
What is the limit of a constant?
Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint: We know that for a limit to exist, the left hand limit and right hand limit must exist, and should be equal to one another and must also be equal to the value of function at that point. Using this definition, we can prove that the limit of a constant is nothing but itself.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the limit of a function exists, only and only if the left hand limit (LHL) and the right hand limit (RHL) exists and are equal to one another. And, the value of the limit of that function is equal to the common value, LHL = RHL = f(x).
We need to find the limit of a constant. So, let us assume a function, $f\left( x \right)=c$, where c is a constant. We are assuming that we need to find the limit of this constant function at $x=a$,i.e., we need to find the value of $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to a}f\left( x \right)$.
Let us first plot the graph of y = c.
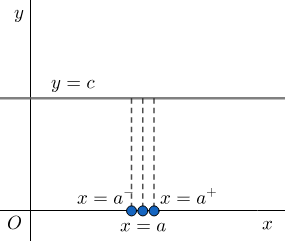
Let us calculate the left hand limit first.
LHL = $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{-}}}f\left( x \right)$
We can see that at $x={{a}^{-}}$, the value of $f\left( x \right)$ is c.
Hence, LHL = c …(i)
For right hand limit, we have
RHL = $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{+}}}f\left( x \right)$
We can see that at $x={{a}^{+}}$, the value of $f\left( x \right)$ is c.
Hence, RHL = c …(ii)
Also, the value of our function at a, i.e., \[f\left( a \right)=c\]…(iii)
Hence, by equation (i), (ii) and (iii), we can say that $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to a}f\left( x \right)=c$.
Or we can also write this as $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to a}\left( c \right)=c$.
Thus, we can now say that the limit of any constant is the same constant.
Hence, $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to a}\left( c \right)=c$.
Note: We must always remember that the limit of a constant value, is always that same value. We should not ignore any of the conditions that are required for the existence of limits at any point.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the limit of a function exists, only and only if the left hand limit (LHL) and the right hand limit (RHL) exists and are equal to one another. And, the value of the limit of that function is equal to the common value, LHL = RHL = f(x).
We need to find the limit of a constant. So, let us assume a function, $f\left( x \right)=c$, where c is a constant. We are assuming that we need to find the limit of this constant function at $x=a$,i.e., we need to find the value of $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to a}f\left( x \right)$.
Let us first plot the graph of y = c.

Let us calculate the left hand limit first.
LHL = $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{-}}}f\left( x \right)$
We can see that at $x={{a}^{-}}$, the value of $f\left( x \right)$ is c.
Hence, LHL = c …(i)
For right hand limit, we have
RHL = $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{+}}}f\left( x \right)$
We can see that at $x={{a}^{+}}$, the value of $f\left( x \right)$ is c.
Hence, RHL = c …(ii)
Also, the value of our function at a, i.e., \[f\left( a \right)=c\]…(iii)
Hence, by equation (i), (ii) and (iii), we can say that $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to a}f\left( x \right)=c$.
Or we can also write this as $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to a}\left( c \right)=c$.
Thus, we can now say that the limit of any constant is the same constant.
Hence, $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to a}\left( c \right)=c$.
Note: We must always remember that the limit of a constant value, is always that same value. We should not ignore any of the conditions that are required for the existence of limits at any point.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




