
What is the chemical name of soap?
Answer
513.6k+ views
Hint :Soaps and detergents are the substances which on dissolving in water, possess the ability to remove dirt particles from the surfaces like human skin, textiles, fabrics and other solids. Soaps are basically the sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids which are formed by the process known as saponification.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Soaps and detergents consist of a chemical structure in which their molecules contain a hydrophobic part which is known as water insoluble part like fatty acids or a long chain carbon group of fatty alcohols or alkyl benzene. Further, it also consists of a hydrophilic part which is known as water soluble part like, salts of metal, sulphate groups and sulfonate groups. The hydrophilic part in the structure of soap is the reason for the solubility of soap in water.
Usually, the hydrophobic part of the molecule gets attached to the dirt particles present on the fibre and the hydrophilic part gets attached to the water molecules and thus, the dirt can easily be removed with the help of soap.
General representation of a soap molecule is as follows:
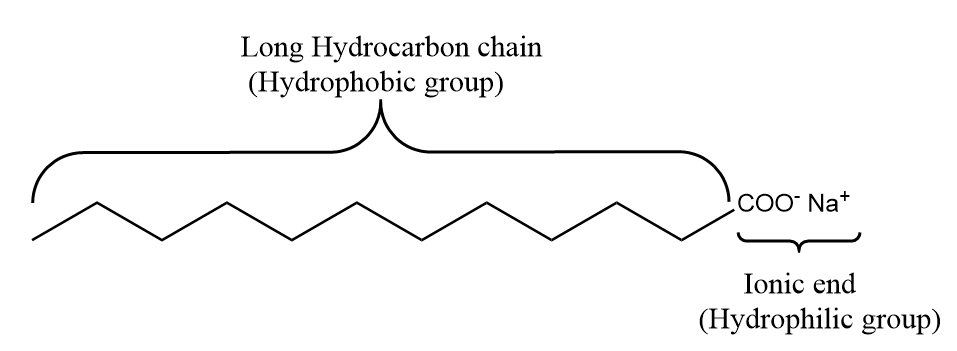
Some of the examples of soap with their chemical formula are as follows:
1. Sodium stearate $ \Rightarrow {C_{17}}{H_{35}}CO{O^ - }N{a^ + } $
2. Sodium palmitate $ \Rightarrow {C_{15}}{H_{31}}CO{O^ - }N{a^ + } $
3. Sodium oleate $ \Rightarrow {C_{17}}{H_{33}}CO{O^ - }N{a^ + } $
Note :
Remember that the major difference between a soap and a detergent is that a soap is a metal salt of fatty acids and it does not dissolve in hard water whereas a detergent is a mixture of surfactants which have a tendency to form lather in hard water. Thus, detergent is a better cleansing agent than soap.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Soaps and detergents consist of a chemical structure in which their molecules contain a hydrophobic part which is known as water insoluble part like fatty acids or a long chain carbon group of fatty alcohols or alkyl benzene. Further, it also consists of a hydrophilic part which is known as water soluble part like, salts of metal, sulphate groups and sulfonate groups. The hydrophilic part in the structure of soap is the reason for the solubility of soap in water.
Usually, the hydrophobic part of the molecule gets attached to the dirt particles present on the fibre and the hydrophilic part gets attached to the water molecules and thus, the dirt can easily be removed with the help of soap.
General representation of a soap molecule is as follows:

Some of the examples of soap with their chemical formula are as follows:
1. Sodium stearate $ \Rightarrow {C_{17}}{H_{35}}CO{O^ - }N{a^ + } $
2. Sodium palmitate $ \Rightarrow {C_{15}}{H_{31}}CO{O^ - }N{a^ + } $
3. Sodium oleate $ \Rightarrow {C_{17}}{H_{33}}CO{O^ - }N{a^ + } $
Note :
Remember that the major difference between a soap and a detergent is that a soap is a metal salt of fatty acids and it does not dissolve in hard water whereas a detergent is a mixture of surfactants which have a tendency to form lather in hard water. Thus, detergent is a better cleansing agent than soap.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




