
Use Mendeleev’s periodic Table to predict the formulas for the oxides of the following elements: $ K,C,Al,Si,Ba $ .
Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint :In Mendeleev's periodic Table, the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their relative atomic masses. Oxides of an element (metal/metalloid/non-metal) describes the chemical formula of that element with oxygen. Valency describes the combining capacity of the element to form compounds.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Valency describes the combining capacity of the element to form compounds. Oxides of an element (metal/metalloid/non-metal) describes the chemical formula of that element with oxygen. According to Mendeleev’s periodic Table, $ K $ belongs to group $ I $ , $ C $ and $ Si $ belong to group $ IV $ , $ Al $ belongs to group $ III $ , $ Ba $ belongs to $ II $ and $ O $ belongs to $ VI $ . In order to predict the formulas for the oxides of the above elements, we use the criss cross method. For this purpose, we need the valency of these elements. The valency of $ K,C,Al,Si,Ba,O $ elements are $ 1,4,3,4,2,2 $ . The crisscross method for the oxides of the $ K,C,Al,Si,Ba $ is illustrated in the following diagram:
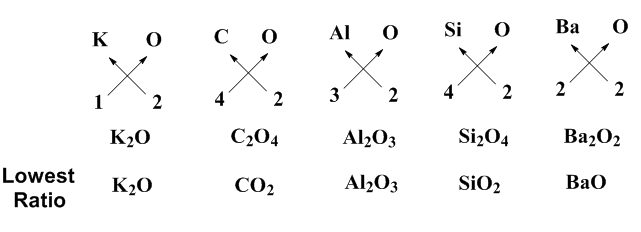
According to the criss cross method, first transpose the valency of cation as subscript of anion and valency of anion as subscript of cation. After that, reduce the formula to the lowest ratio which will give you the required chemical formula for the oxides. On the above basis, the oxides of the elements $ K,C,Al,Si,Ba $ are $ {{K}_{2}}O,C{{O}_{2}},A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}},Si{{O}_{2}},BaO $ .
Note :
It is important to note that the oxides of the elements $ K,C,Al,Si,Ba $ are $ {{K}_{2}}O,C{{O}_{2}},A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}},Si{{O}_{2}},BaO $ . These above formulas are calculated by crisscross method. For this purpose, we should have the knowledge of valency i.e. combining capacity of an element.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Valency describes the combining capacity of the element to form compounds. Oxides of an element (metal/metalloid/non-metal) describes the chemical formula of that element with oxygen. According to Mendeleev’s periodic Table, $ K $ belongs to group $ I $ , $ C $ and $ Si $ belong to group $ IV $ , $ Al $ belongs to group $ III $ , $ Ba $ belongs to $ II $ and $ O $ belongs to $ VI $ . In order to predict the formulas for the oxides of the above elements, we use the criss cross method. For this purpose, we need the valency of these elements. The valency of $ K,C,Al,Si,Ba,O $ elements are $ 1,4,3,4,2,2 $ . The crisscross method for the oxides of the $ K,C,Al,Si,Ba $ is illustrated in the following diagram:

According to the criss cross method, first transpose the valency of cation as subscript of anion and valency of anion as subscript of cation. After that, reduce the formula to the lowest ratio which will give you the required chemical formula for the oxides. On the above basis, the oxides of the elements $ K,C,Al,Si,Ba $ are $ {{K}_{2}}O,C{{O}_{2}},A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}},Si{{O}_{2}},BaO $ .
Note :
It is important to note that the oxides of the elements $ K,C,Al,Si,Ba $ are $ {{K}_{2}}O,C{{O}_{2}},A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}},Si{{O}_{2}},BaO $ . These above formulas are calculated by crisscross method. For this purpose, we should have the knowledge of valency i.e. combining capacity of an element.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




