
What is Boyle temperature?
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Boyle temperature is described for real gases. Real gases do not adhere to the law of ideal gas and the particles of real gases have volumes.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Boyle temperature can be defined as the point in the temperature range in which a real gas starts to behave like an ideal gas at a pressure range. The temperature at which the second coefficient in the expression becomes zero is known as a Boyle temperature. This Boyle temperature balances out the attractive and the repulsive forces that are acting on a gas particle.
We can use the virial equation of state to calculate the Boyle temperature. Boyle temperature can be expressed in the terms of the virial coefficients.
$Z = 1 + \dfrac{B}{{{V_m}}} + ....$
Additional information:
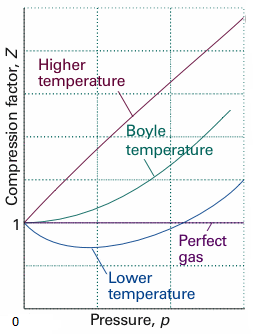
The above graph is plotted between the pressure $p$and compressibility factor$Z$. Boyle temperature is nicely marked in the graph. From this point, the real gas starts to behave like an ideal gas. The compression factor $Z$ is given as,
$Z = \dfrac{{p{V_m}}}{{RT}}$
Here, $Z$is the compressibility factor, ${V_m}$ is the volume,$R$ is the gas constant, $T$ is the
temperature and $p$ is the pressure.
$Z = 1$ for an ideal gas. Real gases show some deviation.
Note: Critical Temperature is different from Boyle's temperature. At the critical temperature, a gas shows non-ideal behavior. Critical temperature is lower than the Boyle temperature. At Boyle temperature a gas starts to behave like an ideal gas and for ideal gas, the compressibility factor is 1, that is, $Z = 1$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Boyle temperature can be defined as the point in the temperature range in which a real gas starts to behave like an ideal gas at a pressure range. The temperature at which the second coefficient in the expression becomes zero is known as a Boyle temperature. This Boyle temperature balances out the attractive and the repulsive forces that are acting on a gas particle.
We can use the virial equation of state to calculate the Boyle temperature. Boyle temperature can be expressed in the terms of the virial coefficients.
$Z = 1 + \dfrac{B}{{{V_m}}} + ....$
Additional information:

The above graph is plotted between the pressure $p$and compressibility factor$Z$. Boyle temperature is nicely marked in the graph. From this point, the real gas starts to behave like an ideal gas. The compression factor $Z$ is given as,
$Z = \dfrac{{p{V_m}}}{{RT}}$
Here, $Z$is the compressibility factor, ${V_m}$ is the volume,$R$ is the gas constant, $T$ is the
temperature and $p$ is the pressure.
$Z = 1$ for an ideal gas. Real gases show some deviation.
Note: Critical Temperature is different from Boyle's temperature. At the critical temperature, a gas shows non-ideal behavior. Critical temperature is lower than the Boyle temperature. At Boyle temperature a gas starts to behave like an ideal gas and for ideal gas, the compressibility factor is 1, that is, $Z = 1$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




