
What is the conjugate of $ C{{H}_{3}}NH_{3}^{+} $ ?
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: We know that according to Brønsted Lowry acid base theory, acid is a proton donor and base is a proton acceptor. When an acid loses a proton, a conjugate base is obtained. When a base accepts a proton, a conjugate acid is obtained.
Complete answer:
As per the theory, a compound that donates a proton in a reaction is said to be acid and is known as Brønsted-Lowry acid. Similarly, a compound that accepts a proton in a reaction is said to be acting as a base and is known as Brønsted-Lowry base. Now, let us understand the concept of conjugate base and acid. A conjugate base is the product of a reaction that is formed from a Brønsted-Lowry acid by donating a proton. A conjugate acid is the product of a reaction that is formed from a Brønsted-Lowry base by accepting a proton.
As you know, a Bronsted - Lowry acid is a chemical species that donates a proton, H+, in a chemical reaction. The species that accepts that proton acts as a Bronsted - Lowry base. Now, a conjugate base is a chemical species that can reform a Bronsted - Lowry acid by accepting a proton. In essence, you can go from an acid to its conjugate base by removing a proton, and from the conjugate base to the original acid by adding a proton.
In your case, you're starting from an acid, the methyl ammonium ion, $ C{{H}_{3}}NH_{3}^{+} $ , to be precise, and must determine its conjugate base. The conjugate base of the methyl ammonium ion will have one less proton. Keep in mind that a proton carries a $ 1+~ $ charge, so you know for a fact that the conjugate base will be neutral. $ C{{H}_{3}}NH_{3}^{+}\to C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}+{{H}^{+}} $
The conjugate base of the methyl ammonium ion is $ C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}} $ , methylamine.
Methyl ammonium ion (weak acid):
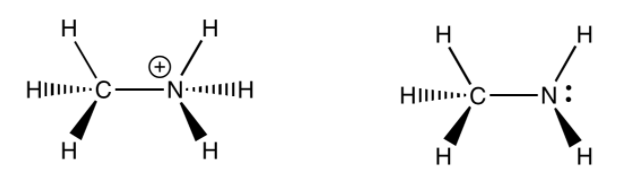
Methylamine (weak base):
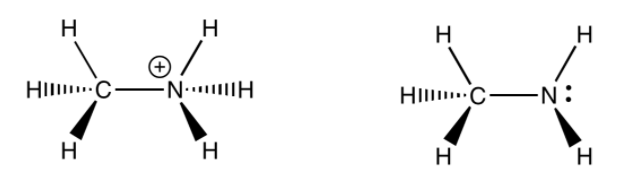
Note:
Remember that Brønsted Lowry acid base theory is similar to Arrhenius' concept of acid and base. The Arrhenius concept is limited to aqueous solutions. However, Brønsted Lowry theory can also be applied to non-aqueous solutions. In Arrhenius theory, a base gives a hydroxide ion. In Brønsted Lowry theory, a base accepts a proton.
Complete answer:
As per the theory, a compound that donates a proton in a reaction is said to be acid and is known as Brønsted-Lowry acid. Similarly, a compound that accepts a proton in a reaction is said to be acting as a base and is known as Brønsted-Lowry base. Now, let us understand the concept of conjugate base and acid. A conjugate base is the product of a reaction that is formed from a Brønsted-Lowry acid by donating a proton. A conjugate acid is the product of a reaction that is formed from a Brønsted-Lowry base by accepting a proton.
As you know, a Bronsted - Lowry acid is a chemical species that donates a proton, H+, in a chemical reaction. The species that accepts that proton acts as a Bronsted - Lowry base. Now, a conjugate base is a chemical species that can reform a Bronsted - Lowry acid by accepting a proton. In essence, you can go from an acid to its conjugate base by removing a proton, and from the conjugate base to the original acid by adding a proton.
In your case, you're starting from an acid, the methyl ammonium ion, $ C{{H}_{3}}NH_{3}^{+} $ , to be precise, and must determine its conjugate base. The conjugate base of the methyl ammonium ion will have one less proton. Keep in mind that a proton carries a $ 1+~ $ charge, so you know for a fact that the conjugate base will be neutral. $ C{{H}_{3}}NH_{3}^{+}\to C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}+{{H}^{+}} $
The conjugate base of the methyl ammonium ion is $ C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}} $ , methylamine.
Methyl ammonium ion (weak acid):
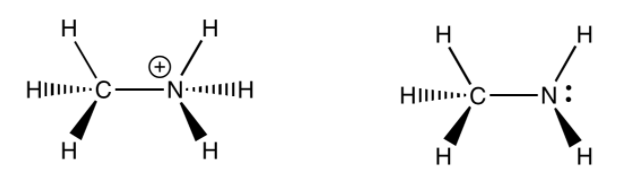
Methylamine (weak base):
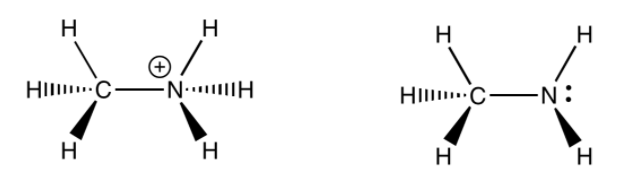
Note:
Remember that Brønsted Lowry acid base theory is similar to Arrhenius' concept of acid and base. The Arrhenius concept is limited to aqueous solutions. However, Brønsted Lowry theory can also be applied to non-aqueous solutions. In Arrhenius theory, a base gives a hydroxide ion. In Brønsted Lowry theory, a base accepts a proton.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




