
What is Buoyancy?
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: When we immerse an object into the water the object tends to rise on the surface. In spite of the gravitational force pulling the object down, some objects tend to come to the surface of the water. We can define buoyancy from this observation. Further let us discuss on what factors this phenomenon takes place and whether all the substances actually come to the surface or not.
Complete answer:
To begin with let us define buoyancy.
Buoyancy is a phenomenon, where a substance immersed in water experiences an upward force which tends to bring the object or a body towards the surface of the water. Now let us understand what causes buoyancy.
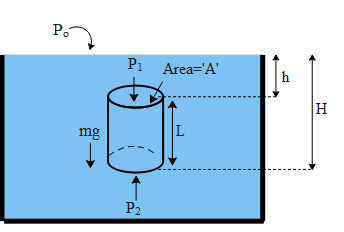
In the above figure let us consider a cylindrical body of mass m, cross sectional area A is completely immersed in water. Let us say the water is open to the atmosphere. Hence the column of the water will exert a pressure on its top and the bottom surface. The pressure on the top surface is ${{P}_{1}}={{P}_{o}}+\rho gh$ and on the bottom surface is ${{P}_{2}}={{P}_{o}}+\rho gH$, ${{P}_{o}}$ is the pressure due to the atmosphere, where $\rho $ is the density of water, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h and H are the respective heights of the top and the bottom surface of the body with respect to the upper surface of water. Pressure on a body is defined as $P=\dfrac{F}{A}$, where F is the force applied on the body across the surface area A. Therefore the force on the top surface (${{F}_{1}}$ ) and the force on the bottom surface (${{F}_{2}}$ ) is given by,
${{F}_{1}}=A\left( {{P}_{o}}+\rho gh \right)\text{ and }{{F}_{2}}=A\left( {{P}_{o}}+\rho gH \right)$.
These two forces are opposite in direction. Hence the resultant i.e. the difference between these forces points upwards which we see as the buoyant force. Hence buoyant force can be mathematically represented as,
$\begin{align}
& \text{Buoyant Force =}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}-{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}}=A\left( {{P}_{o}}+\rho gh \right)-A\left( {{P}_{o}}+\rho gH \right) \\
& = A{{P}_{o}}+A\rho gh-A{{P}_{o}}-A\rho gH \\
&= A\rho gH-A\rho gh \\
& = A\rho g(H-h) \\
\end{align}$
The term H-h is the length (L) of the body as shown in the above figure. Therefore
$\begin{align}
& \text{Buoyant Force}=A\rho g(H-h) \\
& = A\rho gL \\
\end{align}$
The area of the cylinder times the length is equal to the volume (V) of the cylinder. Therefore the above equation can also be written as,
$\begin{align}
& \text{Buoyant Force}=\rho g\left( AL \right) \\
& = \rho gV \\
\end{align}$
Hence the buoyant force on a body with volume V immersed in the water is equal to the upward force acting on it i.e. numerically equal to $\rho gV$.
Note:
It is to be noted that the buoyant force on a body is only proportional to the volume of the body fully or partially immersed in water. The volume of the displaced liquid is equal to the volume of the body immersed in water. From this we can conclude that the weight of the displaced liquid is equal to the buoyant force acting on the body.
Complete answer:
To begin with let us define buoyancy.
Buoyancy is a phenomenon, where a substance immersed in water experiences an upward force which tends to bring the object or a body towards the surface of the water. Now let us understand what causes buoyancy.

In the above figure let us consider a cylindrical body of mass m, cross sectional area A is completely immersed in water. Let us say the water is open to the atmosphere. Hence the column of the water will exert a pressure on its top and the bottom surface. The pressure on the top surface is ${{P}_{1}}={{P}_{o}}+\rho gh$ and on the bottom surface is ${{P}_{2}}={{P}_{o}}+\rho gH$, ${{P}_{o}}$ is the pressure due to the atmosphere, where $\rho $ is the density of water, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h and H are the respective heights of the top and the bottom surface of the body with respect to the upper surface of water. Pressure on a body is defined as $P=\dfrac{F}{A}$, where F is the force applied on the body across the surface area A. Therefore the force on the top surface (${{F}_{1}}$ ) and the force on the bottom surface (${{F}_{2}}$ ) is given by,
${{F}_{1}}=A\left( {{P}_{o}}+\rho gh \right)\text{ and }{{F}_{2}}=A\left( {{P}_{o}}+\rho gH \right)$.
These two forces are opposite in direction. Hence the resultant i.e. the difference between these forces points upwards which we see as the buoyant force. Hence buoyant force can be mathematically represented as,
$\begin{align}
& \text{Buoyant Force =}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}-{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}}=A\left( {{P}_{o}}+\rho gh \right)-A\left( {{P}_{o}}+\rho gH \right) \\
& = A{{P}_{o}}+A\rho gh-A{{P}_{o}}-A\rho gH \\
&= A\rho gH-A\rho gh \\
& = A\rho g(H-h) \\
\end{align}$
The term H-h is the length (L) of the body as shown in the above figure. Therefore
$\begin{align}
& \text{Buoyant Force}=A\rho g(H-h) \\
& = A\rho gL \\
\end{align}$
The area of the cylinder times the length is equal to the volume (V) of the cylinder. Therefore the above equation can also be written as,
$\begin{align}
& \text{Buoyant Force}=\rho g\left( AL \right) \\
& = \rho gV \\
\end{align}$
Hence the buoyant force on a body with volume V immersed in the water is equal to the upward force acting on it i.e. numerically equal to $\rho gV$.
Note:
It is to be noted that the buoyant force on a body is only proportional to the volume of the body fully or partially immersed in water. The volume of the displaced liquid is equal to the volume of the body immersed in water. From this we can conclude that the weight of the displaced liquid is equal to the buoyant force acting on the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




