
Which constituent radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum is used:
A) In RADAR.
B) To photograph internal parts of a human body.
C) For taking photographs of the sky during night and foggy conditions.
Give one reason for your answer in each case.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: The electromagnetic spectrum consists of various types of radiations. Each constituent radiations have different wavelengths and frequencies. These properties are applied to obtain desired use case scenarios.
Complete step by step solution:
The electromagnetic spectrum consists of electromagnetic waves in a wide range of different frequencies having respective wavelengths for that radiation. The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into separate bands which contain a set of radiations.
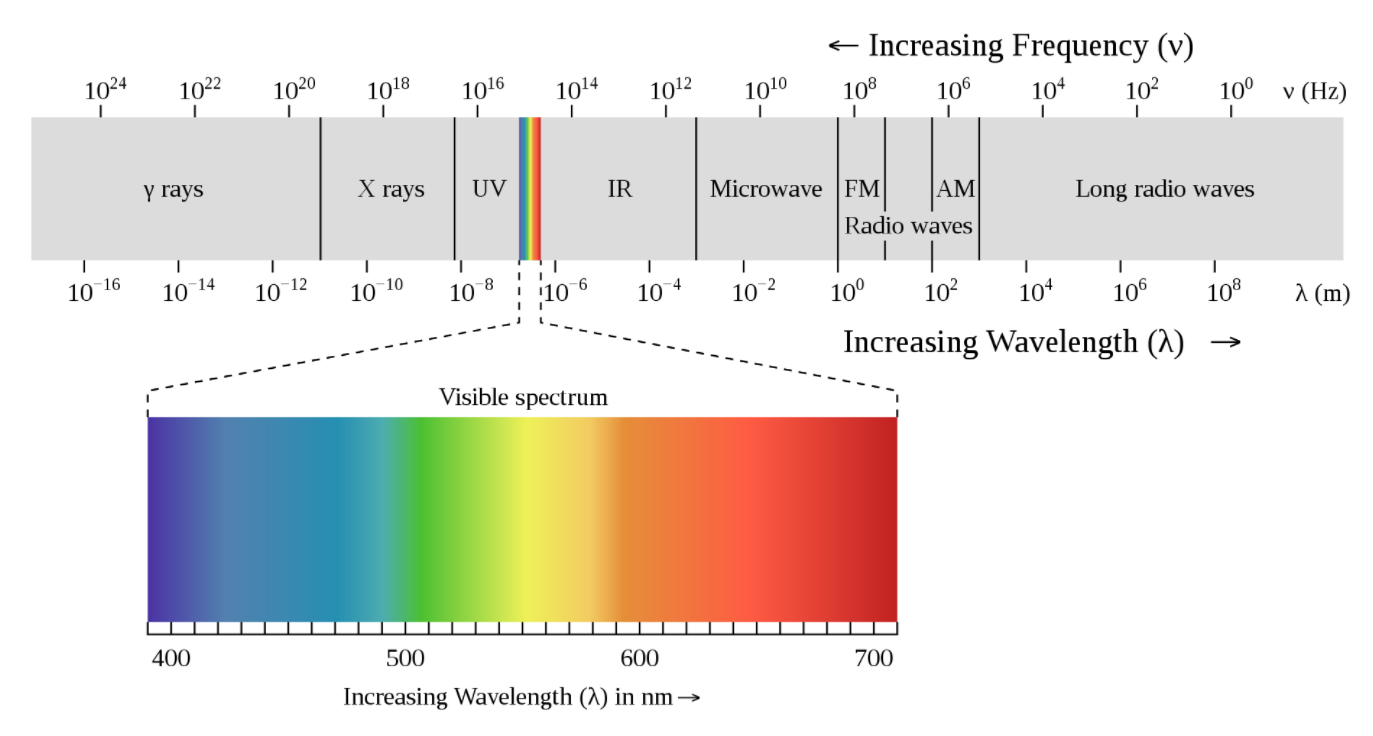
Radiations with low frequency have high wavelength while radiations with high frequency have low wavelengths. This determines which radiations are better to use in particular use case scenarios. For example, when our requirement is long distance communication we choose radiations with longer wavelength.
