
What type of isomerism exists between the following pair of compounds?
${{1}}{{.}}$ ${{Pentan - 1 - ol \;and \; 3 - methylbutane - 1 - ol}}$
${{2}}{{.}}$ Ethanol and Dimethyl ether.
${{3}}{{.}}$ ${{Butan - 1 - ol \; and \;butan - 2 - ol}}$
(A) Chain isomerism, Functional isomerism, Position isomerism.
(B) Function isomerism, Chain isomerism, Position isomerism.
(C) Position isomerism, Chain isomerism, Functional isomerism.
(D) Chain isomerism, Position isomerism, Functional isomerism.
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Isomers are the structures having same molecular formula just the arrangement of the atoms are different which makes difference in length of parent carbon chain , position of groups , branching of chains, different functional group with same elements and this phenomena is called isomerism .
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will know about the types of isomerism
Chain isomerism: It is a type of structural isomerism that occurs in organic compounds. In this type of isomerism the number of carbon remains the same only the branching of carbon is different and the parent chain is also reduced due to more branching.
Functional group isomerism: In this type of isomerism the functional group changes into another functional group which has the same elements means it has the same molecular formula but the functional groups attached are different. Example: aldehyde changes to ketone, alcohol changes to ether etc
Position isomerism: It is an isomerism in which the molecular formula of the compound remains same as well as the functional group remains same only the position of the functional group is changed.
Now we will see the isomerism by drawing structures:
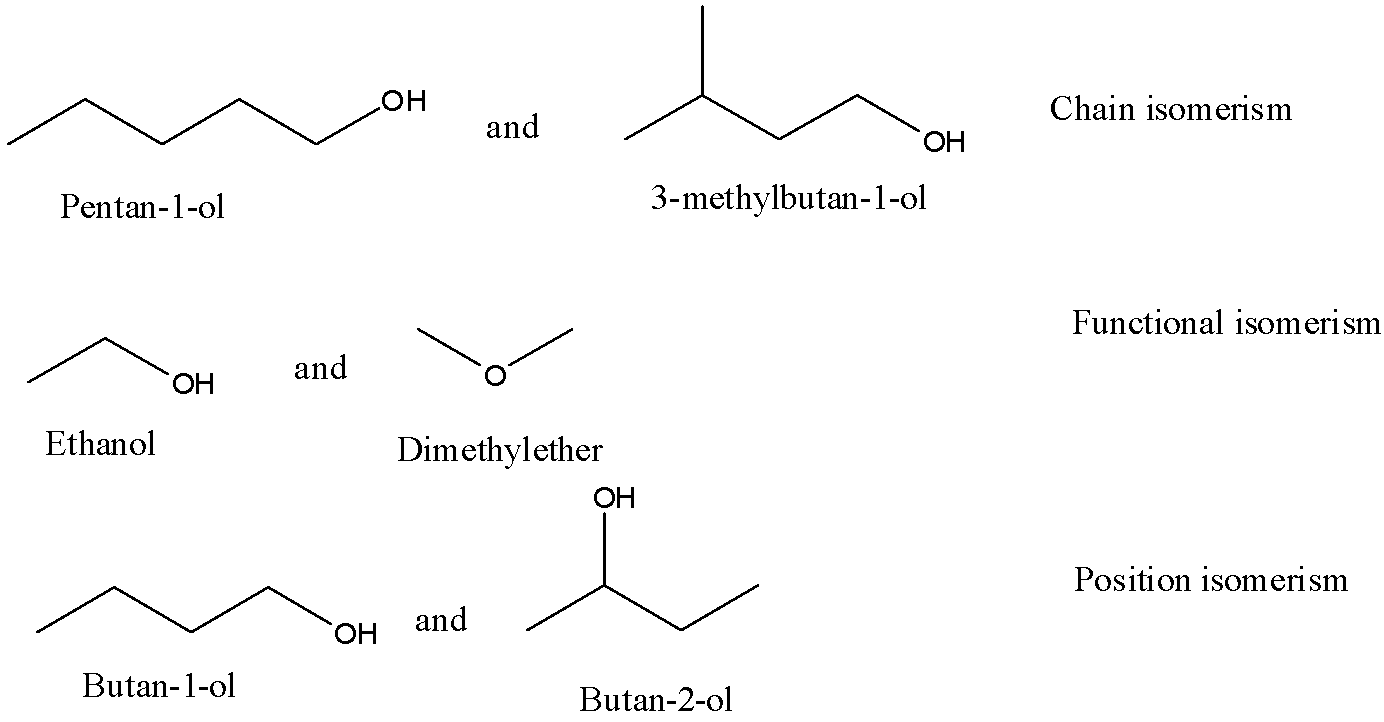
So, the correct answer is A.
Additional information:
These types of isomerism were the structural isomerism in which there is change in the structure of the compound. Some isomerism is optical isomerism in which stereochemistry is also involved.
Note: In structural isomerism the most important characteristic is that the molecular formula does not change only the positions chain size and branching are decreased and branches are increased. The functional groups are completely changed which have totally different properties.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will know about the types of isomerism
Chain isomerism: It is a type of structural isomerism that occurs in organic compounds. In this type of isomerism the number of carbon remains the same only the branching of carbon is different and the parent chain is also reduced due to more branching.
Functional group isomerism: In this type of isomerism the functional group changes into another functional group which has the same elements means it has the same molecular formula but the functional groups attached are different. Example: aldehyde changes to ketone, alcohol changes to ether etc
Position isomerism: It is an isomerism in which the molecular formula of the compound remains same as well as the functional group remains same only the position of the functional group is changed.
Now we will see the isomerism by drawing structures:

So, the correct answer is A.
Additional information:
These types of isomerism were the structural isomerism in which there is change in the structure of the compound. Some isomerism is optical isomerism in which stereochemistry is also involved.
Note: In structural isomerism the most important characteristic is that the molecular formula does not change only the positions chain size and branching are decreased and branches are increased. The functional groups are completely changed which have totally different properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




