
What is the frequency of A.C. in India?
Answer
605.4k+ views
Hint: We know that the current which changes its direction periodically is called Alternating Current (A.C.). The graph of alternating current is of sinusoidal type with respect to time which means its positive in first part and negative in another part and the waveform of current is based on the frequency of current. Using this we will find the answer to our question.
Complete step by step answer:
Before understanding the frequency of A.C. current in India we will understand what is A.C. current. So, A.C. can be defined as “Current which changes its direction periodically is called Alternating Current (A.C.)”. A sample figure of alternating current is as shown below,
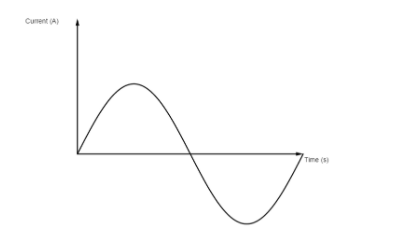
From the figure it can be seen that A.C. current is sinusoidal wave form which means it is positive in half path and negative in another part. The frequency of supplying A.C. current differs in all the countries across the world. In most of the countries the power supply is 50-60 Hz.
In 50 Hz power supply the frequency is of 25 Hz positive and 25 Hz negative in one cycle. As lower frequencies are preferable for manufacturing operations such as rolling, cutting etc. as well as used in railway transmission lines. But at this frequency the light bulbs may flicker so they prefer a negative cycle of the frequency.
In the same way for 60 Hz, the cycle is divided into 30 Hz, and used as per that. But many times 60 Hz frequency is very high in use and much of it gets wasted while supplying so to avoid this India uses 50 Hz, power supply as complete electric supply can reach to each and every corner of the country.
Thus, we can say that the frequency of A.C. current is 50 Hz in India.
Note: Direct current is also a type of current carrying wave form but it is not favorable in larger uses, because in D.C. current the chances of fire due to electrical appliances increases as there is no negative waveform in it. As well as DC power supply cannot be transmitted up to longer distances. So, all over the world A.C. supply is most favorable in electrical supply.
Complete step by step answer:
Before understanding the frequency of A.C. current in India we will understand what is A.C. current. So, A.C. can be defined as “Current which changes its direction periodically is called Alternating Current (A.C.)”. A sample figure of alternating current is as shown below,

From the figure it can be seen that A.C. current is sinusoidal wave form which means it is positive in half path and negative in another part. The frequency of supplying A.C. current differs in all the countries across the world. In most of the countries the power supply is 50-60 Hz.
In 50 Hz power supply the frequency is of 25 Hz positive and 25 Hz negative in one cycle. As lower frequencies are preferable for manufacturing operations such as rolling, cutting etc. as well as used in railway transmission lines. But at this frequency the light bulbs may flicker so they prefer a negative cycle of the frequency.
In the same way for 60 Hz, the cycle is divided into 30 Hz, and used as per that. But many times 60 Hz frequency is very high in use and much of it gets wasted while supplying so to avoid this India uses 50 Hz, power supply as complete electric supply can reach to each and every corner of the country.
Thus, we can say that the frequency of A.C. current is 50 Hz in India.
Note: Direct current is also a type of current carrying wave form but it is not favorable in larger uses, because in D.C. current the chances of fire due to electrical appliances increases as there is no negative waveform in it. As well as DC power supply cannot be transmitted up to longer distances. So, all over the world A.C. supply is most favorable in electrical supply.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