A) In RADAR:
In RADAR, we use Radio Waves. The term RADAR stands for Radio Detection and Ranging. The principle of RADAR is by transmitting waves to a particular object and then recording the received waves by the object and thereby calculating our desired information.
To achieve this, the transmitted wave needs to travel a long distance. For long distance, the wave has to have long wavelengths. Hence, in RADAR we use Radio waves. Radio waves have wavelengths ranging from $\lambda = {10^0} - {10^9}m$.
B) To photograph internal objects of the body.
In this case we use X-Rays. X-Rays have shorter wavelengths and higher frequency. Higher frequency helps reduce penetration and hence reveal location inside the body where it can’t penetrate. Most organs absorb different amounts of the radiation. While bones absorb the least radiations, waves don’t penetrate through it and hence appear white. Also, lungs absorb the most as it contains air, and hence it appears black. They have wavelengths ranging from $\lambda = {10^{ - 8}} - {10^{ - 11}}m$.
C) For taking photographs of the sky during the night and foggy conditions.
Here, Infra-Red Radiations are used. IR radiations have longer wavelengths and lower frequencies. This provides longer penetration by the waves and lesser scattering in the atmosphere and therefore can take photographs in foggy conditions. They have wavelengths ranging from $\lambda = {10^{ - 6}} - {10^{ - 3}}m$.
Note: The wavelength of the radiation is also inversely proportional to the energy of the radiation. A popular use case scenario of RADAR is determining the depth of the sea, where waves are transmitted into the water and waves are received back after some time. The time delay is used to calculate the depth of the sea. X-Rays are not only used in the field of medicine but also in airport security where luggage of passengers are inspected using X-Rays to detect security threats.
Complete step by step solution:
The electromagnetic spectrum consists of electromagnetic waves in a wide range of different frequencies having respective wavelengths for that radiation. The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into separate bands which contain a set of radiations.

Radiations with low frequency have high wavelength while radiations with high frequency have low wavelengths. This determines which radiations are better to use in particular use case scenarios. For example, when our requirement is long distance communication we choose radiations with longer wavelength.
A) In RADAR:
In RADAR, we use Radio Waves. The term RADAR stands for Radio Detection and Ranging. The principle of RADAR is by transmitting waves to a particular object and then recording the received waves by the object and thereby calculating our desired information.
To achieve this, the transmitted wave needs to travel a long distance. For long distance, the wave has to have long wavelengths. Hence, in RADAR we use Radio waves. Radio waves have wavelengths ranging from $\lambda = {10^0} - {10^9}m$.
B) To photograph internal objects of the body.
In this case we use X-Rays. X-Rays have shorter wavelengths and higher frequency. Higher frequency helps reduce penetration and hence reveal location inside the body where it can’t penetrate. Most organs absorb different amounts of the radiation. While bones absorb the least radiations, waves don’t penetrate through it and hence appear white. Also, lungs absorb the most as it contains air, and hence it appears black. They have wavelengths ranging from $\lambda = {10^{ - 8}} - {10^{ - 11}}m$.
C) For taking photographs of the sky during the night and foggy conditions.
Here, Infra-Red Radiations are used. IR radiations have longer wavelengths and lower frequencies. This provides longer penetration by the waves and lesser scattering in the atmosphere and therefore can take photographs in foggy conditions. They have wavelengths ranging from $\lambda = {10^{ - 6}} - {10^{ - 3}}m$.
Note: The wavelength of the radiation is also inversely proportional to the energy of the radiation. A popular use case scenario of RADAR is determining the depth of the sea, where waves are transmitted into the water and waves are received back after some time. The time delay is used to calculate the depth of the sea. X-Rays are not only used in the field of medicine but also in airport security where luggage of passengers are inspected using X-Rays to detect security threats.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




