
What is Macula Densa?
Answer
487.2k+ views
Hint: Juxtaglomerular apparatus is the part of the nephron and helps control the functions of the nephron. The juxtaglomerular apparatus gets its name from the fact that it is located right next to (juxta) the glomerulus. It is formed at the junction of DCT and the afferent arteriole. It controls glomerular filtration rate by controlling the renal blood flow.
Complete solution:
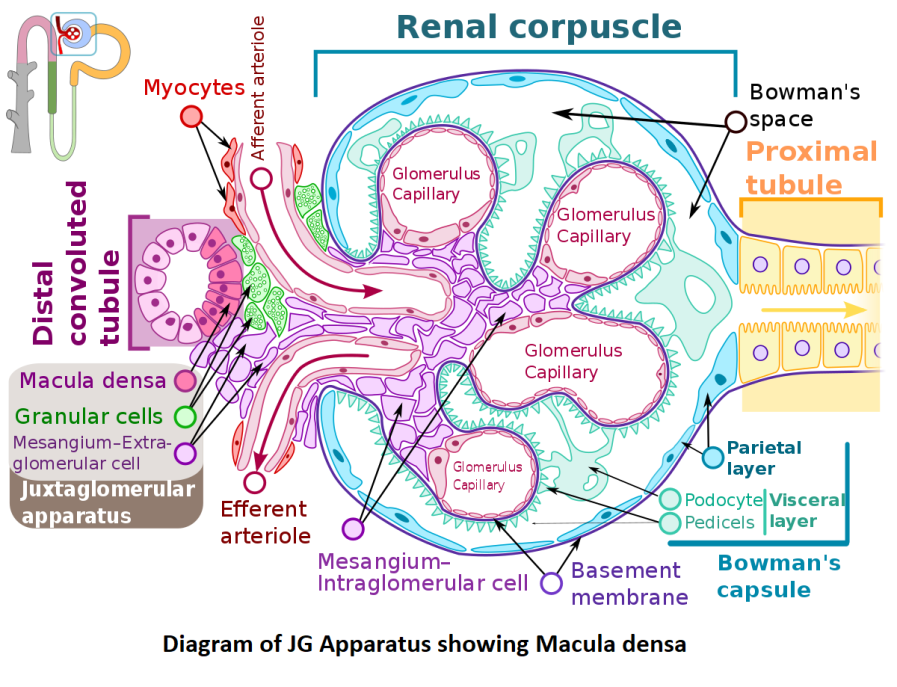
The macula densa is a densely packed specialized cell layer that lines the wall of the distal tubule at the place where the thick ascending limb of the Loop of Henle meets the distal convoluted tubule in the kidney.
The thickening where the distal tubule meets the glomerulus is known as the macula densa.
The concentration of sodium chloride in the distal convoluted tubule affects the cells of the macula densa. When the concentration of sodium chloride in the blood drops, the macula densa sends out a signal that has two effects:
It lowers blood pressure in the afferent arterioles, raising glomerular hydrostatic pressure and assisting in the restoration of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) to normal.
It promotes renin release from the juxtaglomerular cells, which are the principal renin storage sites.
Note:
The macula densa cells contract the afferent arteriole in response to increased salt, lowering blood flow to the glomerulus and the glomerular filtration rate. When blood pressure in the afferent arteriole lowers, the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent arteriole, which are derived from smooth muscle cells, emit renin. Rennin activates Rennin angiotensin aldosterone system which increases blood pressure.
Complete solution:
The macula densa is a densely packed specialized cell layer that lines the wall of the distal tubule at the place where the thick ascending limb of the Loop of Henle meets the distal convoluted tubule in the kidney.
The thickening where the distal tubule meets the glomerulus is known as the macula densa.
The concentration of sodium chloride in the distal convoluted tubule affects the cells of the macula densa. When the concentration of sodium chloride in the blood drops, the macula densa sends out a signal that has two effects:
It lowers blood pressure in the afferent arterioles, raising glomerular hydrostatic pressure and assisting in the restoration of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) to normal.
It promotes renin release from the juxtaglomerular cells, which are the principal renin storage sites.

Note:
The macula densa cells contract the afferent arteriole in response to increased salt, lowering blood flow to the glomerulus and the glomerular filtration rate. When blood pressure in the afferent arteriole lowers, the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent arteriole, which are derived from smooth muscle cells, emit renin. Rennin activates Rennin angiotensin aldosterone system which increases blood pressure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




