
What does intensity mean?
Answer
541.5k+ views
Hint: Intensity can be used to measure the energy transmitted from a source, the more the energy, the more is the intensity. It depends on the power or energy and the area perpendicular to the plane of transmission. Intensity is a characteristic of the source and hence different for different sources. It is a scalar quantity.
Complete step by step solution:
The intensity is the measure of energy transmitted from a source. Intensity is defined as the power that is transmitted per unit area and the area is perpendicular to the direction in which energy is being propagated. The SI unit of intensity is watts per square metre ($W\,{{m}^{-2}}$).
The intensity is given as-
$\begin{align}
& I=\dfrac{P}{{{A}_{\bot }}} \\
& \Rightarrow I=\dfrac{E}{(A\sin \theta )t} \\
\end{align}$
Here, $I$ is the intensity
$P$ is the power
${{A}_{\bot }}$ is the perpendicular component of area
$E$ is the total energy
$\theta $ is the angle between the plane of propagation of energy and area
$t$ is the time taken
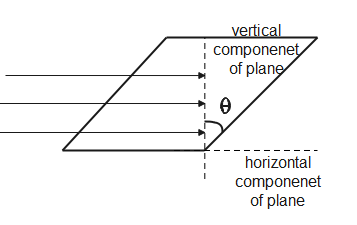
The figure shown above depicts the horizontal and vertical components of area of a plane and the angle between them
The intensity also follows inverse square law which means that the intensity radiating from a source is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source, therefore,
$I\propto \dfrac{1}{{{r}^{2}}}$
Here, $r$ is the distance from the source of energy
Therefore, the intensity is the power transmitted per unit area perpendicular to the plane of transmission.
Note: The intensity can also be calculated as the product of energy density and velocity. Power can also be calculated as the product of force and velocity. The energy of photons in light depends on the intensity; as the intensity increases, the energy of photons also increases and vice versa.
Complete step by step solution:
The intensity is the measure of energy transmitted from a source. Intensity is defined as the power that is transmitted per unit area and the area is perpendicular to the direction in which energy is being propagated. The SI unit of intensity is watts per square metre ($W\,{{m}^{-2}}$).
The intensity is given as-
$\begin{align}
& I=\dfrac{P}{{{A}_{\bot }}} \\
& \Rightarrow I=\dfrac{E}{(A\sin \theta )t} \\
\end{align}$
Here, $I$ is the intensity
$P$ is the power
${{A}_{\bot }}$ is the perpendicular component of area
$E$ is the total energy
$\theta $ is the angle between the plane of propagation of energy and area
$t$ is the time taken

The figure shown above depicts the horizontal and vertical components of area of a plane and the angle between them
The intensity also follows inverse square law which means that the intensity radiating from a source is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source, therefore,
$I\propto \dfrac{1}{{{r}^{2}}}$
Here, $r$ is the distance from the source of energy
Therefore, the intensity is the power transmitted per unit area perpendicular to the plane of transmission.
Note: The intensity can also be calculated as the product of energy density and velocity. Power can also be calculated as the product of force and velocity. The energy of photons in light depends on the intensity; as the intensity increases, the energy of photons also increases and vice versa.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




