
Which cell organelle is the key to the life of a cell?
Answer
513.6k+ views
Hint: All the species are composed of a cell that includes both single-celled and multicellular organisms. The cells provide shape, structure and also help in carrying out different types of functions to keep the system active. The cell contains different functional structures which are called cell organelles which are involved in various cellular functions.
Complete answer:
The cell organelles include both membrane and non-membrane bound organelles which are present within the cells and are distinct in their structures and functions.
Non-membrane-bound cell organelles are cell walls, ribosomes, and cytoskeleton that are present both in the prokaryotic cell as well as in eukaryotic cell while vacuole, lysosome, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum are single membrane-bound organelles that are present only in a eukaryotic cell.
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle that is present in all eukaryotic cells. It is also the largest organelle, the control centre of cellular activities and also the storehouse of the cell’s DNA. The nucleus is dark, round, surrounded by a nuclear membrane and is a porous membrane that forms a wall between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Within the nucleus, there are tiny spherical bodies called nucleolus which has chromosomes.
Chromosomes are thin, thread-like structures that carry genes that are considered to be hereditary units in organisms which means it helps in the inheritance of traits from one generation to another. It regulates the functions of the cell. It contains genes, which control heredity characters and governs critical life processes such as reproduction and growth of the cell. Hence, the nucleus is the cell organelle that controls the characteristics and functions of cells in our body.
The diagram below depicts the Nucleus of a cell.
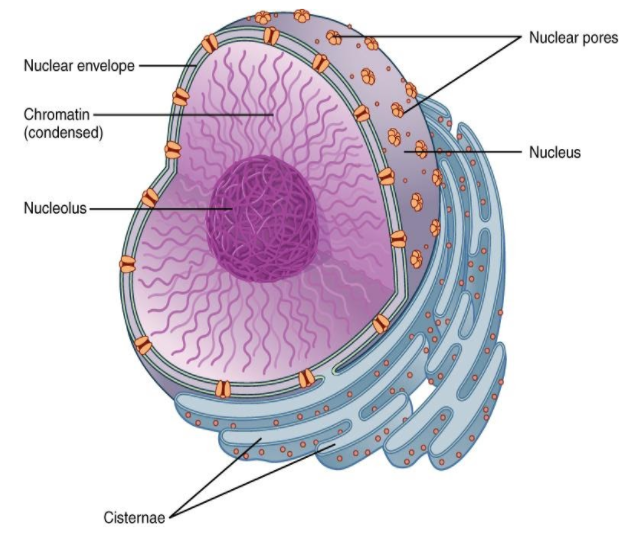
Hence, we can say that the nucleus is the cell organelle that is the key to the life of a cell.
Note: The primary function of the nucleus is to monitor cellular activities like metabolism and growth by making use of DNA’s genetic information. Nucleoli in the nucleus is responsible for the synthesis of protein and RNA. Every type of cell is categorized on the basis of the absence or presence of the nucleus within its cell.
Complete answer:
The cell organelles include both membrane and non-membrane bound organelles which are present within the cells and are distinct in their structures and functions.
Non-membrane-bound cell organelles are cell walls, ribosomes, and cytoskeleton that are present both in the prokaryotic cell as well as in eukaryotic cell while vacuole, lysosome, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum are single membrane-bound organelles that are present only in a eukaryotic cell.
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle that is present in all eukaryotic cells. It is also the largest organelle, the control centre of cellular activities and also the storehouse of the cell’s DNA. The nucleus is dark, round, surrounded by a nuclear membrane and is a porous membrane that forms a wall between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Within the nucleus, there are tiny spherical bodies called nucleolus which has chromosomes.
Chromosomes are thin, thread-like structures that carry genes that are considered to be hereditary units in organisms which means it helps in the inheritance of traits from one generation to another. It regulates the functions of the cell. It contains genes, which control heredity characters and governs critical life processes such as reproduction and growth of the cell. Hence, the nucleus is the cell organelle that controls the characteristics and functions of cells in our body.
The diagram below depicts the Nucleus of a cell.

Hence, we can say that the nucleus is the cell organelle that is the key to the life of a cell.
Note: The primary function of the nucleus is to monitor cellular activities like metabolism and growth by making use of DNA’s genetic information. Nucleoli in the nucleus is responsible for the synthesis of protein and RNA. Every type of cell is categorized on the basis of the absence or presence of the nucleus within its cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




