
What is the function of the root cap?
Answer
510.9k+ views
Hint: Roots are the structure that provides strength to the plant and helps in absorbing water and minerals from the soil. Taproots and fibrous roots are mainly two types of roots found in plants. Some roots are modified to perform functions other than absorption and anchorage. They are involved in photosynthesis, storage of food and sometimes act as a reproductive part of plants.
Complete answer:
Root cap is present at the terminal region of the plant. Root hairs are absent on the root cap. Thus, it is not involved in absorption of water and nutrients from the soil. The root cap is present in most of the plants. The root cap performs the following functions:
The root cap is involved in the protection of growing root tip of plants or root cap meristem.
It secretes mucilage for the easy movement of root tip into the soil. Thus, it provides lubrication and passage for the root to go deeper into the soil to absorb water and minerals from the soil.
The root cap controls the geotropic movement in plants because of the presence of statocytes. The statocytes help in perception of gravity and thus, enables the downward growth of the root cap.
The root cap also protects the delicate stem cells present inside the root tip.
It also helps in the transfer of environmental signals to the growing root tip. Thus, it helps in communication between the soil biota and growing root tip.
Note:
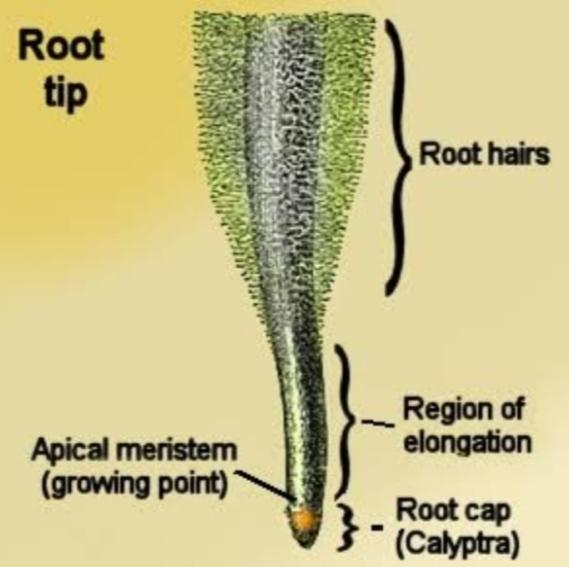
The root consists of mainly four zones- root cap, apical meristem, zone of elongation and root hairs. The apical meristem forms the new root cells. The zone of elongation is involved in the growth of root in length while the roots hairs help in absorbing water and minerals from the soil by increasing the surface area. The root hairs are developed from epidermal cells of the root.
Complete answer:
Root cap is present at the terminal region of the plant. Root hairs are absent on the root cap. Thus, it is not involved in absorption of water and nutrients from the soil. The root cap is present in most of the plants. The root cap performs the following functions:
The root cap is involved in the protection of growing root tip of plants or root cap meristem.
It secretes mucilage for the easy movement of root tip into the soil. Thus, it provides lubrication and passage for the root to go deeper into the soil to absorb water and minerals from the soil.
The root cap controls the geotropic movement in plants because of the presence of statocytes. The statocytes help in perception of gravity and thus, enables the downward growth of the root cap.
The root cap also protects the delicate stem cells present inside the root tip.
It also helps in the transfer of environmental signals to the growing root tip. Thus, it helps in communication between the soil biota and growing root tip.

Note:
The root consists of mainly four zones- root cap, apical meristem, zone of elongation and root hairs. The apical meristem forms the new root cells. The zone of elongation is involved in the growth of root in length while the roots hairs help in absorbing water and minerals from the soil by increasing the surface area. The root hairs are developed from epidermal cells of the root.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




