
Under what conditions of T and P, most gases deviate from ideal gas behaviour?
Answer
512.1k+ views
Hint :In thermodynamics, the ratio of the molar volume of a gas to the molar volume of an ideal gas at the same pressure and temperature is known as the compressibility factor. It is represented by Z and is also known as the gas deviation factor.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Compressibility factor describes the deviation of a real gas from ideal gas behaviour and is a useful thermodynamic property for modifying the ideal gas law to account for the real gas behaviour. An ideal gas is a hypothetical gas in which there are no intermolecular attractive forces between the gas particles. However, under certain conditions, the gases deviate from their ideal behaviour which are as follows:
At low temperatures, gas particles consist of less kinetic energy and thus, move at slower speed and due to this the interaction between the particles is much more likely to happen upon collision. At high pressures, the gas particles are forced into close proximity with each other which causes significant intermolecular interactions.
Now, the interactions can either be attractive or repulsive and the behaviour of the ideal gas deviates accordingly. If the attractive forces dominate then the compressibility factor will be less than one i.e., $ Z < 1 $ whereas if the repulsive forces dominate then the compressibility factor will be greater than one i.e., $ Z > 1 $ .
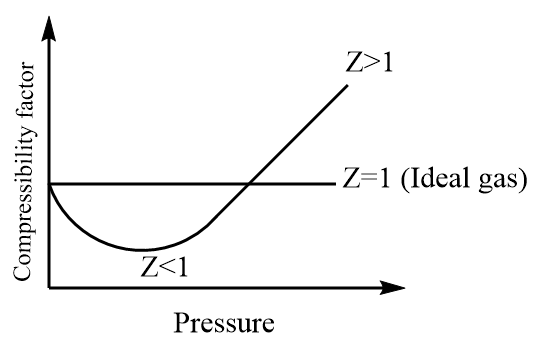
Thus, we can conclude that at low temperature and high pressure, most of the gases deviate from their ideal behaviour.
Note :
It is important to note that the value of compressibility factor for the ideal gas is one and the real gas tends to show the ideal behaviour at high temperature and low pressure conditions because the potential energy due to intermolecular forces become less significant as compared to the kinetic energy of the particles.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Compressibility factor describes the deviation of a real gas from ideal gas behaviour and is a useful thermodynamic property for modifying the ideal gas law to account for the real gas behaviour. An ideal gas is a hypothetical gas in which there are no intermolecular attractive forces between the gas particles. However, under certain conditions, the gases deviate from their ideal behaviour which are as follows:
At low temperatures, gas particles consist of less kinetic energy and thus, move at slower speed and due to this the interaction between the particles is much more likely to happen upon collision. At high pressures, the gas particles are forced into close proximity with each other which causes significant intermolecular interactions.
Now, the interactions can either be attractive or repulsive and the behaviour of the ideal gas deviates accordingly. If the attractive forces dominate then the compressibility factor will be less than one i.e., $ Z < 1 $ whereas if the repulsive forces dominate then the compressibility factor will be greater than one i.e., $ Z > 1 $ .

Thus, we can conclude that at low temperature and high pressure, most of the gases deviate from their ideal behaviour.
Note :
It is important to note that the value of compressibility factor for the ideal gas is one and the real gas tends to show the ideal behaviour at high temperature and low pressure conditions because the potential energy due to intermolecular forces become less significant as compared to the kinetic energy of the particles.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




