
What is a resonance structure?
Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint: Chemical compounds exist in resonating structures. These structures are known as canonical forms, and they do not have any real existence. The structures are represented as Lewis structures, where movement or delocalization of electrons is shown.
Complete answer:
Resonance form or structure of any molecule is known to be used when a single Lewis structure cannot describe the molecule accurately. It can be used in the case of polyatomic ions. The resonating structures are of no real existence, as any molecule cannot exist for more than a fraction of time.
Resonance structures contain the same number of bonding, and non bonding electrons as in the Lewis structure. The resonance structures have the same energy and, same position of nuclei. The resonance structures show the shifting of electrons, and can be seen in compounds containing double bonds. More the number of resonating structures a molecule has, the more stable the molecule is considered.
Resonance can be explained by the fact that delocalization of electrons in a compound, results in various canonical forms of a molecule. The delocalization is shown for a carbon dioxide$C{{O}_{2}}$ molecule as,
\[\left[ :\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{O}}\,\equiv C-\underset{\centerdot \centerdot }{\overset{\overset{-}{\mathop{\centerdot \centerdot }}\,}{\mathop{O}}}\,:\,\leftrightarrow \,:\ddot{O}=\ddot{O}:\,\leftrightarrow :\underset{\centerdot \centerdot }{\overset{\overset{-}{\mathop{\centerdot \centerdot }}\,}{\mathop{O}}}\,-C\equiv \overset{\oplus }{\mathop{O}}\,: \right]\]
The 3 resonating structures of $C{{O}_{2}}$, shows the delocalization of electrons. Through this delocalization the molecule gains stability. The molecule gains stability because the energy of the resonance hybrid structure is less than the energy of any of the canonical forms.
Another structure of resonance are in the case of aromatic compounds, as
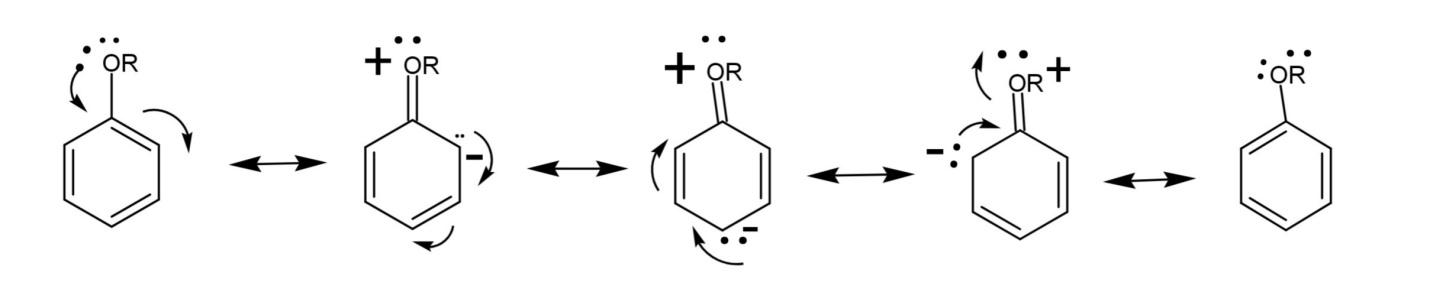
The resonance of an ether group attached with a benzene ring is shown, and the ortho and para positions getting a partial negative charge is shown. This increases the reactivity of these positions.
Hence, a resonance structure is a structure that has canonical forms of the Lewis structure showing delocalization of electrons in a molecule.
Note:
The delocalization of electrons in any molecule is accompanied by the reduction in energy, more the delocalization of electrons, more is the reduction in the energy observed. These structures only increase the stability of a molecule while decreasing the energy.
Complete answer:
Resonance form or structure of any molecule is known to be used when a single Lewis structure cannot describe the molecule accurately. It can be used in the case of polyatomic ions. The resonating structures are of no real existence, as any molecule cannot exist for more than a fraction of time.
Resonance structures contain the same number of bonding, and non bonding electrons as in the Lewis structure. The resonance structures have the same energy and, same position of nuclei. The resonance structures show the shifting of electrons, and can be seen in compounds containing double bonds. More the number of resonating structures a molecule has, the more stable the molecule is considered.
Resonance can be explained by the fact that delocalization of electrons in a compound, results in various canonical forms of a molecule. The delocalization is shown for a carbon dioxide$C{{O}_{2}}$ molecule as,
\[\left[ :\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{O}}\,\equiv C-\underset{\centerdot \centerdot }{\overset{\overset{-}{\mathop{\centerdot \centerdot }}\,}{\mathop{O}}}\,:\,\leftrightarrow \,:\ddot{O}=\ddot{O}:\,\leftrightarrow :\underset{\centerdot \centerdot }{\overset{\overset{-}{\mathop{\centerdot \centerdot }}\,}{\mathop{O}}}\,-C\equiv \overset{\oplus }{\mathop{O}}\,: \right]\]
The 3 resonating structures of $C{{O}_{2}}$, shows the delocalization of electrons. Through this delocalization the molecule gains stability. The molecule gains stability because the energy of the resonance hybrid structure is less than the energy of any of the canonical forms.
Another structure of resonance are in the case of aromatic compounds, as

The resonance of an ether group attached with a benzene ring is shown, and the ortho and para positions getting a partial negative charge is shown. This increases the reactivity of these positions.
Hence, a resonance structure is a structure that has canonical forms of the Lewis structure showing delocalization of electrons in a molecule.
Note:
The delocalization of electrons in any molecule is accompanied by the reduction in energy, more the delocalization of electrons, more is the reduction in the energy observed. These structures only increase the stability of a molecule while decreasing the energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




