
Using integration, find the area of the region bounded by the line $y=1+\left| x+1 \right|,x=-2,x=3\ and\ y=0$.
Answer
616.8k+ views
Hint: We will first start by drawing the graph of curves $y=1+\left| x+1 \right|,x=-2,x=3\ and\ y=0$. Then we will use the fact that the algebraic area under a curve $f\left( x \right)$ can be found by integration as $\int{f\left( x \right)dx}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, before starting the solution we first to understand that the physical significance of \[\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}\] is,
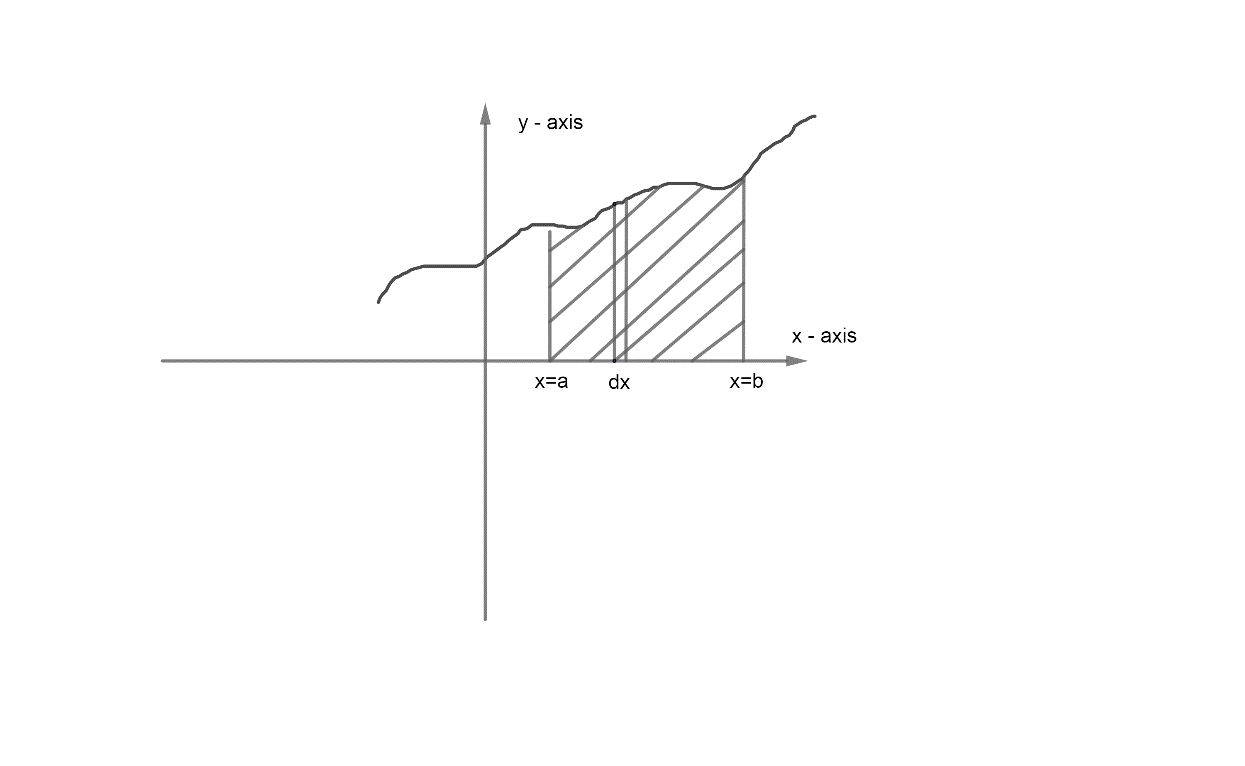
Now, we can see from the graph that \[\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}\] is nothing but the area bounded by the line $y=f\left( x \right),x=a,x=b\ and\ x-axis$.
Now, we know that the graph of $y=1+\left| x+1 \right|$ is shifted 1 units upward and 1 units leftwards from the origin of the graph of $y=\left( x \right)$. So, we have the graph by using the concept of shifted origin as,
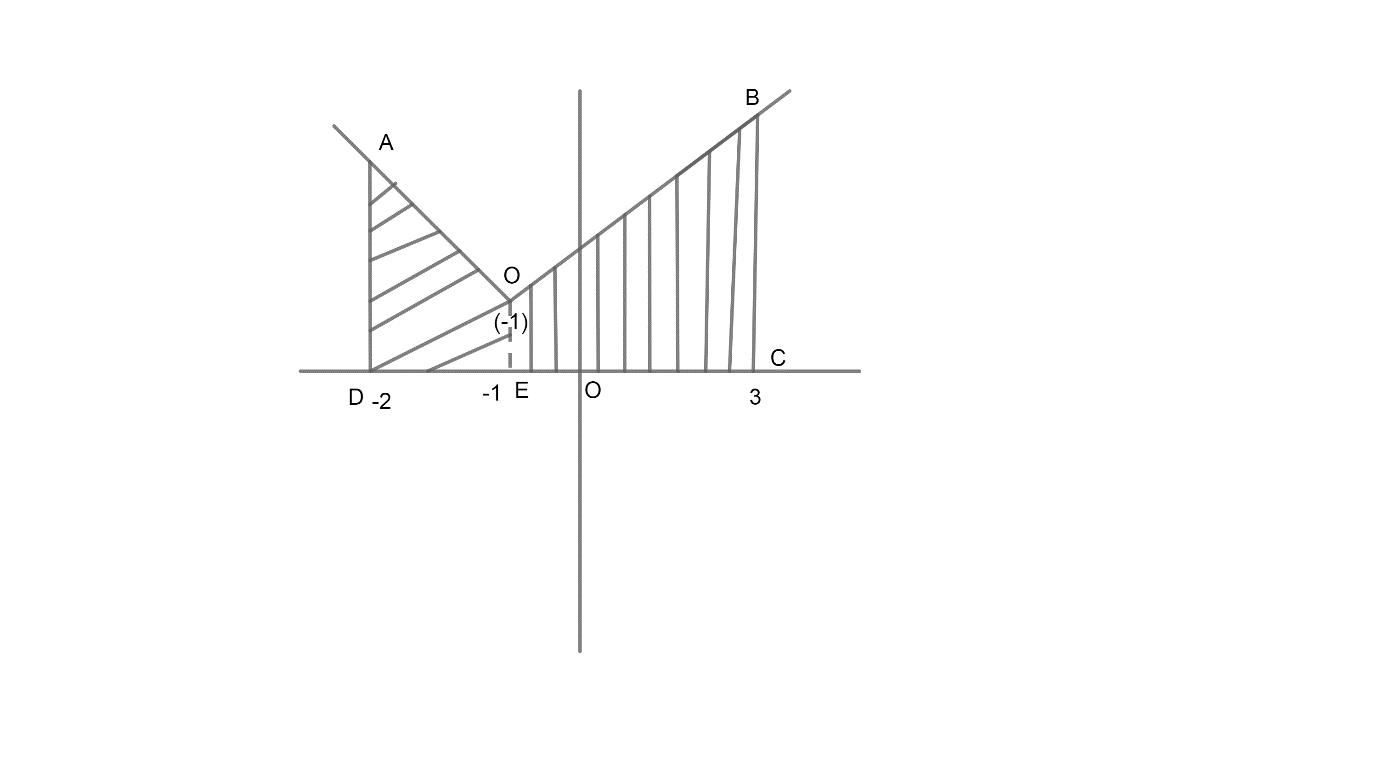
Now, we will first find the area of region ADEO. So, we have the equation of line AO as,
$\begin{align}
& y=1-x-1 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-x \\
\end{align}$
So, we have the area of region,
$ADEO=\int\limits_{-2}^{-1}{\left( -x \right)dx}$
We have put the limits as x = -1 to x = -2 from the graph. Also, we know that $\int{{{x}^{n}}dx}=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}$. So, we have,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left. \dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right|_{-2}^{-1} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow -\left( \dfrac{1}{2}-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow -\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}sq\ units \\
\end{align}$
Now, similarly we will find the area of region OECB as,
$\int\limits_{-1}^{3}{\left( x+2 \right)dx}$
We have put the limits as x = -1 to x = 3 by referring the graph and again using the fact that $\int{{{x}^{n}}dx}=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}$. We have,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}+2x \right)_{-1}^{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}}{2}+2\left( 3-\left( -1 \right) \right) \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{9}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}+2\left( 3+1 \right) \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{9-1}{2}+2\times 4 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{8}{2}+2\times 4 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 4+8 \\
& \Rightarrow 12sq\ units \\
\end{align}$
So, the total area bounded by the region is,
ar of region ADEO + ar of region OECD
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}+12 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3+24}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{27}{2}sq\ units \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the total area bounded by the given curves is $\dfrac{27}{2}sq\ units$.
