
Use Huygens’s principle to show how a plane wavelength propagates from a denser to rarer medium. Hence verify Snell’s law of refraction.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: The law of Snell is a formula that describes the correlation between angles of incidence, refraction, when relating to light or other waves that cross the frontier among two different isotropic media, including water, glass or air. The law of Snell is a formula that describes the relationship between angles of incidence and refraction.
Complete step by step solution:
The Huygens Theory notes that each wave front point is a source of wavelets that propagate at the same speed forward. The current direction of the wave front at every moment is the envelope of the secondary wavelets at that moment. If light emits from a source, the particles surrounding it tend to vibrate and all such vibrating particles are called a wave front. If the disruption on the wave front of point $P$ at the refracted wave front approaches point $P$ , the disruption from point $Q$ at the refractive surface approaches point $Q$ . It should still be the same time taken by light to pass from an occurrence front to the corresponding point on the broken front. The refractive index is the vacuum rate ratio, $c$ to the light velocity of a given medium $v$ .
$n = \dfrac{c}{v}$
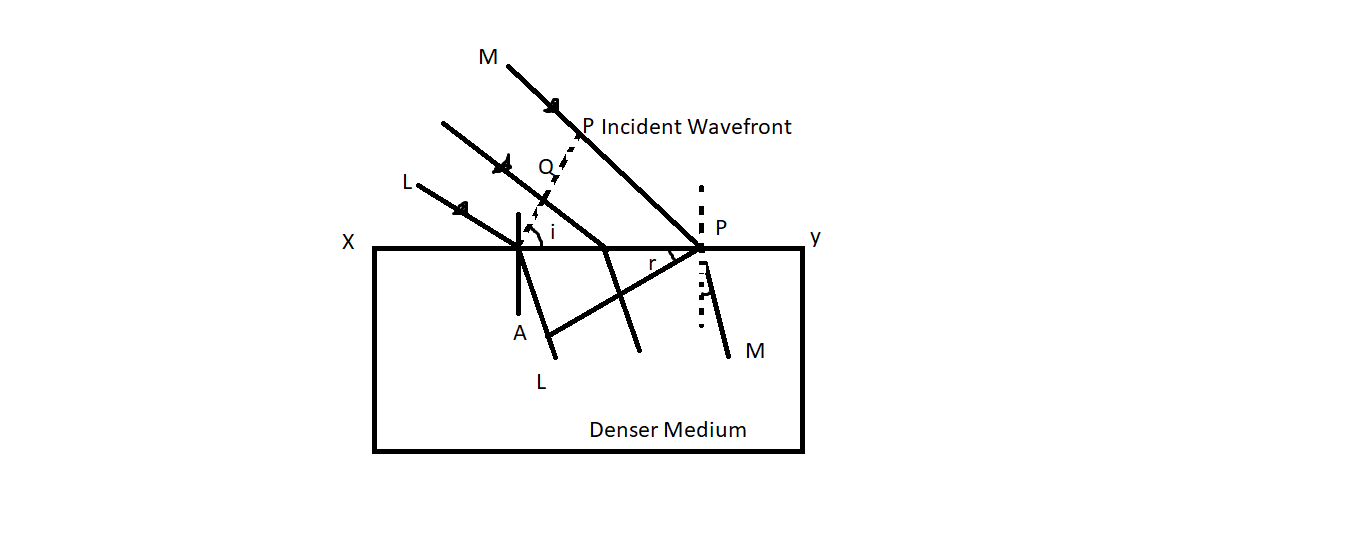
In the triangles, we can see that
$\sin i = \dfrac{{{v_1}t}}{x}$ and $\sin r = \dfrac{{{v_2}t}}{x}$
Where $i$ and $r$ are incident and refracted angles respectively.
$\dfrac {{\sin i}} {{\sin r}} = \dfrac{{{v_1}}}{{{v_2}}}$
Where ${v_1} $ and ${v_2} $ are velocities in first and second medium respectively.
If $c$ is the speed of light in vacuum then,
${v_1} = \dfrac{c}{{{n_1}}}$ and ${v_2} = \dfrac{c}{{{n_2}}}$
Therefore, we get
$\dfrac {{\sin i}} {{\sin r}} = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}$
This is Snell's law of refraction.
Note: Optical law is used for tracing rays to measure the incidence or refraction angles and the refractive index of a substance is found in experimental optics. The law also applies to Metamaterials which permit "backwards" to bend light with a negative refractive index at the negative angle of refraction.
Complete step by step solution:
The Huygens Theory notes that each wave front point is a source of wavelets that propagate at the same speed forward. The current direction of the wave front at every moment is the envelope of the secondary wavelets at that moment. If light emits from a source, the particles surrounding it tend to vibrate and all such vibrating particles are called a wave front. If the disruption on the wave front of point $P$ at the refracted wave front approaches point $P$ , the disruption from point $Q$ at the refractive surface approaches point $Q$ . It should still be the same time taken by light to pass from an occurrence front to the corresponding point on the broken front. The refractive index is the vacuum rate ratio, $c$ to the light velocity of a given medium $v$ .
$n = \dfrac{c}{v}$

In the triangles, we can see that
$\sin i = \dfrac{{{v_1}t}}{x}$ and $\sin r = \dfrac{{{v_2}t}}{x}$
Where $i$ and $r$ are incident and refracted angles respectively.
$\dfrac {{\sin i}} {{\sin r}} = \dfrac{{{v_1}}}{{{v_2}}}$
Where ${v_1} $ and ${v_2} $ are velocities in first and second medium respectively.
If $c$ is the speed of light in vacuum then,
${v_1} = \dfrac{c}{{{n_1}}}$ and ${v_2} = \dfrac{c}{{{n_2}}}$
Therefore, we get
$\dfrac {{\sin i}} {{\sin r}} = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}$
This is Snell's law of refraction.
Note: Optical law is used for tracing rays to measure the incidence or refraction angles and the refractive index of a substance is found in experimental optics. The law also applies to Metamaterials which permit "backwards" to bend light with a negative refractive index at the negative angle of refraction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




