
Which is the primary $CO_{2}$ acceptor for the $C_{3}$ plant and $C_{4}$ plant.
Answer
526.5k+ views
Hint: Plants, which do not have the adaptation to combat photorespiration (a wasteful process), such plants are known as $C_{3}$ plants. $C_{4}$ plants can efficiently combat photorespiration and can fix (assimilate or take in) the carbon dioxide more efficiently than $C_{3}$ plants.
Complete answer:
The primary $CO_{2}$ acceptor of $C_{3}$ and $C_{4}$ plants is RuBP (Ribulose 1-5-bisphosphate) and PEP (Phosphoenolpyruvate), respectively.
C3 cycle or Calvin cycle: In the Calvin cycle, the carbon dioxide acceptor molecule is RuBP and the enzyme catalyzing this reaction is RuBP carboxylase. In this process, the reduction of carbon dioxide gives the first stable product, a three-carbon compound, which is 3-phosphoglyceric acid or 3PGA. The plant which follows the $C_{4}$ pathway is called $C_{3}$ plants.
First reaction of $C_{3}$ cycle:
$6Ribulose-1-5-bisphosphate(RuBP)+6CO_{2}+6H_{2}O\rightarrow 12\times3-Phosphoglyceric acid (3PGA)$
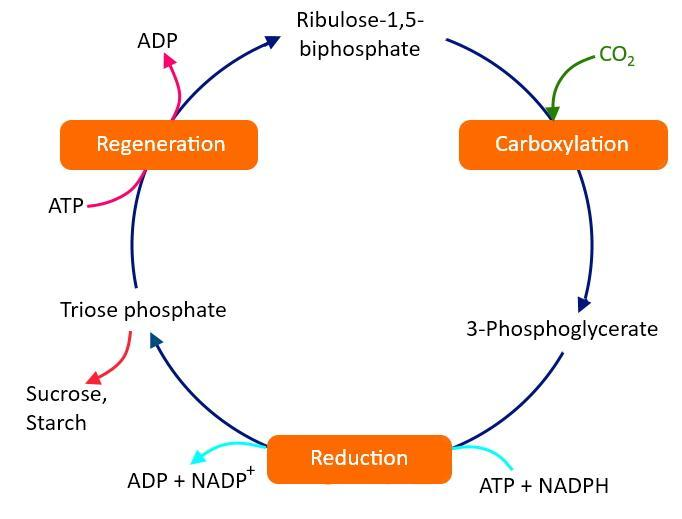
Figure: Complete the $C_{3}$ cycle.
$C_{4}$ cycle (Hatch and Slack Pathway): The primary acceptor of the carbon dioxide molecule is the PEP (phosphoenolpyruvic acid) which is present in the chloroplast of the mesophyll cells. The first stable compound produced in the oxaloacetic acid, in the presence of enzyme PEP carboxylase. Since oxaloacetic acid is the first stable 4-carbon compound, it is named as a $C_{4}$ cycle.
The first reaction of the $C_{4}$ cycle:
$PEP+CO_{2}+H_{2}O\rightarrow Oxalo-acetic acid+H_{3}PO_{4}$
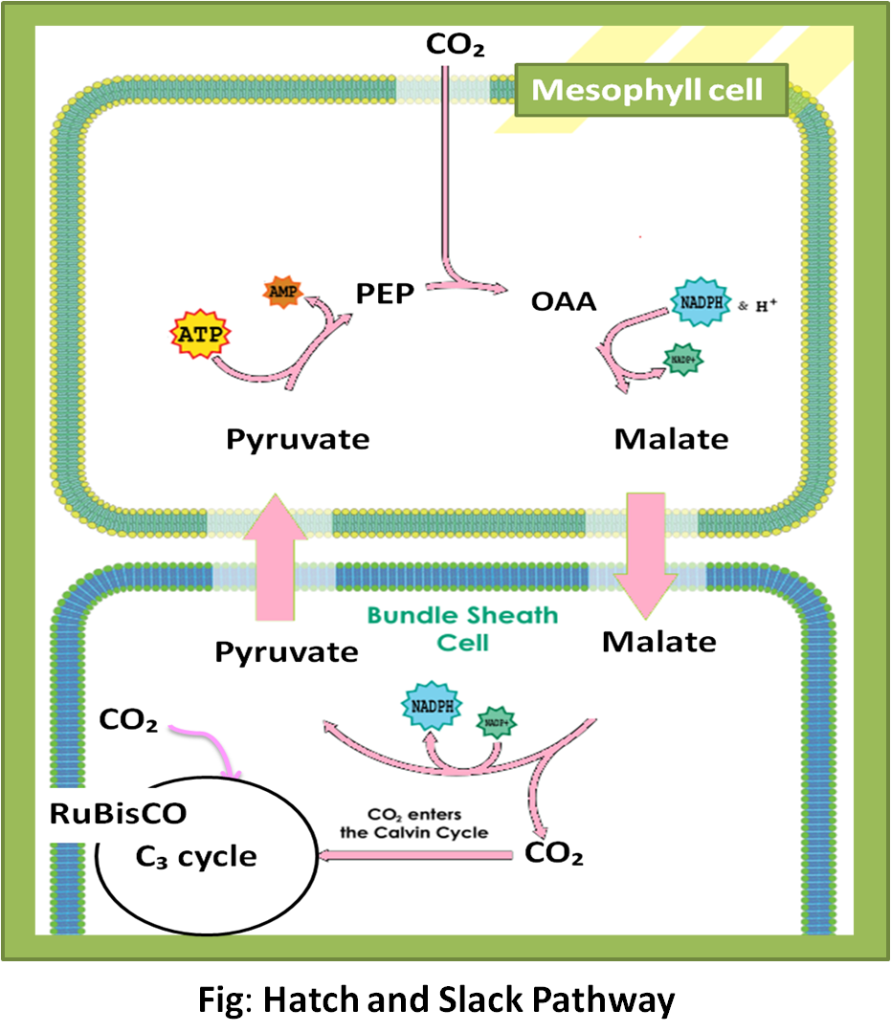
Additional Information:
Photorespiration: It is a reverse process as compared to photosynthesis. It involves the uptake of $O_{2}$ and the release of $CO_{2}$ in light and results from the biosynthesis of glycolate in the chloroplast. After which, the glycolate acid is metabolized in the same leaf cell. Peroxisomes are the cellular site for photorespiration.
Photorespiration is a wasteful process because no energy-rich compound is produced and loss of carbon takes place during such a process. This process has a significant impact on $C_{3}$ plants but in $C_{4}$ plants such a process is insignificant.
Note:
- The leaves of $C_{3}$ plants do not show kranz anatomy (where the mesophyll cells are clustered around the bundle sheath cells in a ring-like structure). $C_{3}$ plants exhibit dark reactions where they utilize the products of the light reaction and do not require sunlight. 95% of plants on earth are $C_{3}$ type.
