
What is the use of tissues in multicellular organisms?
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: A unicellular organism has only one cell to perform all sets of functions such as digestion, excretion, reproduction etc. which is in contrast to multicellular organisms. The complexity of an organism is synonymous with the type and range of tissues present in it.
Complete answer:
In a multicellular organism, the division of labour can be observed wherein different sets of function are performed by separate cells. The cells which have a similar origin, appearance, dimension and perform identical functions together form tissues. Combination of tissues working as a unit to perform a specific function or a series of related functions form an organ. Further, several organs constitute an organ-system.
As we proceed from lower phylum to higher phylum, we can witness a gradual development in the function of tissues and their specificities. In higher organisms, the following sets of tissues are observed:
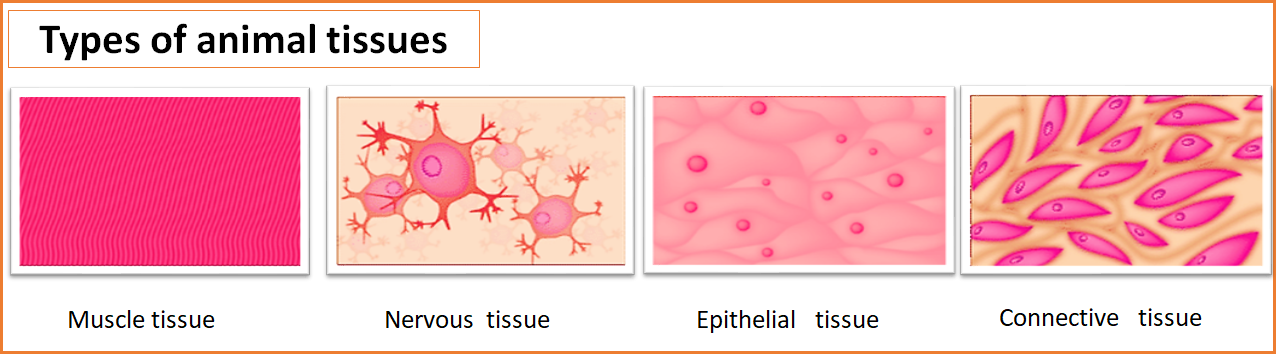
Epithelial tissue lines body cavities and forms glands. They occur on external and internal exposed surfaces of the body parts where they form a protective covering.
Connective tissue is the most abundant and distributed widely in the body. Its function is to bind together different tissues or organs and support various structures of the animal body.
Muscular tissue brings about movements of the body parts and locomotion of an organism through their special property of contractility.
Nervous tissue helps in the control and coordination of various body parts through their unique property of excitability and conductivity.
Note: -The word ‘tissue’ was coined by Xavier Bichat, a French anatomist and physiologist. It is derived from the French word ‘tisser’ which means ‘to weave’.
-Histology is the study of tissues. The term ‘histology’ is coined by Mayer. It is derived from the term ‘histos’ and ‘logos’ which means ‘tissues’ and ‘study’ respectively.
-Marcello Malpighi is regarded as ‘the founder of histology’.
Complete answer:
In a multicellular organism, the division of labour can be observed wherein different sets of function are performed by separate cells. The cells which have a similar origin, appearance, dimension and perform identical functions together form tissues. Combination of tissues working as a unit to perform a specific function or a series of related functions form an organ. Further, several organs constitute an organ-system.
As we proceed from lower phylum to higher phylum, we can witness a gradual development in the function of tissues and their specificities. In higher organisms, the following sets of tissues are observed:
Epithelial tissue lines body cavities and forms glands. They occur on external and internal exposed surfaces of the body parts where they form a protective covering.
Connective tissue is the most abundant and distributed widely in the body. Its function is to bind together different tissues or organs and support various structures of the animal body.
Muscular tissue brings about movements of the body parts and locomotion of an organism through their special property of contractility.
Nervous tissue helps in the control and coordination of various body parts through their unique property of excitability and conductivity.

Note: -The word ‘tissue’ was coined by Xavier Bichat, a French anatomist and physiologist. It is derived from the French word ‘tisser’ which means ‘to weave’.
-Histology is the study of tissues. The term ‘histology’ is coined by Mayer. It is derived from the term ‘histos’ and ‘logos’ which means ‘tissues’ and ‘study’ respectively.
-Marcello Malpighi is regarded as ‘the founder of histology’.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




