
What is the type of hybridisation of each carbon in the following compounds?
$(a)C{H_3}Cl$
$(b){(C{H_3})_2}CO$
$(c)C{H_3}CN$
$(d)HCON{H_2}$
$(e)C{H_3}CH = CHCN$
Answer
495.3k+ views
Hint: Hybridisation can be defined as the mixing of valence orbitals which lead to the formation of sigma bonds. The types of orbitals that are included in mixing and the number of sigma bonds formed helps to determine the hybridisation state of carbon in an organic compound. In the solution we will see how the number of sigma bonds formed by the carbon atom determines its hybridisation state.
Complete answer:
We know that hybridisation state can be defined as the mixing of valence orbitals which lead to the formation of sigma bonds. The types of orbitals that are included in mixing and the number of sigma bonds formed helps to determine the hybridisation state of carbon (central atom) in any given organic compound.
Now, we will see how sigma bonds relate to the hybridisation of carbon atoms.
Therefore, on the basis of above table we will determine the hybridisation state of carbon atom in each of the given compounds:
$(a)C{H_3}Cl$
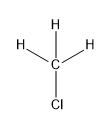
In this compound, carbon forms four sigma bonds. Hence, the hybridisation state of carbon is $s{p^3}$ .
$(b){(C{H_3})_2}CO$
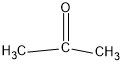
In this compound, carbon forms three sigma bonds. Hence, the hybridisation state of carbon is $s{p^2}$ .
$(c)C{H_3}CN$
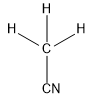
In this compound, carbon forms four sigma bonds. Hence, the hybridisation state of carbon is $s{p^3}$ .
$(d)HCON{H_2}$
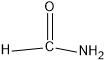
In this compound, carbon forms three sigma bonds. Hence, the hybridisation state of carbon is $s{p^2}$ .
$(e)C{H_3}CH = CHCN$
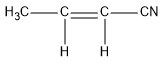
In this compound, carbon at the end forms four sigma bonds. Hence, the hybridisation state of that carbon is $s{p^3}$ . The two middle carbon atoms have three sigma bonds and the hybridisation state is $s{p^2}$ . The carbon attached to nitrogen atom forms two sigma bonds and hybridisation state of this carbon is $sp.$
Note:
This is how we find the hybridisation state of carbon in organic compounds. For inorganic compounds, to find the hybridisation state of the central atom, we need to know the valence shell configuration of the central atom, the monovalent ions present in the compound and the cationic or ionic charge present on the compound.
Complete answer:
We know that hybridisation state can be defined as the mixing of valence orbitals which lead to the formation of sigma bonds. The types of orbitals that are included in mixing and the number of sigma bonds formed helps to determine the hybridisation state of carbon (central atom) in any given organic compound.
Now, we will see how sigma bonds relate to the hybridisation of carbon atoms.
| No. of sigma bonds that carbon forms | Hybridisation state |
| $4$ | $s{p^3}$ |
| $3$ | $s{p^2}$ |
| $2$ | $sp$ |
Therefore, on the basis of above table we will determine the hybridisation state of carbon atom in each of the given compounds:
$(a)C{H_3}Cl$

In this compound, carbon forms four sigma bonds. Hence, the hybridisation state of carbon is $s{p^3}$ .
$(b){(C{H_3})_2}CO$

In this compound, carbon forms three sigma bonds. Hence, the hybridisation state of carbon is $s{p^2}$ .
$(c)C{H_3}CN$

In this compound, carbon forms four sigma bonds. Hence, the hybridisation state of carbon is $s{p^3}$ .
$(d)HCON{H_2}$

In this compound, carbon forms three sigma bonds. Hence, the hybridisation state of carbon is $s{p^2}$ .
$(e)C{H_3}CH = CHCN$

In this compound, carbon at the end forms four sigma bonds. Hence, the hybridisation state of that carbon is $s{p^3}$ . The two middle carbon atoms have three sigma bonds and the hybridisation state is $s{p^2}$ . The carbon attached to nitrogen atom forms two sigma bonds and hybridisation state of this carbon is $sp.$
Note:
This is how we find the hybridisation state of carbon in organic compounds. For inorganic compounds, to find the hybridisation state of the central atom, we need to know the valence shell configuration of the central atom, the monovalent ions present in the compound and the cationic or ionic charge present on the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




