
Which bone is bigger, the ulna or radius?
Answer
462k+ views
Hint: All of the bones and joints in the body are part of the skeletal system. Each bone is a complex living organ composed of numerous cells, protein fibres, and minerals. The skeleton serves as a scaffold, supporting and protecting the soft tissues that comprise the rest of the body.
Complete answer:
In most vertebrate animals, a bone is a rigid tissue that forms part of the skeleton. Bones protect the body's organs, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support, and allow mobility. Bones have a complex internal and external structure and come in a variety of shapes and sizes. They are lightweight while remaining strong and hard, and they serve multiple functions.
The ulna is a long bone in the forearm that extends from the elbow to the smallest finger and is located on the medial side of the forearm when in anatomical position. It runs parallel to the radius, the forearm's other long bone. The ulna is typically longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. As a result, the radius is considered to be the greater of the two.
The radius, also known as the radial bone, is one of two large bones in the forearm, the other being the ulna. It runs parallel to the ulna and extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist. The ulna is typically longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. As a result, the radius is considered to be the greater of the two. It is a long bone that is prism-shaped and has a slight longitudinal curve.
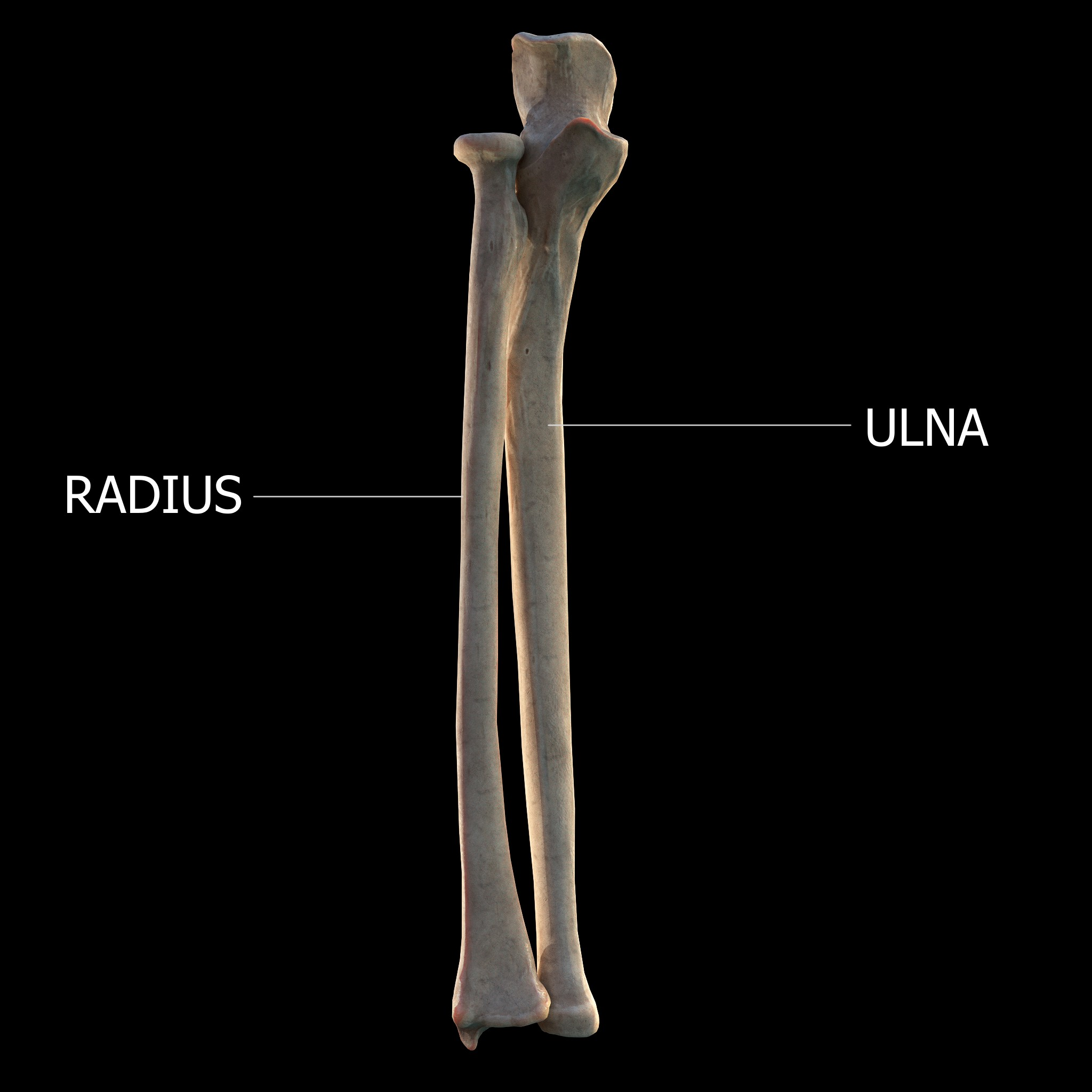
Thus, Ulna is longer than the radius.
Note: The ulna has a bony process near the elbow called the olecranon process, which is a hook-like structure that fits into the humerus's olecranon fossa. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the humeral trochlea. There is also a radial notch for the radius head and an ulnar tuberosity to which muscles attach. The radius is made up of a body and two extremities. The radius's upper extremity consists of a somewhat cylindrical head that articulates with the ulna and humerus, a neck, and a [[radial tuberosity]].
Complete answer:
In most vertebrate animals, a bone is a rigid tissue that forms part of the skeleton. Bones protect the body's organs, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support, and allow mobility. Bones have a complex internal and external structure and come in a variety of shapes and sizes. They are lightweight while remaining strong and hard, and they serve multiple functions.
The ulna is a long bone in the forearm that extends from the elbow to the smallest finger and is located on the medial side of the forearm when in anatomical position. It runs parallel to the radius, the forearm's other long bone. The ulna is typically longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. As a result, the radius is considered to be the greater of the two.
The radius, also known as the radial bone, is one of two large bones in the forearm, the other being the ulna. It runs parallel to the ulna and extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist. The ulna is typically longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. As a result, the radius is considered to be the greater of the two. It is a long bone that is prism-shaped and has a slight longitudinal curve.

Thus, Ulna is longer than the radius.
Note: The ulna has a bony process near the elbow called the olecranon process, which is a hook-like structure that fits into the humerus's olecranon fossa. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the humeral trochlea. There is also a radial notch for the radius head and an ulnar tuberosity to which muscles attach. The radius is made up of a body and two extremities. The radius's upper extremity consists of a somewhat cylindrical head that articulates with the ulna and humerus, a neck, and a [[radial tuberosity]].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




