
Which among the following is the strongest acid $?$
A. $CH{I_3}$
B. $CHC{l_3}$
C. $CHB{r_3}$
D. $CH{(CN)_3}$
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: Acids are substances that can release $[{H^ + }]$ in solution. The strength of acids are measured by their pKa value. Stronger the acid, lesser will be its pKa value. Strong acids have a stable conjugate base after releasing their $[{H^ + }]$ . On releasing the proton, they attain a negative charge.
Complete answer:
We know that acids are proton donors which on releasing the protons forms a conjugate base. A conjugate base is a potent proton acceptor. The conjugate bases of above species are given below.
(a)
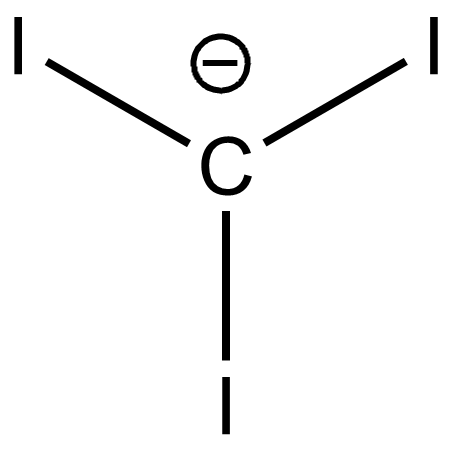
(b)
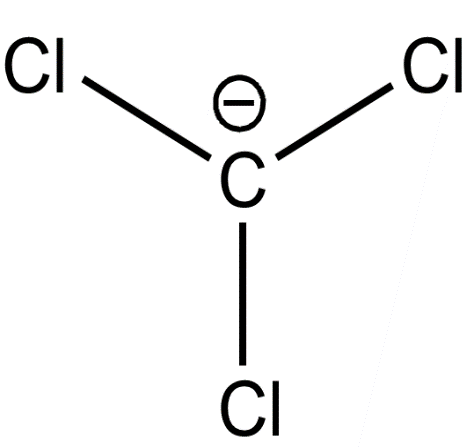
(c)
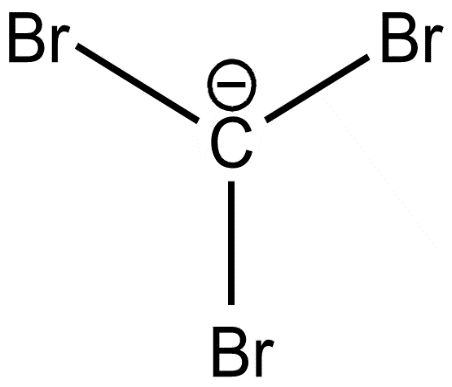
(d)
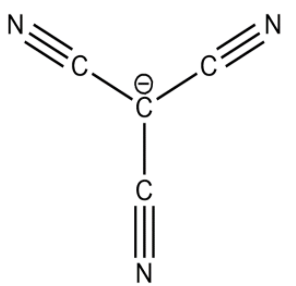
On releasing $[{H^ + }]$ carbanions are formed. The stability of carbanions of trihalides are determined by inductive and delocalisation of electrons. Here, all the above carbanions have the $ - I$ effect. In addition to it, the vacant d orbitals of halides form back bonding with carbon p orbitals.
It is more effective and stronger in Cl. It forms $2p\pi - 3d\pi $ overlap and delocalisation of electrons lowers the energy and increases the stability. In the cases of Br and I the d orbitals are very large and therefore effective back bonding does not take place. The conjugate base of trichloromethane or chloroform is more stable and therefore more acidic.
In the case of tricyanomethane, the carbanion is stabilised by metamerism in addition to $ - I$ effect.
Resonating structures are formed between carbon and nitrogen and negative charge lies on nitrogen which gives a stable structure. Hence, the delocalisation of negative charge gives rise to the most stable conjugate base.
Therefore, $(D)\,\,CH{(CN)_3}$ is the strongest acid .
Note:
In the case of halides, $CH{F_3}$ may seem to be the strongest acid, but it is not. F is the most electronegative element and therefore has more $ - I$ effect. It can pull the electron density and makes the release of $[{H^ + }]$ easier. But it does not have a vacant d orbital. Therefore, effective delocalisation of electrons cannot happen in the conjugate base making it less stable. It is a weak acid.
Complete answer:
We know that acids are proton donors which on releasing the protons forms a conjugate base. A conjugate base is a potent proton acceptor. The conjugate bases of above species are given below.
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

On releasing $[{H^ + }]$ carbanions are formed. The stability of carbanions of trihalides are determined by inductive and delocalisation of electrons. Here, all the above carbanions have the $ - I$ effect. In addition to it, the vacant d orbitals of halides form back bonding with carbon p orbitals.
It is more effective and stronger in Cl. It forms $2p\pi - 3d\pi $ overlap and delocalisation of electrons lowers the energy and increases the stability. In the cases of Br and I the d orbitals are very large and therefore effective back bonding does not take place. The conjugate base of trichloromethane or chloroform is more stable and therefore more acidic.
In the case of tricyanomethane, the carbanion is stabilised by metamerism in addition to $ - I$ effect.
Resonating structures are formed between carbon and nitrogen and negative charge lies on nitrogen which gives a stable structure. Hence, the delocalisation of negative charge gives rise to the most stable conjugate base.
Therefore, $(D)\,\,CH{(CN)_3}$ is the strongest acid .
Note:
In the case of halides, $CH{F_3}$ may seem to be the strongest acid, but it is not. F is the most electronegative element and therefore has more $ - I$ effect. It can pull the electron density and makes the release of $[{H^ + }]$ easier. But it does not have a vacant d orbital. Therefore, effective delocalisation of electrons cannot happen in the conjugate base making it less stable. It is a weak acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




