
What is the equation for Snell’s law ?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this question, we will be looking at the basic concept of geometrical optics. We will use the properties of reflection and refraction through a surface.Basically refraction is the bending of a wave when it passes from one medium to another. The bending is caused due to the differences in density between the two substances.
Complete step by step answer:
Initially, we will study what we mean by refraction? Refraction can be defined as the bending of a ray of light wave from its original path across the boundary separating two different mediums having different refractive index. This phenomena is caused due to the change in the speed of the propagation of the light wave due to the change in the medium of propagation.
Then, a question will arise to you: what is a Snell’s law and what does it represent? Snell’s law is an important formula which is used to describe the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction when we refer to a light or any other wave which is passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air.
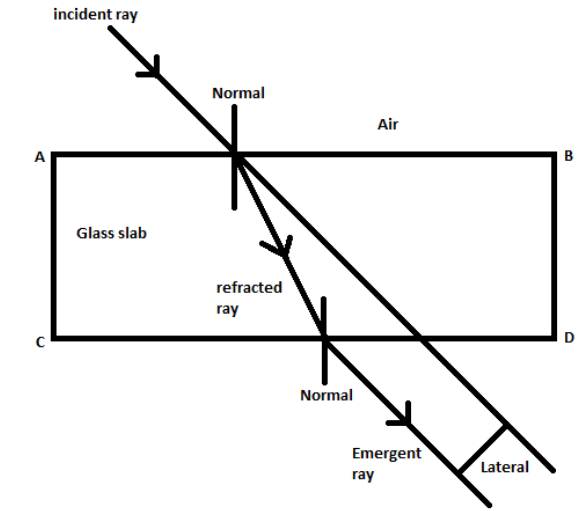
The formula for Snell’s law is given by
\[{{n}_{1}}\sin {{\theta }_{1}}={{n}_{2}}\sin {{\theta }_{2}}\]
Where ${{n}_{1}}$ is the refractive index of medium $1$ , ${{n}_{2}}$ is the refractive index of medium $2$, ${{\theta }_{1}}$is the angle of incidence and ${{\theta }_{2}}$ is the angle of refraction.
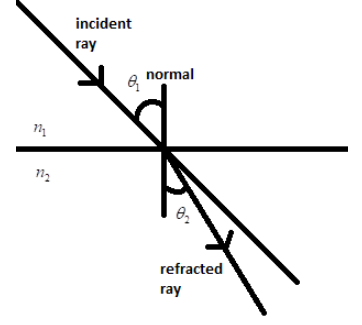
Here, the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction, the incident ray and the refracted ray, all lie within the same plane.
Note: It is important to note that this law is mainly used to calculate the refractive index of the mediums and also the angle of refraction and incident if and only if three out of the four quantities are provided. A light ray refracts whenever it travels at an angle into a medium of different refractive index. This change in speed results in a change in direction. As an example, consider air travelling into water. The speed of light decreases as it continues to travel at a different angle.
Complete step by step answer:
Initially, we will study what we mean by refraction? Refraction can be defined as the bending of a ray of light wave from its original path across the boundary separating two different mediums having different refractive index. This phenomena is caused due to the change in the speed of the propagation of the light wave due to the change in the medium of propagation.
Then, a question will arise to you: what is a Snell’s law and what does it represent? Snell’s law is an important formula which is used to describe the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction when we refer to a light or any other wave which is passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air.

The formula for Snell’s law is given by
\[{{n}_{1}}\sin {{\theta }_{1}}={{n}_{2}}\sin {{\theta }_{2}}\]
Where ${{n}_{1}}$ is the refractive index of medium $1$ , ${{n}_{2}}$ is the refractive index of medium $2$, ${{\theta }_{1}}$is the angle of incidence and ${{\theta }_{2}}$ is the angle of refraction.

Here, the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction, the incident ray and the refracted ray, all lie within the same plane.
Note: It is important to note that this law is mainly used to calculate the refractive index of the mediums and also the angle of refraction and incident if and only if three out of the four quantities are provided. A light ray refracts whenever it travels at an angle into a medium of different refractive index. This change in speed results in a change in direction. As an example, consider air travelling into water. The speed of light decreases as it continues to travel at a different angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




