
What happens during anaphase?
Answer
493.5k+ views
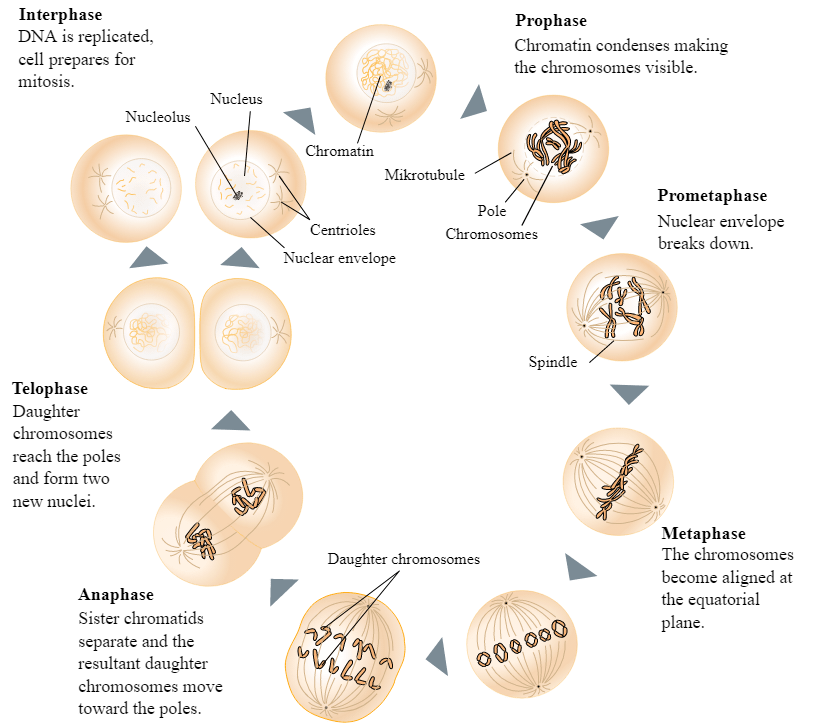
Hint: Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase are the stages of mitosis, which are sometimes followed by cytokinesis. The phrase "interphase" refers to all of the stages preceding mitosis, including the G1, S, and G2 phases. Interphase, prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, cytokinesis I, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II, and cytokinesis II are the stages of meiosis.
Complete answer:
Anaphase is the fourth phase of mitosis, the process by which a parent cell's replicated genetic material is separated into two identical daughter cells from the nucleus. The replicated chromosomes, known as sister chromatids, are oriented along the equator of the cell on the equatorial plane before anaphase begins. The sister chromatids are two identical DNA copies that are linked at the centromere.
Each pair of chromosomes is divided into two identical, independent chromosomes during anaphase. The mitotic spindle is a structure that separates the chromosomes. The mitotic spindle is made up of microtubules, which are long proteins connected to a chromosome on one end and the cell pole on the other. At their centromeres, the sister chromatids are split at the same time. The spindle then pulls the divided chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. Anaphase guarantees that each daughter cell has the same set of chromosomes, and it is followed by telophase, the fifth and final phase of mitosis. The spindle then pulls the divided chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell.
Anaphase guarantees that each daughter cell has the same set of chromosomes, and it is followed by telophase, the fifth and final phase of mitosis.
Note:
Anaphase. Sister chromatids split from one another and are drawn to the cell's opposite poles. The non-chromosomal microtubules push the spindle's two poles apart, while the chromosome-attached microtubules pull the chromosomes towards the poles. The sister chromatids move to opposing poles of the cells, which is the main event of Anaphase.
Complete answer:
Anaphase is the fourth phase of mitosis, the process by which a parent cell's replicated genetic material is separated into two identical daughter cells from the nucleus. The replicated chromosomes, known as sister chromatids, are oriented along the equator of the cell on the equatorial plane before anaphase begins. The sister chromatids are two identical DNA copies that are linked at the centromere.
Each pair of chromosomes is divided into two identical, independent chromosomes during anaphase. The mitotic spindle is a structure that separates the chromosomes. The mitotic spindle is made up of microtubules, which are long proteins connected to a chromosome on one end and the cell pole on the other. At their centromeres, the sister chromatids are split at the same time. The spindle then pulls the divided chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. Anaphase guarantees that each daughter cell has the same set of chromosomes, and it is followed by telophase, the fifth and final phase of mitosis. The spindle then pulls the divided chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell.
Anaphase guarantees that each daughter cell has the same set of chromosomes, and it is followed by telophase, the fifth and final phase of mitosis.

Note:
Anaphase. Sister chromatids split from one another and are drawn to the cell's opposite poles. The non-chromosomal microtubules push the spindle's two poles apart, while the chromosome-attached microtubules pull the chromosomes towards the poles. The sister chromatids move to opposing poles of the cells, which is the main event of Anaphase.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




