
What are Grana and Stroma?
Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: Chloroplast is a cell organelle found in plant cells majorly and contains grana and stroma, which help in photosynthesis. Photosynthesis occurs in two stages. A chloroplast is a type of organelle found in the cells of plants and algae that is responsible for photosynthesis, or the conversion of solar energy into chemical energy for growth.
Complete answer:
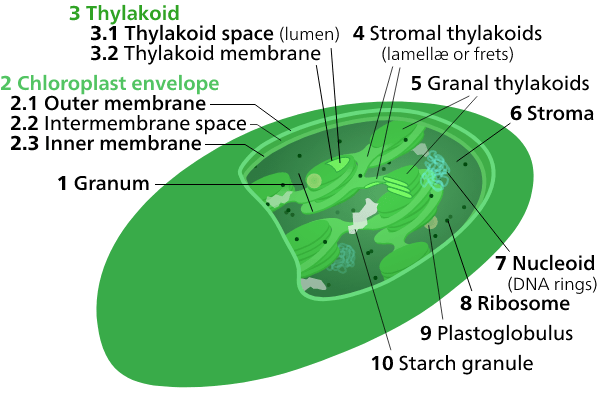
The whitish fluid that surrounds the grana within the chloroplast is called stroma. Within the stroma are grana (thylakoid stacks) and sub-organelles or daughter cells, where photosynthesis begins before the chemical changes in the stroma are completed.
There are two stages to photosynthesis. Light-dependent processes catch light energy and use it to generate the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH in the first stage. The light-independent reactions utilise these products to fix carbon by trapping and reducing carbon dioxide during the second stage.
The Calvin cycle, often known as light-independent processes, is a sequence of biological redox events that occur in the stroma. Carbon fixation, reduction processes, and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration are the three phases.
The stroma also contains chloroplast DNA and chloroplast ribosomes, as well as molecular processes such as chloroplast DNA replication and transcription/translation of some chloroplast proteins.
Note :
Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts, which are the structural places where light energy is turned into food. Chloroplasts' principal function is to capture light energy in order to convert carbon dioxide gas into sugar. Chloroplasts create oxygen gas as part of this process, which is essential for animal life. Pigments are molecules found in chloroplasts.
Complete answer:
The whitish fluid that surrounds the grana within the chloroplast is called stroma. Within the stroma are grana (thylakoid stacks) and sub-organelles or daughter cells, where photosynthesis begins before the chemical changes in the stroma are completed.
There are two stages to photosynthesis. Light-dependent processes catch light energy and use it to generate the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH in the first stage. The light-independent reactions utilise these products to fix carbon by trapping and reducing carbon dioxide during the second stage.
The Calvin cycle, often known as light-independent processes, is a sequence of biological redox events that occur in the stroma. Carbon fixation, reduction processes, and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration are the three phases.
The stroma also contains chloroplast DNA and chloroplast ribosomes, as well as molecular processes such as chloroplast DNA replication and transcription/translation of some chloroplast proteins.

Note :
Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts, which are the structural places where light energy is turned into food. Chloroplasts' principal function is to capture light energy in order to convert carbon dioxide gas into sugar. Chloroplasts create oxygen gas as part of this process, which is essential for animal life. Pigments are molecules found in chloroplasts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




