
What is the bond order of $ Cl{O_2} $ ?
Answer
488.7k+ views
Hint: To solve these types of questions we should first draw the Lewis structure. We count the number of total bonds and then divide it by the number of elements in which these bonds are made with the central atom.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We can solve this question, by first drawing the Lewis dot structure of $ Cl{O_2} $
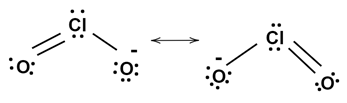
In the above figure, the total number of bonds is $ 3 $ . And if we try to draw different structures, these bonds will rearrange themselves between two elements. Or we can calculate it by counting the number of resonating structures this molecule can make.
$ {\text{Bond Order}} = \dfrac{{{\text{Total number of bonds}}}}{{{\text{Total number of resonating structures}}}} $
$ {\text{Bond Order}} = \dfrac{3}{2} = 1.5 $
So, from the above calculation we found that the bond order of $ Cl{O_2} $ is $ 1.5 $ .
Now, we will calculate formal charge on each oxygen atom-
$ {\text{Formal charge = valence electrons - nonbonding valence electrons - }}\dfrac{{{\text{bonding electrons}}}}{2} $
$ = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{2}{2} $
$ = - 1 $
The formal charge on each oxygen is $ - 1 $ .
Note:
We should also know about bond length. It is defined as the distance between the centers of two covalently bonded atoms. The length of the bond is determined by the number of bonded electrons (the bond order). If bond order is high, there will be stronger pull between two atoms and there will be shorter bond length. Therefore, bond length increases in the following order: triple bond < double bond < single bond.
Chlorine dioxide gas $ (Cl{O_2}) $ is used to sterilize medical and laboratory equipment, surfaces, rooms and tools. Chlorine dioxide can be used as oxidizer or disinfectant. It is a very strong oxidizer and it effectively kills pathogenic microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria and viruses.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We can solve this question, by first drawing the Lewis dot structure of $ Cl{O_2} $

In the above figure, the total number of bonds is $ 3 $ . And if we try to draw different structures, these bonds will rearrange themselves between two elements. Or we can calculate it by counting the number of resonating structures this molecule can make.
$ {\text{Bond Order}} = \dfrac{{{\text{Total number of bonds}}}}{{{\text{Total number of resonating structures}}}} $
$ {\text{Bond Order}} = \dfrac{3}{2} = 1.5 $
So, from the above calculation we found that the bond order of $ Cl{O_2} $ is $ 1.5 $ .
Now, we will calculate formal charge on each oxygen atom-
$ {\text{Formal charge = valence electrons - nonbonding valence electrons - }}\dfrac{{{\text{bonding electrons}}}}{2} $
$ = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{2}{2} $
$ = - 1 $
The formal charge on each oxygen is $ - 1 $ .
Note:
We should also know about bond length. It is defined as the distance between the centers of two covalently bonded atoms. The length of the bond is determined by the number of bonded electrons (the bond order). If bond order is high, there will be stronger pull between two atoms and there will be shorter bond length. Therefore, bond length increases in the following order: triple bond < double bond < single bond.
Chlorine dioxide gas $ (Cl{O_2}) $ is used to sterilize medical and laboratory equipment, surfaces, rooms and tools. Chlorine dioxide can be used as oxidizer or disinfectant. It is a very strong oxidizer and it effectively kills pathogenic microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria and viruses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