Note: While solving the question it is important to note how we have drawn the graph of $\left( y-1 \right)=\left| x-\left( -1 \right) \right|$ from the graph of $y=\left| x \right|$ by using the concept of shifted origin.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, before starting the solution we first to understand that the physical significance of \[\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}\] is,

Now, we can see from the graph that \[\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f\left( x \right)dx}\] is nothing but the area bounded by the line $y=f\left( x \right),x=a,x=b\ and\ x-axis$.
Now, we know that the graph of $y=1+\left| x+1 \right|$ is shifted 1 units upward and 1 units leftwards from the origin of the graph of $y=\left( x \right)$. So, we have the graph by using the concept of shifted origin as,

Now, we will first find the area of region ADEO. So, we have the equation of line AO as,
$\begin{align}
& y=1-x-1 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-x \\
\end{align}$
So, we have the area of region,
$ADEO=\int\limits_{-2}^{-1}{\left( -x \right)dx}$
We have put the limits as x = -1 to x = -2 from the graph. Also, we know that $\int{{{x}^{n}}dx}=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}$. So, we have,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left. \dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{2} \right|_{-2}^{-1} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow -\left( \dfrac{1}{2}-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow -\left( -\dfrac{3}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}sq\ units \\
\end{align}$
Now, similarly we will find the area of region OECB as,
$\int\limits_{-1}^{3}{\left( x+2 \right)dx}$
We have put the limits as x = -1 to x = 3 by referring the graph and again using the fact that $\int{{{x}^{n}}dx}=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}$. We have,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}+2x \right)_{-1}^{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{2}-\dfrac{{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}}{2}+2\left( 3-\left( -1 \right) \right) \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{9}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}+2\left( 3+1 \right) \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{9-1}{2}+2\times 4 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{8}{2}+2\times 4 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 4+8 \\
& \Rightarrow 12sq\ units \\
\end{align}$
So, the total area bounded by the region is,
ar of region ADEO + ar of region OECD
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}+12 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3+24}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{27}{2}sq\ units \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the total area bounded by the given curves is $\dfrac{27}{2}sq\ units$.
Note: While solving the question it is important to note how we have drawn the graph of $\left( y-1 \right)=\left| x-\left( -1 \right) \right|$ from the graph of $y=\left| x \right|$ by using the concept of shifted origin.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




