
Unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells
a) Lack of a plasma membrane
b) Do not have a nucleus
c) Have RNA, not DNA
d) All of the above
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: The prokaryotes are the organism that lacks the cell nucleus and the eukaryotes are the organism that have cell nucleus present. Prokaryotes are either unicellular or multicellular. Eukaryotes are the organisms having complex body structures.
Complete answer:
Prokaryotic organisms usually lack a plasma membrane. They have cell walls composed of the peptidoglycan. The DNA present in the prokaryotes is called the plasmid. It has the same function as that of the DNA. It is double-stranded and circular in shape. The replication in plasmid occurs through the theta model of replication. They usually lack the non-coding regions in their genome and have a very condensed genome.
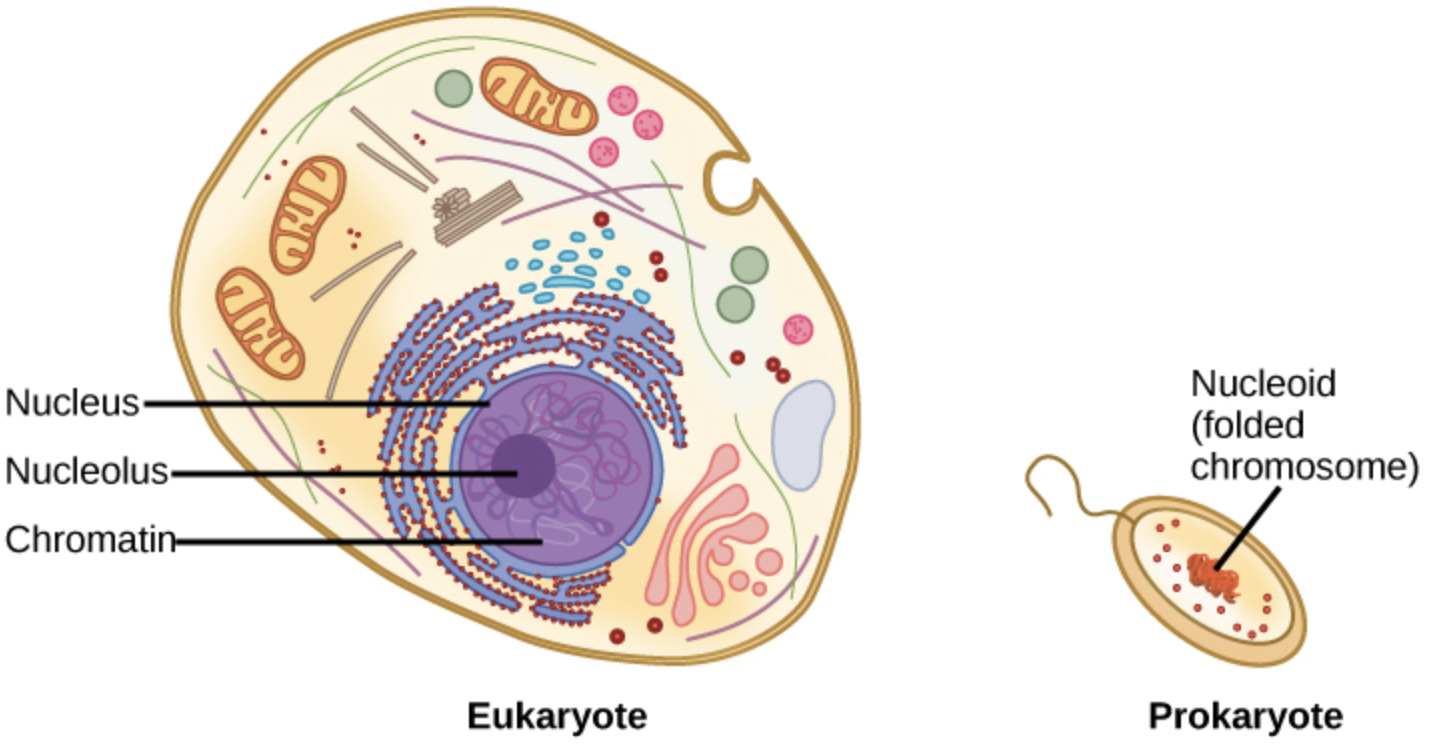
In prokaryotes a well-defined nucleus is absent whereas there is the presence of the nucleoid which is similar to the nuclear membrane. In the eukaryotic organism, the cell wall is absent, and if present it is then made up of the polysaccharide. In them, a well-defined nucleus is present which has a well-defined nuclear membrane present. The DNA present in the eukaryotes is double-stranded linear DNA. There are other membrane-bound organelles present in it.
So, the answer is ‘d) All of the above’.
Note: In prokaryotes membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum are absent. The ribosome present in it is of the 70S whereas, in the eukaryotes, it is 80S. The cell division in the prokaryotes occurs through binary fission whereas, in eukaryotes, it occurs through the mitosis. The prokaryotic cells are present in the archaea and bacteria. The eukaryotic cells are present in the higher levels of animals. There is a presence of chloroplast in the eukaryotic plant cells and in prokaryotes, the chlorophyll is scattered in the cytoplasm.
Complete answer:
Prokaryotic organisms usually lack a plasma membrane. They have cell walls composed of the peptidoglycan. The DNA present in the prokaryotes is called the plasmid. It has the same function as that of the DNA. It is double-stranded and circular in shape. The replication in plasmid occurs through the theta model of replication. They usually lack the non-coding regions in their genome and have a very condensed genome.

In prokaryotes a well-defined nucleus is absent whereas there is the presence of the nucleoid which is similar to the nuclear membrane. In the eukaryotic organism, the cell wall is absent, and if present it is then made up of the polysaccharide. In them, a well-defined nucleus is present which has a well-defined nuclear membrane present. The DNA present in the eukaryotes is double-stranded linear DNA. There are other membrane-bound organelles present in it.
So, the answer is ‘d) All of the above’.
Note: In prokaryotes membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum are absent. The ribosome present in it is of the 70S whereas, in the eukaryotes, it is 80S. The cell division in the prokaryotes occurs through binary fission whereas, in eukaryotes, it occurs through the mitosis. The prokaryotic cells are present in the archaea and bacteria. The eukaryotic cells are present in the higher levels of animals. There is a presence of chloroplast in the eukaryotic plant cells and in prokaryotes, the chlorophyll is scattered in the cytoplasm.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




