
What is elution?
Answer
513.9k+ views
Hint: When an electric field is provided between two electrodes that are completely submerged in a colloidal solution, the colloidal particles tend to gravitate towards one electrode or the other. Electrophoresis is the movement of particles under the influence of an electric field.
The first person to notice this was Ferdinand Frederic Reuss. Cataphoresis refers to positively charged particles (cations) moving towards the cathode, while anaphoresis refers to negatively charged particles (anions) moving towards the anode.
Complete answer:
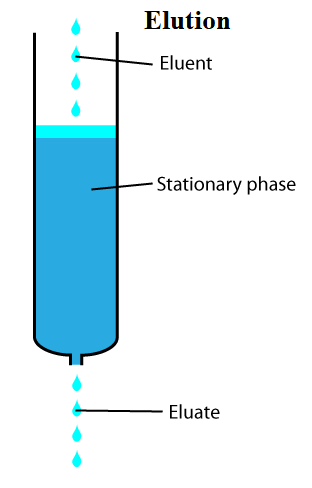
Elution is the process of extracting one material from another by washing with a solvent, as in the washing of loaded ion-exchange resins to remove trapped ions in analytical and organic chemistry.
An analyte is generally adsorbed, or "bound to", an adsorbent in a liquid chromatography column in a liquid chromatography experiment. A solid phase (stationary phase) adsorbent is a powder that is coated on a solid support. Adsorbents can have varied affinities to "hold" onto other molecules, forming a thin coating on the surface of their particles, depending on their composition.
Elution, on the other hand, is the process of eliminating analytes from an adsorbent by passing a solvent through the adsorbent/ analyte combination. The solvent molecules can either pass by the adsorbent/ analyte complex or displace the analyte by binding to the adsorbent in its stead as they "elute", or move down the chromatography column. The analyte can be transported out of the column for analysis once the solvent molecules have displaced it.
As a result, the mobile phase normally flows into a detector or is collected for compositional analysis as it exits the column.
Note:
When charged macromolecules are placed in an electric field, their charge causes them to migrate towards the negative or positive pole. Because nucleic acid has a negative charge, it migrates to the anode.
Slab electrophoresis and capillary electrophoresis are the two forms of this technology.
Types of Electrophoresis:
1. Capillary electrophoresis
2. Gel electrophoresis
3. Paper electrophoresis
4. Slab electrophoresis
5. Zone electrophoresis
6. Immunoelectrophoresis
7. Isoelectrofocusing
The first person to notice this was Ferdinand Frederic Reuss. Cataphoresis refers to positively charged particles (cations) moving towards the cathode, while anaphoresis refers to negatively charged particles (anions) moving towards the anode.
Complete answer:
Elution is the process of extracting one material from another by washing with a solvent, as in the washing of loaded ion-exchange resins to remove trapped ions in analytical and organic chemistry.
An analyte is generally adsorbed, or "bound to", an adsorbent in a liquid chromatography column in a liquid chromatography experiment. A solid phase (stationary phase) adsorbent is a powder that is coated on a solid support. Adsorbents can have varied affinities to "hold" onto other molecules, forming a thin coating on the surface of their particles, depending on their composition.
Elution, on the other hand, is the process of eliminating analytes from an adsorbent by passing a solvent through the adsorbent/ analyte combination. The solvent molecules can either pass by the adsorbent/ analyte complex or displace the analyte by binding to the adsorbent in its stead as they "elute", or move down the chromatography column. The analyte can be transported out of the column for analysis once the solvent molecules have displaced it.
As a result, the mobile phase normally flows into a detector or is collected for compositional analysis as it exits the column.

Note:
When charged macromolecules are placed in an electric field, their charge causes them to migrate towards the negative or positive pole. Because nucleic acid has a negative charge, it migrates to the anode.
Slab electrophoresis and capillary electrophoresis are the two forms of this technology.
Types of Electrophoresis:
1. Capillary electrophoresis
2. Gel electrophoresis
3. Paper electrophoresis
4. Slab electrophoresis
5. Zone electrophoresis
6. Immunoelectrophoresis
7. Isoelectrofocusing
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




