
What is the hybridisation in 1-propene ?
Answer
494.1k+ views
Hint: Propene, sometimes spelled propylene, is an unsaturated organic compound having the formula $C{{H}_{3}}CH=C{{H}_{2}}$ . It is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons, with only one double bond. It's a colourless gas with a slight whiff of petroleum.
Complete answer:
In valence bond theory, hybridisation is the idea of combining atomic orbitals to produce new hybrid orbitals (with different energies, shapes, and other properties than the component atomic orbitals) appropriate for electron pairing to form chemical bonds. Hybrid orbitals are symmetrically arranged in space and are important in explaining molecular geometry and atomic bonding characteristics. Hybrid orbitals are usually created by combining atomic orbitals with similar energies.
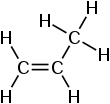
Two carbon atoms are $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised in propene. One carbon atom has undergone $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization. There are three orbitals from $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization and four orbitals from $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization in total. As a result, propene has a total of ten hybrid orbitals.
Carbon $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridises in this molecule because the double bond between the carbons requires only one$\pi $ (pi) bond, and only three bonds are generated per carbon atom. The 2s orbital is combined with just two of the three accessible 2p orbitals, commonly designated \[2{{p}_{x}}\] and \[2{{p}_{y}}\], in $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridisation. Unhybridized is the third 2p orbital (\[2{{p}_{z}}\]).
A molecular geometry model with one atom in the centre and three atoms at the corners of an equilateral triangle, termed peripheral atoms, all on one plane is known as trigonal planar in chemistry. All three ligands are identical in an ideal trigonal planar species, and all bond angles are \[120{}^\circ \].
Note:
Baldwin's principles, for example, are one of the most striking instances of hybridisation theory in organic chemistry. When sketching reaction processes, a traditional bonding diagram with two atoms sharing two electrons is occasionally required. Bonding in alkenes and methane is explained by hybridisation theory. The quantity of p or s character, which is determined mostly by orbital hybridisation, may be used to predict molecule characteristics like acidity or basicity with high accuracy.
Complete answer:
In valence bond theory, hybridisation is the idea of combining atomic orbitals to produce new hybrid orbitals (with different energies, shapes, and other properties than the component atomic orbitals) appropriate for electron pairing to form chemical bonds. Hybrid orbitals are symmetrically arranged in space and are important in explaining molecular geometry and atomic bonding characteristics. Hybrid orbitals are usually created by combining atomic orbitals with similar energies.

Two carbon atoms are $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised in propene. One carbon atom has undergone $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization. There are three orbitals from $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization and four orbitals from $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization in total. As a result, propene has a total of ten hybrid orbitals.
Carbon $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridises in this molecule because the double bond between the carbons requires only one$\pi $ (pi) bond, and only three bonds are generated per carbon atom. The 2s orbital is combined with just two of the three accessible 2p orbitals, commonly designated \[2{{p}_{x}}\] and \[2{{p}_{y}}\], in $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridisation. Unhybridized is the third 2p orbital (\[2{{p}_{z}}\]).
A molecular geometry model with one atom in the centre and three atoms at the corners of an equilateral triangle, termed peripheral atoms, all on one plane is known as trigonal planar in chemistry. All three ligands are identical in an ideal trigonal planar species, and all bond angles are \[120{}^\circ \].
Note:
Baldwin's principles, for example, are one of the most striking instances of hybridisation theory in organic chemistry. When sketching reaction processes, a traditional bonding diagram with two atoms sharing two electrons is occasionally required. Bonding in alkenes and methane is explained by hybridisation theory. The quantity of p or s character, which is determined mostly by orbital hybridisation, may be used to predict molecule characteristics like acidity or basicity with high accuracy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