- The leaves of $C_{4}$ plants possess kranz anatomy, and the chloroplasts of these plants are dimorphic. About 5% of plants on earth are $C_{4}$ type.
Complete answer:
The primary $CO_{2}$ acceptor of $C_{3}$ and $C_{4}$ plants is RuBP (Ribulose 1-5-bisphosphate) and PEP (Phosphoenolpyruvate), respectively.
C3 cycle or Calvin cycle: In the Calvin cycle, the carbon dioxide acceptor molecule is RuBP and the enzyme catalyzing this reaction is RuBP carboxylase. In this process, the reduction of carbon dioxide gives the first stable product, a three-carbon compound, which is 3-phosphoglyceric acid or 3PGA. The plant which follows the $C_{4}$ pathway is called $C_{3}$ plants.
First reaction of $C_{3}$ cycle:
$6Ribulose-1-5-bisphosphate(RuBP)+6CO_{2}+6H_{2}O\rightarrow 12\times3-Phosphoglyceric acid (3PGA)$

Figure: Complete the $C_{3}$ cycle.
$C_{4}$ cycle (Hatch and Slack Pathway): The primary acceptor of the carbon dioxide molecule is the PEP (phosphoenolpyruvic acid) which is present in the chloroplast of the mesophyll cells. The first stable compound produced in the oxaloacetic acid, in the presence of enzyme PEP carboxylase. Since oxaloacetic acid is the first stable 4-carbon compound, it is named as a $C_{4}$ cycle.
The first reaction of the $C_{4}$ cycle:
$PEP+CO_{2}+H_{2}O\rightarrow Oxalo-acetic acid+H_{3}PO_{4}$

Additional Information:
Photorespiration: It is a reverse process as compared to photosynthesis. It involves the uptake of $O_{2}$ and the release of $CO_{2}$ in light and results from the biosynthesis of glycolate in the chloroplast. After which, the glycolate acid is metabolized in the same leaf cell. Peroxisomes are the cellular site for photorespiration.
Photorespiration is a wasteful process because no energy-rich compound is produced and loss of carbon takes place during such a process. This process has a significant impact on $C_{3}$ plants but in $C_{4}$ plants such a process is insignificant.
Note:
- The leaves of $C_{3}$ plants do not show kranz anatomy (where the mesophyll cells are clustered around the bundle sheath cells in a ring-like structure). $C_{3}$ plants exhibit dark reactions where they utilize the products of the light reaction and do not require sunlight. 95% of plants on earth are $C_{3}$ type.
- The leaves of $C_{4}$ plants possess kranz anatomy, and the chloroplasts of these plants are dimorphic. About 5% of plants on earth are $C_{4}$ type.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




