
Which d-orbitals have a different shape from the rest of all d-orbitals?
A. ${d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}$
B. ${d_{{z^2}}}$
C. ${d_{xz}}$
D. ${d_{xy}}$
E. ${d_{xy}}$
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint:An orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of Bohr’s orbit. In contrast to his concept of a circular orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. The d orbital contains 10 electrons. The d orbital is a clover shape because the electron is pushed out four times during the rotation.
Complete step by step answer:
The d orbital has ten protons to complete a fourth level of tetrahedral structure. With three spin aligned protons, it would have a spherical shape, yet four times during the rotation will have gluons that align with protons of the opposite spin to force an electron.
Now, we see the figure of all d-orbitals except ${d_{{z^2}}}$ because it has four lobes and has only two lobes.
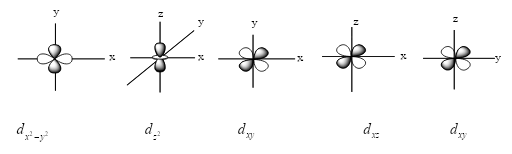
From the above figure, we see that the d-orbitals are in different shapes. ${d_{{z^2}}}$orbital has a different shape from rest of all d-orbitals.
${d_{{z^2}}}$ degenerate with other d orbitals, it has no nodal planes, instead it has 2 nodal cones. Instead of having 4 lobes, it has 2 lobes and 1 ring. That’s why this orbital is so different from the rest.
Hence, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:The standard procedure in differential calculus is to use a linear combination of two functions to produce one independent one. So ${d_{{z^2}}}$ looks different because it is a linear combination of two functions. In this orbital, 2 lobes lie on the z-axis as we see.
Complete step by step answer:
The d orbital has ten protons to complete a fourth level of tetrahedral structure. With three spin aligned protons, it would have a spherical shape, yet four times during the rotation will have gluons that align with protons of the opposite spin to force an electron.
Now, we see the figure of all d-orbitals except ${d_{{z^2}}}$ because it has four lobes and has only two lobes.

From the above figure, we see that the d-orbitals are in different shapes. ${d_{{z^2}}}$orbital has a different shape from rest of all d-orbitals.
${d_{{z^2}}}$ degenerate with other d orbitals, it has no nodal planes, instead it has 2 nodal cones. Instead of having 4 lobes, it has 2 lobes and 1 ring. That’s why this orbital is so different from the rest.
Hence, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:The standard procedure in differential calculus is to use a linear combination of two functions to produce one independent one. So ${d_{{z^2}}}$ looks different because it is a linear combination of two functions. In this orbital, 2 lobes lie on the z-axis as we see.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




