
What is the function of cytochrome C ?
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: Cytochromes are a type of protein which contains a haem group. They help in transport of electrons in the electron transport system in mitochondria and carry out redox reactions in the cells. Because of the presence of the haem group they are also called haem-proteins.
Complete answer:
International union of biochemistry and molecular biology (IUBMB) have classified the cytochrome into four types which are cytochrome a, cytochrome b, cytochrome c, and cytochrome d. Out of these cytochromes’ cytochrome c is a water-soluble substance. It is loosely attached to the inner membrane of mitochondria. It contains an iron metal centre which helps it in the electron transport chain.
Electron transport chain is made up of different compounds which help in oxidative phosphorylation in case of aerobic respiration producing large amounts of ATP. The whole transport process is carried out by a series of redox reactions. The ETC is made up of four complexes which are complex I, II, III, IV. These complexes are made up of proteins. Transport of electrons occurs from complex I to complex IV through different molecules.
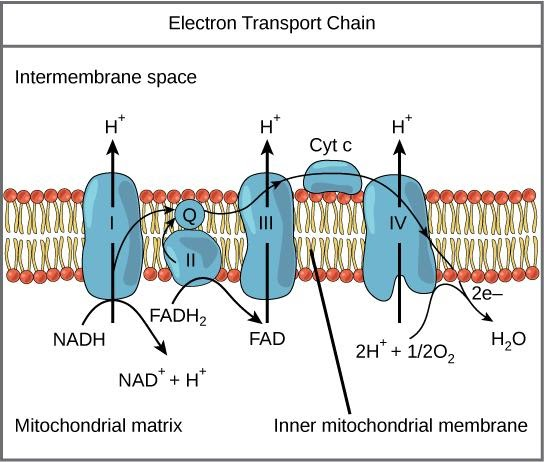
Cytochrome c is a movable electron carrier which helps in the transfer of electrons from complex III to complex IV. Cytochrome c accepts electrons from complex III where ubiquinone acts as an electron donor. Then it moves to the complex IV and cytochrome c undergoes through oxidation, releasing the electron into it.
Note:-
ATP is known as the currency of energy which acts as a fuel for the working of the cell. Cytochrome c plays an important role in the ETC without which ATP would not be produced. Due to the presence of the haem group at its centre it could carry out different redox reactions causing transport of electrons.
Complete answer:
International union of biochemistry and molecular biology (IUBMB) have classified the cytochrome into four types which are cytochrome a, cytochrome b, cytochrome c, and cytochrome d. Out of these cytochromes’ cytochrome c is a water-soluble substance. It is loosely attached to the inner membrane of mitochondria. It contains an iron metal centre which helps it in the electron transport chain.
Electron transport chain is made up of different compounds which help in oxidative phosphorylation in case of aerobic respiration producing large amounts of ATP. The whole transport process is carried out by a series of redox reactions. The ETC is made up of four complexes which are complex I, II, III, IV. These complexes are made up of proteins. Transport of electrons occurs from complex I to complex IV through different molecules.

Cytochrome c is a movable electron carrier which helps in the transfer of electrons from complex III to complex IV. Cytochrome c accepts electrons from complex III where ubiquinone acts as an electron donor. Then it moves to the complex IV and cytochrome c undergoes through oxidation, releasing the electron into it.
Note:-
ATP is known as the currency of energy which acts as a fuel for the working of the cell. Cytochrome c plays an important role in the ETC without which ATP would not be produced. Due to the presence of the haem group at its centre it could carry out different redox reactions causing transport of electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




