
How do you use the rational root theorem to find the roots of $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 $ ?
Answer
531k+ views
Hint: In this problem we need to find the roots of the equation by using the rational root theorem. We know that the rational root theorem says that ‘if $ {{a}_{n}}{{x}^{n}}~+~{{a}_{n-\text{ }1}}{{x}^{n~-\text{ }1}}~+\text{ }\ldots \text{ }+~{{a}_{1}}{{x}^{1}}~+~{{a}_{0}}~=\text{ }0 $ is a polynomial in the variable $ x $ thus for a polynomial equation to have a rational solution $ \dfrac{p}{q} $ , $ q $ must be divide $ {{a}_{n}} $ and $ p $ must be divide $ {{a}_{0}} $ ’. So, we will first equate the given equation with the canonical form of a polynomial. Now we will write the factors for the constant and coefficient of $ {{x}^{4}} $ . Now we will write all the possible roots for the given equation from the factors written above. Now we will substitute those values and check for the rational roots of the equation.
Complete step by step answer:
Given equation, $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 $ .
In the above equation
Coefficient of $ {{x}^{4}} $ is $ 1 $ .
Coefficient of $ {{x}^{3}} $ is $ 1 $ .
Coefficient of $ {{x}^{2}} $ is $ -2 $ .
Coefficient of $ x $ is $ 0 $ .
Constant is $ -290 $ .
Now the factors of $ 290 $ are $ 1 $ , $ 2 $ , $ 5 $ , $ 10 $ , $ 29 $ , $ 58 $ , $ 145 $ , $ 290 $ .
So the possible roots of the given equation are $ \pm 1 $ , $ \pm 2 $ , $ \pm 5 $ , $ \pm 10 $ , $ \pm 29 $ , $ \pm 58 $ , $ \pm 145 $ , $ \pm 290 $ .
To find the exact roots of the given equation we need to substitute each value in the given equation and calculate the result.
Substituting $ x=1 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 1 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( 1 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -290\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=1 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Substituting $ x=-1 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( -1 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( -1 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 1-1-2-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -292\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=-1 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Substituting $ x=2 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 2 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( 2 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 16+8-8-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -274\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=2 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Substituting $ x=-2 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( -2 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( -2 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 16-8-8-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -290\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=-2 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Substituting $ x=5 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 5 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( 5 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 625+125-50-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 410\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=5 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Substituting $ x=-5 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( -5 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( -5 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( -5 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 625-125-50-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 160\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=-5 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Hence there are no zeros with $ \left| x \right|\le 2 $ and $ \left| x \right|\ge 5 $ .
So, given equations don’t have any rational roots. It has one negative irrational root in $ \left( -5,-2 \right) $ and one positive irrational root in $ \left( 5,2 \right) $ along with two complex numbers.
Note:
We can also plot a graph for the given equation to find the solutions of the given equation. When we plot a graph of the given equation it looks like given below
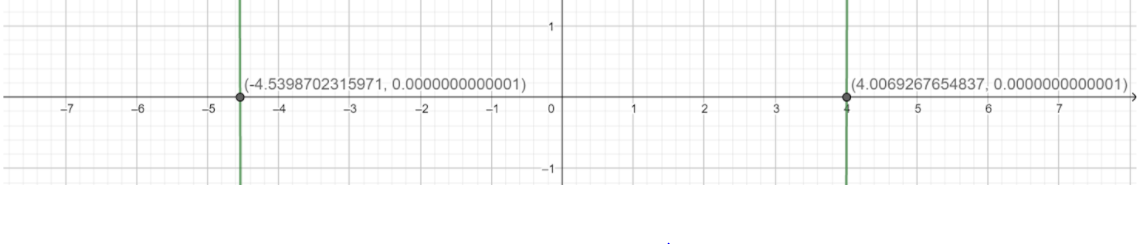
In the graph also we can observe that the given equation has no rational roots.
Complete step by step answer:
Given equation, $ {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 $ .
In the above equation
Coefficient of $ {{x}^{4}} $ is $ 1 $ .
Coefficient of $ {{x}^{3}} $ is $ 1 $ .
Coefficient of $ {{x}^{2}} $ is $ -2 $ .
Coefficient of $ x $ is $ 0 $ .
Constant is $ -290 $ .
Now the factors of $ 290 $ are $ 1 $ , $ 2 $ , $ 5 $ , $ 10 $ , $ 29 $ , $ 58 $ , $ 145 $ , $ 290 $ .
So the possible roots of the given equation are $ \pm 1 $ , $ \pm 2 $ , $ \pm 5 $ , $ \pm 10 $ , $ \pm 29 $ , $ \pm 58 $ , $ \pm 145 $ , $ \pm 290 $ .
To find the exact roots of the given equation we need to substitute each value in the given equation and calculate the result.
Substituting $ x=1 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 1 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( 1 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -290\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=1 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Substituting $ x=-1 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( -1 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( -1 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 1-1-2-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -292\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=-1 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Substituting $ x=2 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 2 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( 2 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 16+8-8-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -274\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=2 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Substituting $ x=-2 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( -2 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( -2 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 16-8-8-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -290\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=-2 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Substituting $ x=5 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 5 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( 5 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 625+125-50-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 410\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=5 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Substituting $ x=-5 $ in the given equation, then we will get
$ \begin{align}
& {{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}-2{{x}^{2}}+0x-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( -5 \right)}^{4}}+{{\left( -5 \right)}^{3}}-2{{\left( -5 \right)}^{2}}-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 625-125-50-290=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 160\ne 0 \\
\end{align} $
Hence, $ x=-5 $ is not the perfect root of the given equation.
Hence there are no zeros with $ \left| x \right|\le 2 $ and $ \left| x \right|\ge 5 $ .
So, given equations don’t have any rational roots. It has one negative irrational root in $ \left( -5,-2 \right) $ and one positive irrational root in $ \left( 5,2 \right) $ along with two complex numbers.
Note:
We can also plot a graph for the given equation to find the solutions of the given equation. When we plot a graph of the given equation it looks like given below

In the graph also we can observe that the given equation has no rational roots.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




