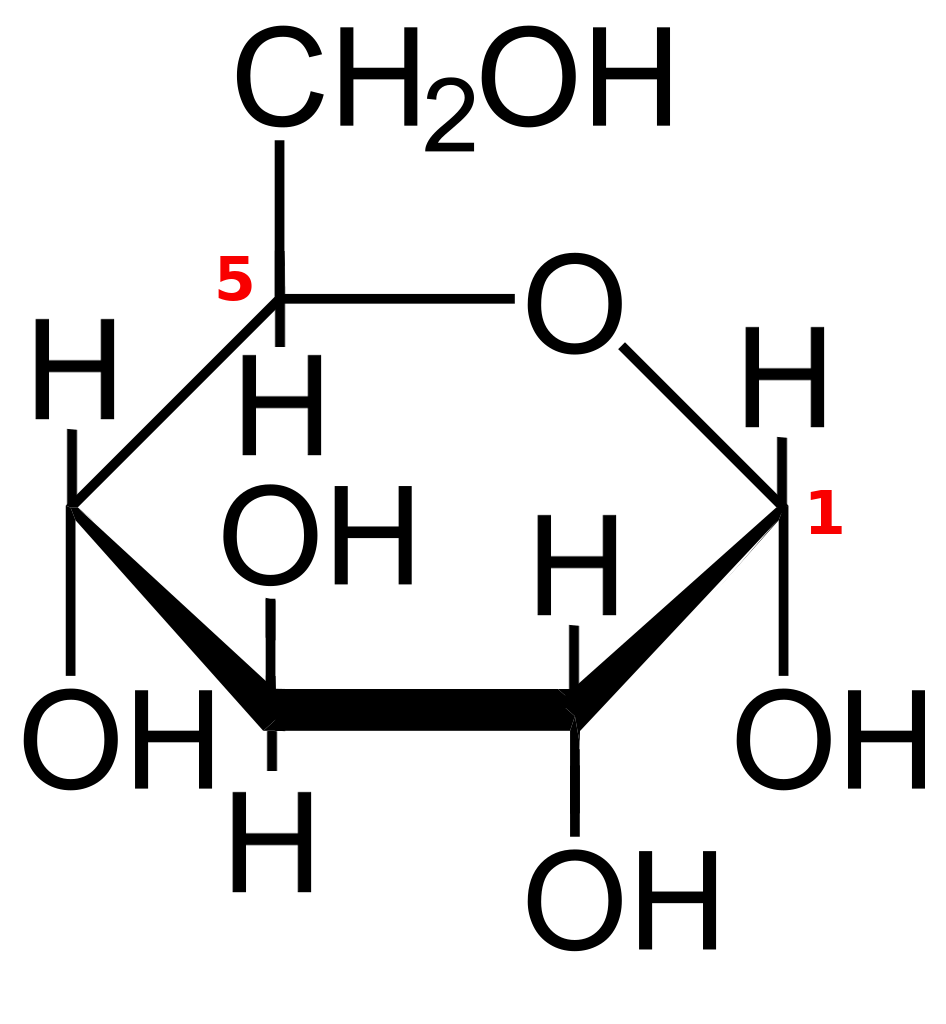
Sucrose is made up of two monomers α-D-Glucose and β-D-Fructose.
Cellulose made up of β -D-Glucose.
Starch made up of α-D-Glucose.
Lactose is made up of two monomers β-D-Galactose and β-D-Glucose.
So, the correct answer is A. β -D-Glucose.
The stoichiometric formula for carbohydrates is ($CH_2O$)n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In other words, the carbon-to-hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio in carbohydrate molecules is 1:2:1. This formula also explains how the term "carbohydrate" came to be: the components are carbon ("carbo") and water (thus "hydrate"). Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides are the three forms of carbohydrates.
The notation 'a-' indicates that the hydroxyl group linked to C-1 and the -$CH_2OH$ group at C-5 are on opposing sides of the ring's plane (a trans arrangement), whereas 'ß-' indicates that they are on the same side of the plane (a cis arrangement).
Cellulose, the other primary glucose polysaccharide present in plants, has a structural rather than a nutritive function. One of the most abundant organic substances in the biosphere is cellulose. Each year, a lot of cellulose is generated and destroyed on Earth. It's a non-branched polymer made up of glucose residues linked together by -1,4 links.
Note:-
The covalent chemical links that connect ring-shaped sugar molecules to other molecules are known as glycosidic bonds. They can be O-linked or N-linked because they are formed by a condensation process between an alcohol or amine from one molecule and the anomeric carbon of the sugar.
Complete answer:
Glucose is made up of two isomers of the aldohexose sugars, one of which (D-glucose) is physiologically active. L-glucose, the mirror counterpart of D-glucose, cannot be utilised by cells. The open-chain form of glucose (either 'D-' or 'L-') is in equilibrium in solutions with many cyclic isomers, each of which contains a ring of carbons closed by one oxygen atom.
There are two types of D-glucose: alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-glucose. Only the direction in which the -H and -OH groups point to carbon 1 differs. Starch is generated when alpha-glucose molecules are chemically bonded to create a polymer. When beta-glucose molecules are linked together to create a polymer, the result is cellulose.

Sucrose is made up of two monomers α-D-Glucose and β-D-Fructose.
Cellulose made up of β -D-Glucose.
Starch made up of α-D-Glucose.
Lactose is made up of two monomers β-D-Galactose and β-D-Glucose.
So, the correct answer is A. β -D-Glucose.
The stoichiometric formula for carbohydrates is ($CH_2O$)n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In other words, the carbon-to-hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio in carbohydrate molecules is 1:2:1. This formula also explains how the term "carbohydrate" came to be: the components are carbon ("carbo") and water (thus "hydrate"). Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides are the three forms of carbohydrates.
The notation 'a-' indicates that the hydroxyl group linked to C-1 and the -$CH_2OH$ group at C-5 are on opposing sides of the ring's plane (a trans arrangement), whereas 'ß-' indicates that they are on the same side of the plane (a cis arrangement).
Cellulose, the other primary glucose polysaccharide present in plants, has a structural rather than a nutritive function. One of the most abundant organic substances in the biosphere is cellulose. Each year, a lot of cellulose is generated and destroyed on Earth. It's a non-branched polymer made up of glucose residues linked together by -1,4 links.
Note:-
The covalent chemical links that connect ring-shaped sugar molecules to other molecules are known as glycosidic bonds. They can be O-linked or N-linked because they are formed by a condensation process between an alcohol or amine from one molecule and the anomeric carbon of the sugar.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




