
What is the vector projection formula?
Answer
537.3k+ views
Hint: A vector is a quantity which has a magnitude and a defined direction. It is represented by an arrow over its head. Although it has a magnitude and direction, it does not have a specific location, that is, if it is moved parallel to itself, it does not change. The projection of a vector on another vector is the orthogonal projection of the first vector along the length of the second vector.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first assign some terms that we are going to use in our solution. Let there be a vector $ \widehat{b}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}$ and vector $\overrightarrow{b}$, such that, we have to find the projection of $\overrightarrow{a}$ on $\overrightarrow{b}$, when the angle between these two vectors is denoted by $\theta $ .
This can be represented with the help of the following diagram:
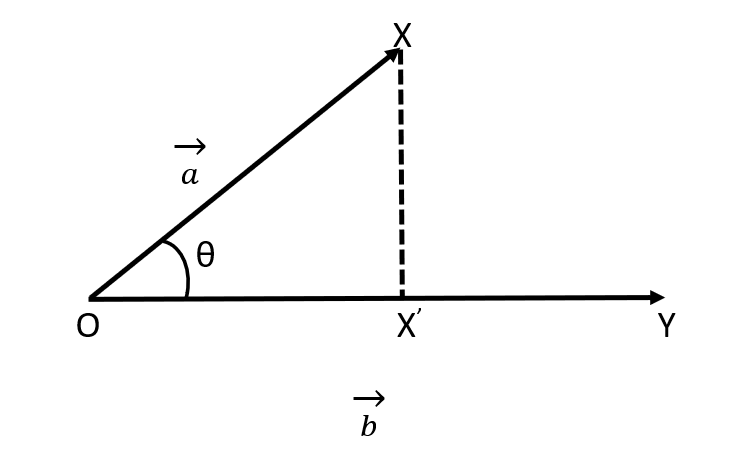
Here, OX represents the vector $\overrightarrow{a}$ and OY represents the vector$\overrightarrow{b}$ and OX’ is the required projection of vector $\overrightarrow{a}$ on $\overrightarrow{b}$.
Now, we can calculate this projection if we know the length of the section OX’ and the unit vector along $\overrightarrow{b}$. Calculating the length of section OX’, we have:
$\Rightarrow OX'=\left| \overrightarrow{a} \right|\cos \theta $
Using the dot product rule, we have:
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}=\left| \overrightarrow{a} \right|.\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|\cos \theta $
This can be simplified as:
$\Rightarrow \left| \overrightarrow{a} \right|\cos \theta =\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}$
Thus, OX’ will be equal to:
$\Rightarrow OX'=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}$ ......... (1)
Now, we need to calculate the unit vector along the $\overrightarrow{b}$. This can be done as follows:
$\Rightarrow \widehat{b}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}$ ......... (2)
Thus, the vector projection of $\overrightarrow{a}$ along $\overrightarrow{b}$can be written as:
$\Rightarrow pro{{j}_{b}}a=OX'\left( \widehat{b} \right)$
From equation number (1) and (2), we have:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow pro{{j}_{b}}a=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}\times \dfrac{\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|} \\
& \therefore pro{{j}_{b}}a=\left[ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{{{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}^{2}}} \right].\overrightarrow{b} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the vector projection formula for a vector $\overrightarrow{a}$ on vector $\overrightarrow{b}$ can be written as $\left[ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{{{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}^{2}}} \right].\overrightarrow{b}$ .
Note: While solving problems involving vector projection, one should remember the above derived formula thoroughly. Also, we can see that the formula for vector projection is situational and dependent on the angle made between the two vectors.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first assign some terms that we are going to use in our solution. Let there be a vector $ \widehat{b}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}$ and vector $\overrightarrow{b}$, such that, we have to find the projection of $\overrightarrow{a}$ on $\overrightarrow{b}$, when the angle between these two vectors is denoted by $\theta $ .
This can be represented with the help of the following diagram:

Here, OX represents the vector $\overrightarrow{a}$ and OY represents the vector$\overrightarrow{b}$ and OX’ is the required projection of vector $\overrightarrow{a}$ on $\overrightarrow{b}$.
Now, we can calculate this projection if we know the length of the section OX’ and the unit vector along $\overrightarrow{b}$. Calculating the length of section OX’, we have:
$\Rightarrow OX'=\left| \overrightarrow{a} \right|\cos \theta $
Using the dot product rule, we have:
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}=\left| \overrightarrow{a} \right|.\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|\cos \theta $
This can be simplified as:
$\Rightarrow \left| \overrightarrow{a} \right|\cos \theta =\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}$
Thus, OX’ will be equal to:
$\Rightarrow OX'=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}$ ......... (1)
Now, we need to calculate the unit vector along the $\overrightarrow{b}$. This can be done as follows:
$\Rightarrow \widehat{b}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}$ ......... (2)
Thus, the vector projection of $\overrightarrow{a}$ along $\overrightarrow{b}$can be written as:
$\Rightarrow pro{{j}_{b}}a=OX'\left( \widehat{b} \right)$
From equation number (1) and (2), we have:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow pro{{j}_{b}}a=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}\times \dfrac{\overrightarrow{b}}{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|} \\
& \therefore pro{{j}_{b}}a=\left[ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{{{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}^{2}}} \right].\overrightarrow{b} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the vector projection formula for a vector $\overrightarrow{a}$ on vector $\overrightarrow{b}$ can be written as $\left[ \dfrac{\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}}{{{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}^{2}}} \right].\overrightarrow{b}$ .
Note: While solving problems involving vector projection, one should remember the above derived formula thoroughly. Also, we can see that the formula for vector projection is situational and dependent on the angle made between the two vectors.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




