
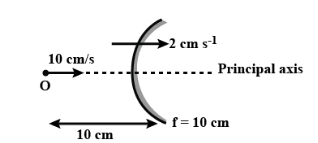
What is the velocity (in cm per second) of the image in the situation shown below. (O=object, f=focal length). Object moves with velocity 10 $\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}$ and mirror moves with velocity 2$\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}$ as shown.

Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: In the question we are given a mirror, an object moves with certain velocity and also mirror moves with some significant speed hence the image which will be obtained by us will have some velocity with which it will be moving with say V. The solution lies in the eqn $\dfrac{1}{v}$ +$\dfrac{1}{u}$ =$\dfrac{1}{f}$. This will give us the position of the image and then by differentiating the mirror eqn the velocity will be known.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1:
There are two types of mirror: concave mirror and convex mirror. Before starting the solution we must know about the mirror formula and how to use it. It is an eqn relating object distance and image distance with focal length is known as a mirror equation. It is also known as a mirror formula. In a spherical mirror the distance between the Principal focus and pole of the mirror is called Focal Length(f).
Mirror formula is $\dfrac{1}{v}$ +$\dfrac{1}{u}$ =$\dfrac{1}{f}$ here, v is the position of the image, u is the position of object and f is the focal length.
Step 2:
Now, coming to the question we have given that the object and mirror is moving with a particular speed and need to determine the velocity of the image. Focal length is 10cm and distance of object is also 10cm(from figure).
By the mirror formula we will get the position of the image. $\dfrac{1}{v}$ +$\dfrac{1}{u}$ =$\dfrac{1}{f}$, here u will be of negative sign because it is on the back side of the mirror.
F=10cm, and u=(-10)cm then ; $\dfrac{1}{v}$ +$\dfrac{1}{{ - 10}}$ =$\dfrac{1}{{10}}$ ……...(eqn 1)
On solving the given values we will get v=5cm which means the position of the image is 5cm far from the mirror and in a positive direction.
Step 3:
Now we need to know the velocity.
The velocity is written as change in distance per unit time =$\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}$ where \[dx\] is change in distance. Following same for mirror formula
$\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}$ =−10$\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}$(change in object distance w.r.t time is given in question)
Same for the mirror we will write $\dfrac{{d(x + a)}}{{dt}}$ =2$\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}$, which means $\dfrac{{da}}{{dt}}$ = (−10+2) $\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}$
Which is equal to − 8$\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}$(relative speed)
Then $\dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$ (image velocity)=${v_i}$ = 2
Differentiating eqn 1 w.r.t. time we will get, $\dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$ =${\left( {\dfrac{5}{{10}}} \right)^2}$ $\dfrac{{da}}{{dt}}$
Which is equals to ${v_i}$ − 2=${\left( {\dfrac{5}{{10}}} \right)^2}$ $\left( { - 8\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}} \right)$
\[{v_i}\]= zero.
This implies the velocity of the image will be zero.
Additional Information:
Uses of concave mirror:
Shaving mirrors.
Head mirrors.
Ophthalmoscope.
Astronomical telescopes.
Headlights.
Solar furnaces.
Uses of convex mirror:
Sunglasses. We might have used sunglasses many times.
Vehicle mirrors.
Magnifying glasses.
For security purposes.
Street light reflectors.
Note: Points of error:
- Differential equation is sensitive and need to be taken care while differentiating.
- Putting values on right place.
- In the mirror formula the sign should be considered for image and object both. Positive if in front of mirror and negative if in opposite of mirror.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1:
There are two types of mirror: concave mirror and convex mirror. Before starting the solution we must know about the mirror formula and how to use it. It is an eqn relating object distance and image distance with focal length is known as a mirror equation. It is also known as a mirror formula. In a spherical mirror the distance between the Principal focus and pole of the mirror is called Focal Length(f).
Mirror formula is $\dfrac{1}{v}$ +$\dfrac{1}{u}$ =$\dfrac{1}{f}$ here, v is the position of the image, u is the position of object and f is the focal length.
Step 2:
Now, coming to the question we have given that the object and mirror is moving with a particular speed and need to determine the velocity of the image. Focal length is 10cm and distance of object is also 10cm(from figure).
By the mirror formula we will get the position of the image. $\dfrac{1}{v}$ +$\dfrac{1}{u}$ =$\dfrac{1}{f}$, here u will be of negative sign because it is on the back side of the mirror.
F=10cm, and u=(-10)cm then ; $\dfrac{1}{v}$ +$\dfrac{1}{{ - 10}}$ =$\dfrac{1}{{10}}$ ……...(eqn 1)
On solving the given values we will get v=5cm which means the position of the image is 5cm far from the mirror and in a positive direction.
Step 3:
Now we need to know the velocity.
The velocity is written as change in distance per unit time =$\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}$ where \[dx\] is change in distance. Following same for mirror formula
$\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}$ =−10$\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}$(change in object distance w.r.t time is given in question)
Same for the mirror we will write $\dfrac{{d(x + a)}}{{dt}}$ =2$\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}$, which means $\dfrac{{da}}{{dt}}$ = (−10+2) $\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}$
Which is equal to − 8$\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}$(relative speed)
Then $\dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$ (image velocity)=${v_i}$ = 2
Differentiating eqn 1 w.r.t. time we will get, $\dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}$ =${\left( {\dfrac{5}{{10}}} \right)^2}$ $\dfrac{{da}}{{dt}}$
Which is equals to ${v_i}$ − 2=${\left( {\dfrac{5}{{10}}} \right)^2}$ $\left( { - 8\dfrac{m}{{\sec }}} \right)$
\[{v_i}\]= zero.
This implies the velocity of the image will be zero.
Additional Information:
Uses of concave mirror:
Shaving mirrors.
Head mirrors.
Ophthalmoscope.
Astronomical telescopes.
Headlights.
Solar furnaces.
Uses of convex mirror:
Sunglasses. We might have used sunglasses many times.
Vehicle mirrors.
Magnifying glasses.
For security purposes.
Street light reflectors.
Note: Points of error:
- Differential equation is sensitive and need to be taken care while differentiating.
- Putting values on right place.
- In the mirror formula the sign should be considered for image and object both. Positive if in front of mirror and negative if in opposite of mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




