
What is the wavefront of light waves?
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: When a wave is generated from a source, it starts travelling in a particular direction. Different points of the wave have different phases. The continuous locus of all the points having the same phase is known as a wavefront. The perpendicular line drawn from at any point on the wavefront represents the direction of the propagation of the wave at that point.
Complete solution:
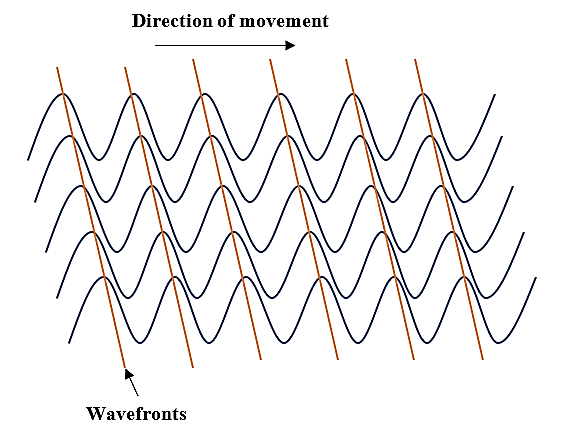
Wave front is a surface or line in the path of a wave motion on which the disturbances at every point have the same phase. The sum of rays passing through a surface produces or creates a wavefront. The wavefront surface is always perpendicular to the ray which denotes the direction of the propagation of the light wave. Wavefronts travel with the speed of light in all directions in an isotropic medium. Depending on the source of light, there can be three types of wave fronts:
1) Spherical wavefront
2) Plane wavefront
3) Cylindrical wavefront
When the identical waves having a common origin travel through a homogeneous medium, the corresponding troughs and crests are in phase at any instant.
Thus, the wavefront of light waves is the imaginary surface representing corresponding points of a light wave that vibrate in the same phase.
Note:
Students must remember although the wavefront has a definite direction of propagation, it is not a vector quantity. It is a time varying function which denotes a surface. The nature of the wavefront depends on the nature of the source through which light is produced. For parallel rays, the wavefront is a plane surface. Whereas for diverging or converging rays, the wavefront is spherical. If the source is distributed by the slit then the wavefront will be cylindrical.
Complete solution:

Wave front is a surface or line in the path of a wave motion on which the disturbances at every point have the same phase. The sum of rays passing through a surface produces or creates a wavefront. The wavefront surface is always perpendicular to the ray which denotes the direction of the propagation of the light wave. Wavefronts travel with the speed of light in all directions in an isotropic medium. Depending on the source of light, there can be three types of wave fronts:
1) Spherical wavefront
2) Plane wavefront
3) Cylindrical wavefront
When the identical waves having a common origin travel through a homogeneous medium, the corresponding troughs and crests are in phase at any instant.
Thus, the wavefront of light waves is the imaginary surface representing corresponding points of a light wave that vibrate in the same phase.
Note:
Students must remember although the wavefront has a definite direction of propagation, it is not a vector quantity. It is a time varying function which denotes a surface. The nature of the wavefront depends on the nature of the source through which light is produced. For parallel rays, the wavefront is a plane surface. Whereas for diverging or converging rays, the wavefront is spherical. If the source is distributed by the slit then the wavefront will be cylindrical.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




