
What is the value of $\cos ( - \pi )$?
Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: Here the question has a trigonometric function, we have to find the exact value of $\cos ( - \pi )$. Before that first we have to find the exact value of \[\cos \left( \pi \right)\], this can find by using a ASTC rule of trigonometry by rewrite the given angle in the form of addition or difference of standard angle and further simplify by using a standard trigonometric value we get the required exact value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
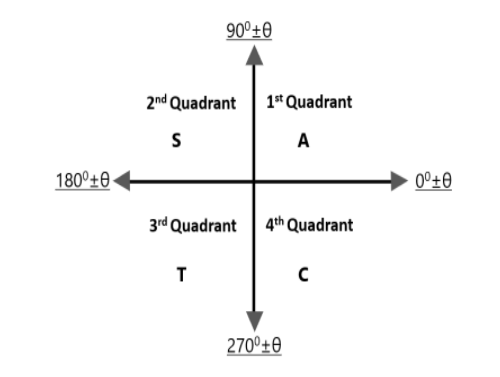
‘ASTC’ abbreviated as 'all sin cos tan' rule in trigonometry. The first letter of the first word in this phrase is 'A'. This may be taken to indicate that all trigonometric ratios in the first quadrant are positive. The first letter of the second word ‘S’ indicates that sine and its reciprocal cosecant are positive in the 2nd quadrant. The first letter of the third word ‘T’ indicates that tangent and its reciprocal cotangent is positive in the third quadrant. The first letter of the last word ‘C’ indicates that cosine and its reciprocal secant are positive in the fourth quadrant.
Consider the given question.
We have to find the value of $\cos ( - \pi )$.
First, solve the value of $\cos (\pi )$.
The value of \[\cos \left( \pi \right)\] or the value of \[\cos {\left( {180} \right)^ \circ }\] degrees can be represented in terms of different angles like \[{0^ \circ }\], \[{90^ \circ } = \dfrac{\pi }{2}\] and \[{270^ \circ } = \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}\].
The angle \[\cos \left( \pi \right)\] can be written as \[\cos {\left( {\pi - 0} \right)^ \circ }\] or \[\cos {\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} - \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)^ \circ }\]
Now Consider,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = \cos {\left( {\pi - 0} \right)^ \circ }\]
By ASTC rule of trigonometry, the angle \[\pi - 0\] i.e., \[{180^ \circ } - \theta \] lies in the second quadrant. cosine function is negative here, hence the angle must in negative, then
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = - \cos {\left( 0 \right)^ \circ }\]
We know that the exact value of \[\cos {0^ \circ } = 1\], then
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = - 1\]
Or
Consider
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = \cos {\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} - \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)^ \circ }\]
By ASTC rule of trigonometry, the angle \[\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} - \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)\] i.e., \[{270^ \circ } - \theta \] lies in the third quadrant. cosine function is negative here and in angle \[{270^ \circ }\] the ratio cosine changes to sine, then
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = - \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)\]
We know that the exact value of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = 1\], then we get
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = - 1\]
Now, we know the value of \[\cos \left( \pi \right) = - 1\], then replace \[\pi \] by \[ - \pi \]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - \pi } \right)\]
As we know cosine or cos is an even function. This means that \[\cos \left( { - \theta } \right) = \cos \left( \theta \right)\], then we have
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - \pi } \right) = \cos \left( \pi \right)\]
Substitute the value of \[\cos \left( \pi \right)\], then we get
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - \pi } \right) = - 1\]
Hence, the exact value of \[\cos \left( { - \pi } \right) = - 1\].
So, the correct answer is “-1”.
Note: Before solving questions of this kind we should be fully aware of all the trigonometric functions and their values. We should note that the value of $\cos (\pi )$ and $\cos ( - \pi )$ is $ - 1$, The value of both is the same. But the value of $\sin \pi = 0 $. These are called the undefined trigonometric functions because their angle lies on an axis.
Complete step-by-step answer:

‘ASTC’ abbreviated as 'all sin cos tan' rule in trigonometry. The first letter of the first word in this phrase is 'A'. This may be taken to indicate that all trigonometric ratios in the first quadrant are positive. The first letter of the second word ‘S’ indicates that sine and its reciprocal cosecant are positive in the 2nd quadrant. The first letter of the third word ‘T’ indicates that tangent and its reciprocal cotangent is positive in the third quadrant. The first letter of the last word ‘C’ indicates that cosine and its reciprocal secant are positive in the fourth quadrant.
Consider the given question.
We have to find the value of $\cos ( - \pi )$.
First, solve the value of $\cos (\pi )$.
The value of \[\cos \left( \pi \right)\] or the value of \[\cos {\left( {180} \right)^ \circ }\] degrees can be represented in terms of different angles like \[{0^ \circ }\], \[{90^ \circ } = \dfrac{\pi }{2}\] and \[{270^ \circ } = \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}\].
The angle \[\cos \left( \pi \right)\] can be written as \[\cos {\left( {\pi - 0} \right)^ \circ }\] or \[\cos {\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} - \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)^ \circ }\]
Now Consider,
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = \cos {\left( {\pi - 0} \right)^ \circ }\]
By ASTC rule of trigonometry, the angle \[\pi - 0\] i.e., \[{180^ \circ } - \theta \] lies in the second quadrant. cosine function is negative here, hence the angle must in negative, then
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = - \cos {\left( 0 \right)^ \circ }\]
We know that the exact value of \[\cos {0^ \circ } = 1\], then
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = - 1\]
Or
Consider
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = \cos {\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} - \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)^ \circ }\]
By ASTC rule of trigonometry, the angle \[\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2} - \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)\] i.e., \[{270^ \circ } - \theta \] lies in the third quadrant. cosine function is negative here and in angle \[{270^ \circ }\] the ratio cosine changes to sine, then
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = - \sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)\]
We know that the exact value of \[\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = 1\], then we get
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( \pi \right) = - 1\]
Now, we know the value of \[\cos \left( \pi \right) = - 1\], then replace \[\pi \] by \[ - \pi \]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - \pi } \right)\]
As we know cosine or cos is an even function. This means that \[\cos \left( { - \theta } \right) = \cos \left( \theta \right)\], then we have
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - \pi } \right) = \cos \left( \pi \right)\]
Substitute the value of \[\cos \left( \pi \right)\], then we get
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - \pi } \right) = - 1\]
Hence, the exact value of \[\cos \left( { - \pi } \right) = - 1\].
So, the correct answer is “-1”.
Note: Before solving questions of this kind we should be fully aware of all the trigonometric functions and their values. We should note that the value of $\cos (\pi )$ and $\cos ( - \pi )$ is $ - 1$, The value of both is the same. But the value of $\sin \pi = 0 $. These are called the undefined trigonometric functions because their angle lies on an axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




