
What is the atomic structure of $ A{l^{3 + }} $ ?
Answer
492.6k+ views
Hint: Atomic structure is defined as the structure of the atom which includes the number of neutrons, number of electrons, and number of protons present in the atom. Electrons are negatively charged particles that revolve around the nucleus, which is present at the centre of an atom.
Complete answer:
Aluminium has atomic number 13, so to attain noble gas configuration aluminium loses three electrons leading to the formation of $ A{l^{3 + }} $ cation. For calculating the number of neutrons, electrons, and protons in $ A{l^{3 + }} $ cation:
Step 1: Calculation of the number of neutrons:
For calculating the number of neutrons for any cation or an atom, the difference between the mass number of the atom or cation and the atomic number gives the number of neutrons. So, the mass number of $ A{l^{3 + }} $ + is 27 grams whereas the atomic number of $ A{l^{3 + }} $ cation is 13. Therefore, the number of neutrons in $ A{l^{3 + }} $ ion is
$ 27 - 13 = {\text{ }}14 $
Hence, 14 electrons are present in $ A{l^{3 + }} $ ions.
Step 2: Calculation of the number of electrons:
For calculating the number of electrons in an atom is equal to its atomic number but for cation, the number of electrons is equal to the difference between the atomic number and the number of electrons lost. So, the number of electrons in $ A{l^{3 + }} $ is
$ 13 - 3 = 10 $
Therefore, 10 electrons are present in $ A{l^{3 + }} $ ions.
Step 3: Calculation of the number of protons:
For calculating the number of protons in an atom or cation, the number of protons is equal to the atomic number. Therefore, the number of protons in the $ A{l^{3 + }} $ ion is 13.
Step 4: Stating the electronic configuration:
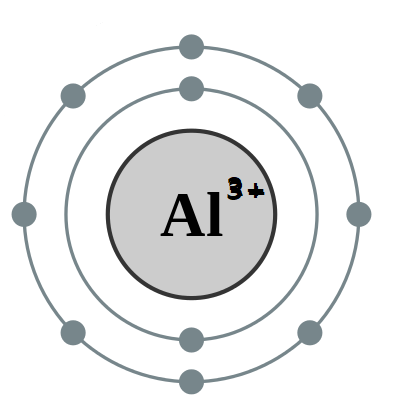
Electronic configuration of Aluminium is $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^1} $ .
After removing three electrons the electronic configuration of $ A{l^{3 + }} $ ion is $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6} $ .
Note:
$ A{l^{3 + }} $ cation is formed by the removal of three electrons from the aluminium atom, with a +3 charge. An aluminium cation is a monatomic trication. Metals are electropositive i.e. they lose electrons to form a positively charged cation. Aluminium ions are silvery and protected by an oxide coating.
Complete answer:
Aluminium has atomic number 13, so to attain noble gas configuration aluminium loses three electrons leading to the formation of $ A{l^{3 + }} $ cation. For calculating the number of neutrons, electrons, and protons in $ A{l^{3 + }} $ cation:
Step 1: Calculation of the number of neutrons:
For calculating the number of neutrons for any cation or an atom, the difference between the mass number of the atom or cation and the atomic number gives the number of neutrons. So, the mass number of $ A{l^{3 + }} $ + is 27 grams whereas the atomic number of $ A{l^{3 + }} $ cation is 13. Therefore, the number of neutrons in $ A{l^{3 + }} $ ion is
$ 27 - 13 = {\text{ }}14 $
Hence, 14 electrons are present in $ A{l^{3 + }} $ ions.
Step 2: Calculation of the number of electrons:
For calculating the number of electrons in an atom is equal to its atomic number but for cation, the number of electrons is equal to the difference between the atomic number and the number of electrons lost. So, the number of electrons in $ A{l^{3 + }} $ is
$ 13 - 3 = 10 $
Therefore, 10 electrons are present in $ A{l^{3 + }} $ ions.
Step 3: Calculation of the number of protons:
For calculating the number of protons in an atom or cation, the number of protons is equal to the atomic number. Therefore, the number of protons in the $ A{l^{3 + }} $ ion is 13.
Step 4: Stating the electronic configuration:
Electronic configuration of Aluminium is $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^1} $ .
After removing three electrons the electronic configuration of $ A{l^{3 + }} $ ion is $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6} $ .

Note:
$ A{l^{3 + }} $ cation is formed by the removal of three electrons from the aluminium atom, with a +3 charge. An aluminium cation is a monatomic trication. Metals are electropositive i.e. they lose electrons to form a positively charged cation. Aluminium ions are silvery and protected by an oxide coating.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




