
What are Aromatic hydrocarbons?
Answer
495.6k+ views
Hint: Hydrocarbons are organic compounds mainly consisting of carbon atom chains or rings through single, double or triple bonds. The hydrocarbons containing single bonds only are called saturated hydrocarbons and the ones with double bonds are called unsaturated hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons are special unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Complete answer:
Aromatic hydrocarbons are the hydrocarbons that are present in the form of rings of carbon atoms with alternative double bonds. But every conjugated hydrocarbon ring or every unsaturated organic compound is not an aromatic hydrocarbon. Thus there are a certain set of rules that must be followed in order to be called an aromatic hydrocarbon and these rules are called Huckel’s rules.
Huckel's rule can be stated as follows:
The hydrocarbon must be planar in nature
The compound must contain \[4n + 2\] number of \[\pi \] electrons
The compound must have a cyclic conjugation, i.e. a cyclic continuous delocalization of \[\pi \] electrons must be present inside the compound.
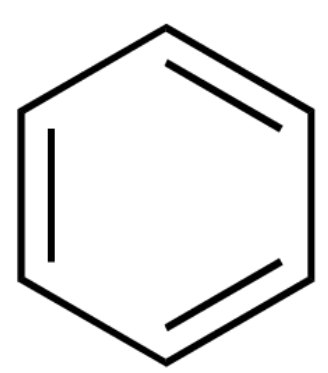
Based on the given rules many organic compounds can be classified as aromatic compounds. One popular example of aromatic hydrocarbon is benzene with three alternative \[\pi \] bonds. It is a six membered carbon ring that has resonating structures due to which the \[\pi \] bonds keep delocalizing throughout the ring.
Note:
Even though all carbon atoms are not connected through a double bond in an aromatic hydrocarbon, the resonance or conjugation makes all the carbon-carbon bonds partially double bonded in nature due to which all the bond lengths are equal and an unsubstituted aromatic hydrocarbon is equally vulnerable to an electrophilic attack.
Complete answer:
Aromatic hydrocarbons are the hydrocarbons that are present in the form of rings of carbon atoms with alternative double bonds. But every conjugated hydrocarbon ring or every unsaturated organic compound is not an aromatic hydrocarbon. Thus there are a certain set of rules that must be followed in order to be called an aromatic hydrocarbon and these rules are called Huckel’s rules.
Huckel's rule can be stated as follows:
The hydrocarbon must be planar in nature
The compound must contain \[4n + 2\] number of \[\pi \] electrons
The compound must have a cyclic conjugation, i.e. a cyclic continuous delocalization of \[\pi \] electrons must be present inside the compound.
Based on the given rules many organic compounds can be classified as aromatic compounds. One popular example of aromatic hydrocarbon is benzene with three alternative \[\pi \] bonds. It is a six membered carbon ring that has resonating structures due to which the \[\pi \] bonds keep delocalizing throughout the ring.

Note:
Even though all carbon atoms are not connected through a double bond in an aromatic hydrocarbon, the resonance or conjugation makes all the carbon-carbon bonds partially double bonded in nature due to which all the bond lengths are equal and an unsubstituted aromatic hydrocarbon is equally vulnerable to an electrophilic attack.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




