
Volume of thoracic chamber increases in the anteroposterior and dorsoventral axis in the human by?
(a)Contraction of diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
(b)Relaxation of diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
(c)Relaxation of the diaphragm and abdominal muscles
(d)None of the above
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: A layer of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that stretches across the bottom of the thoracic cavity is the thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm.
Complete answer:
Thoracic chamber volume rises in human anteroposterior and dorso-ventral axes through diaphragm and external intercostal muscle contractions. It travels inferiorly into the abdominal cavity as the diaphragm contracts, providing a greater thoracic cavity and more space for the lungs. External intercostal muscle contraction pushes the ribs inward and outward, allowing the rib cage to expand, which raises the thoracic cavity width.
Additional Information: The diaphragm divides the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity, containing the heart and lungs, and plays an essential role in respiration: the volume of the thoracic cavity increases as the diaphragm contracts, generating a negative pressure there that pulls air into the lungs. In anatomy, the term diaphragm created by Gerard of Cremona may refer to other flat structures, such as the urogenital diaphragm or the pelvic diaphragm, but the thoracic diaphragm is typically referred to as the diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric, because the broad liver lies under the right half of the diaphragm, the right half is higher up (higher) to the left half. Because of the proximity of the nucleus, there is also a theory that the diaphragm on the other hand is lower.
So, the correct answer is ‘contraction of diaphragm and external intercostal muscles’.
Note: Other mammals have diaphragms, and other vertebrates have diaphragm-like structures, such as amphibians and reptiles, but significant anatomy specifics that differ, such as the location of the lungs in the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is a muscle and fibrous tissue structure in C form that divides the thoracic cavity from the abdomen. The dome bends upwards. The floor of the thoracic cavity forms the superior surface of the dome, and the roof of the abdominal cavity forms the inferior surface.
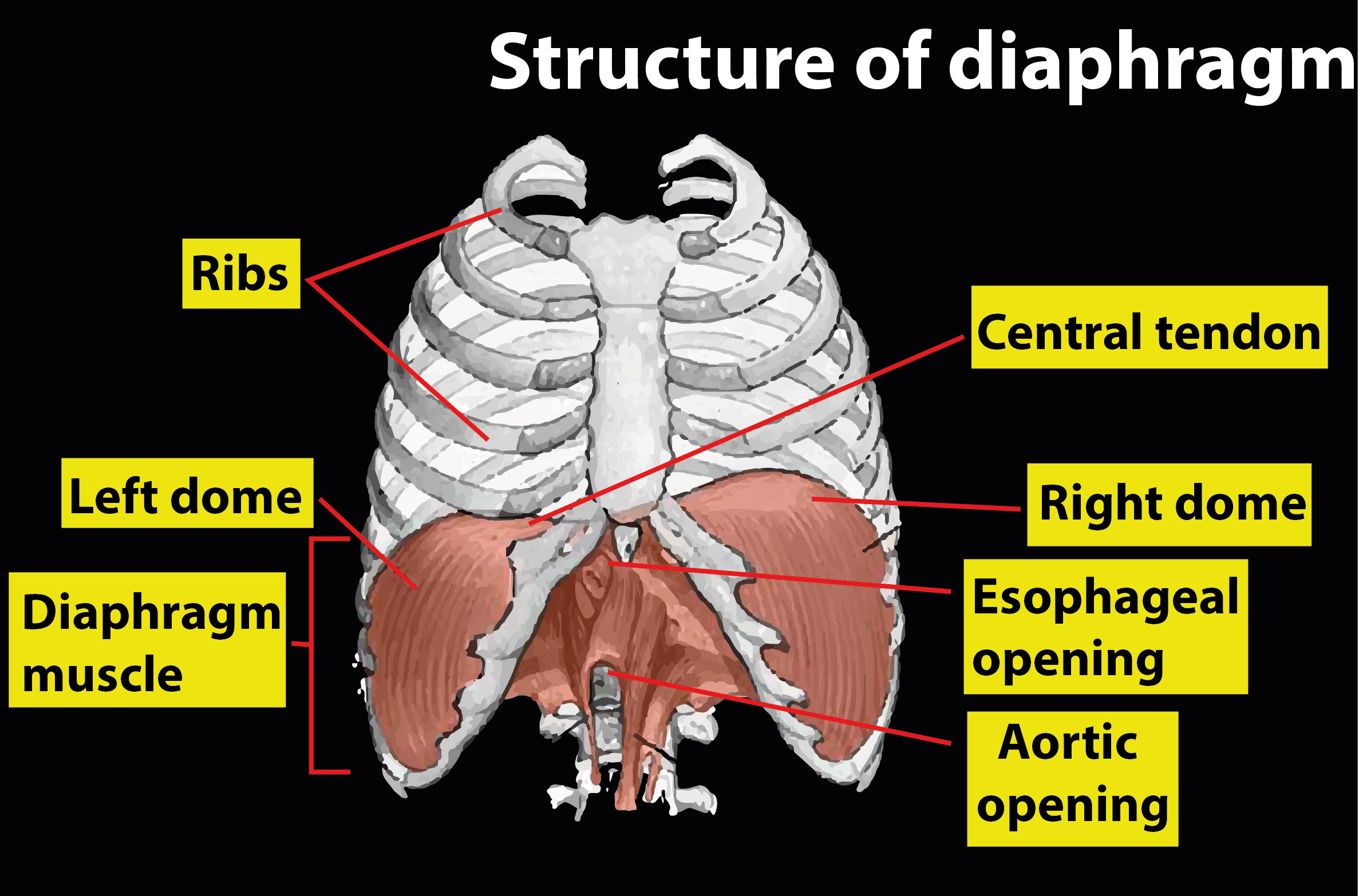
Complete answer:
Thoracic chamber volume rises in human anteroposterior and dorso-ventral axes through diaphragm and external intercostal muscle contractions. It travels inferiorly into the abdominal cavity as the diaphragm contracts, providing a greater thoracic cavity and more space for the lungs. External intercostal muscle contraction pushes the ribs inward and outward, allowing the rib cage to expand, which raises the thoracic cavity width.
Additional Information: The diaphragm divides the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity, containing the heart and lungs, and plays an essential role in respiration: the volume of the thoracic cavity increases as the diaphragm contracts, generating a negative pressure there that pulls air into the lungs. In anatomy, the term diaphragm created by Gerard of Cremona may refer to other flat structures, such as the urogenital diaphragm or the pelvic diaphragm, but the thoracic diaphragm is typically referred to as the diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric, because the broad liver lies under the right half of the diaphragm, the right half is higher up (higher) to the left half. Because of the proximity of the nucleus, there is also a theory that the diaphragm on the other hand is lower.
So, the correct answer is ‘contraction of diaphragm and external intercostal muscles’.
Note: Other mammals have diaphragms, and other vertebrates have diaphragm-like structures, such as amphibians and reptiles, but significant anatomy specifics that differ, such as the location of the lungs in the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is a muscle and fibrous tissue structure in C form that divides the thoracic cavity from the abdomen. The dome bends upwards. The floor of the thoracic cavity forms the superior surface of the dome, and the roof of the abdominal cavity forms the inferior surface.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




