
What happens during metaphase?
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: Mitosis is a form of cell division in which one mother cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells. Mitosis is divided into four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Complete answer:
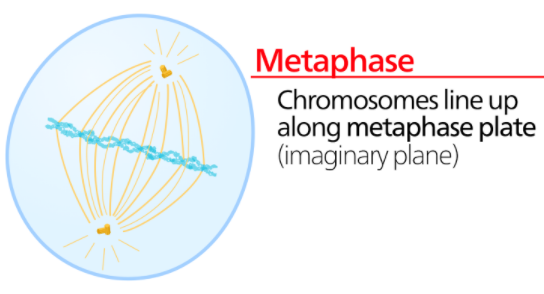
Mitosis is the mechanism by which duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell is divided into two identical daughter cells. Metaphase is the third stage of mitosis. During metaphase, the cell's chromosomes meet in the centre of the cell, creating a molecular tug of war. The chromosomes have been replicated and remained at a central point known as the centromere are called sister chromatids.
Before metaphase, protein structures known as kinetochores formed around the centromere. Kinetochore microtubules are long protein filaments that extend from the cell's poles and attach to the kinetochores.
During metaphase, the spindle has gathered all of the chromosomes and arranged them in the centre of the cell, ready to divide.
- All of the chromosomes meet at the metaphase plate, which is a term for the plane where the chromosomes line up rather than a physical structure.
- At this time, each chromosome's two kinetochores should be connected to microtubules from opposite spindle poles.
Before entering anaphase, the cell will ensure that all chromosomes are at the metaphase plate and that their kinetochores are correctly attached to microtubules. The spindle checkpoint ensures that the sister chromatids split evenly between the two daughter cells when they separate in the next step. When a chromosome is misaligned or attached, the cell will stop dividing before the issue is resolved.
Note: Mitosis is absolutely necessary for life because it generates new cells for growth and replaces worn-out cells. Depending on the type of cell and the species of organism, mitosis can take minutes or hours. It is affected by the time of day, the temperature, and chemicals.
Complete answer:
Mitosis is the mechanism by which duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell is divided into two identical daughter cells. Metaphase is the third stage of mitosis. During metaphase, the cell's chromosomes meet in the centre of the cell, creating a molecular tug of war. The chromosomes have been replicated and remained at a central point known as the centromere are called sister chromatids.
Before metaphase, protein structures known as kinetochores formed around the centromere. Kinetochore microtubules are long protein filaments that extend from the cell's poles and attach to the kinetochores.
During metaphase, the spindle has gathered all of the chromosomes and arranged them in the centre of the cell, ready to divide.
- All of the chromosomes meet at the metaphase plate, which is a term for the plane where the chromosomes line up rather than a physical structure.
- At this time, each chromosome's two kinetochores should be connected to microtubules from opposite spindle poles.
Before entering anaphase, the cell will ensure that all chromosomes are at the metaphase plate and that their kinetochores are correctly attached to microtubules. The spindle checkpoint ensures that the sister chromatids split evenly between the two daughter cells when they separate in the next step. When a chromosome is misaligned or attached, the cell will stop dividing before the issue is resolved.

Note: Mitosis is absolutely necessary for life because it generates new cells for growth and replaces worn-out cells. Depending on the type of cell and the species of organism, mitosis can take minutes or hours. It is affected by the time of day, the temperature, and chemicals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




