
What type of compound is sulfur hexafluoride is an example of?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: A chemical compound consisting of more than two atoms held together by chemical bonds. The bonds are either formed by sharing of electrons, or by transfer of electrons. Sulfur hexafluoride consists of sharing of electrons to complete each other’s octet. It has a chemical formula of $S{{F}_{6}}$.
Complete answer:
Chemical compounds consist of atoms that are held by chemical bonds between them. When two atoms of relatively less difference in their electronegativity are held together in a molecule, then they give rise to covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are formed by sharing of the valence electrons of the atoms in the molecule to complete their octet and become stable.
We have been given sulfur hexafluoride, which has sulfur and fluorine. Both these compounds are electronegative. So, they form a covalent compound. The covalent nature of an atom and the distribution of the valence electrons as bond pairs and lone pairs define the shape and geometry of that molecule.
In sulfur hexafluoride, $S{{F}_{6}}$all the valence electrons from sulfur (that is 6) and from 6 fluorine atoms (6$\times $7) are distributed as bond pairs. The 6 fluorine atoms form 6 bonds with sulfur that completes the octet, as the 6 valence electrons of sulfur contribute to complete the octet of fluorine that needs only 1 electron to fulfill its shell. So, the structure of$S{{F}_{6}}$is,
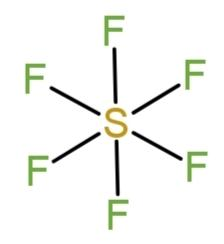
As all are bond pairs they acquire stable positions that make the compound’s shape square bi pyramidal with the octahedral geometry.
Hence, sulfur hexafluoride is an example of octahedral covalent compound.
Note:
The shapes according to the distribution of electrons as bond and lone pairs is determined through VSEPR theory that states that the shape of electron depends on the bond and lone pair of electrons due to their repulsions as, lone pair – lone pair repulsion > bond pair – lone pair repulsion > bond pair – bond pair repulsion.
Complete answer:
Chemical compounds consist of atoms that are held by chemical bonds between them. When two atoms of relatively less difference in their electronegativity are held together in a molecule, then they give rise to covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are formed by sharing of the valence electrons of the atoms in the molecule to complete their octet and become stable.
We have been given sulfur hexafluoride, which has sulfur and fluorine. Both these compounds are electronegative. So, they form a covalent compound. The covalent nature of an atom and the distribution of the valence electrons as bond pairs and lone pairs define the shape and geometry of that molecule.
In sulfur hexafluoride, $S{{F}_{6}}$all the valence electrons from sulfur (that is 6) and from 6 fluorine atoms (6$\times $7) are distributed as bond pairs. The 6 fluorine atoms form 6 bonds with sulfur that completes the octet, as the 6 valence electrons of sulfur contribute to complete the octet of fluorine that needs only 1 electron to fulfill its shell. So, the structure of$S{{F}_{6}}$is,

As all are bond pairs they acquire stable positions that make the compound’s shape square bi pyramidal with the octahedral geometry.
Hence, sulfur hexafluoride is an example of octahedral covalent compound.
Note:
The shapes according to the distribution of electrons as bond and lone pairs is determined through VSEPR theory that states that the shape of electron depends on the bond and lone pair of electrons due to their repulsions as, lone pair – lone pair repulsion > bond pair – lone pair repulsion > bond pair – bond pair repulsion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




