
What type of cell division occurs when our wounds are healed?
Answer
528.6k+ views
Hint: Mitosis is the process which divides the nucleus, replicates the genome and leads to the production of two new cells with identical genomes from one parent cell. When we suffer any kind of wound, the epidermis layer of the skin carries out the mitosis cell division in the affected area. The process increases the number of cells which fills up the places of the destroyed cells.
Complete answer:
Mitosis is a cell division process in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. The process has different stages, namely, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes which have been already duplicated, condense and attach to spindle fibers. These fibres pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell which results in two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The rest of the cell then continues to divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of the normal two is a mitotic error which is termed as tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). The mitotic cell division occurs only in eukaryotic cells. Each resultant daughter cell should be genetically identical to the parent cell. Therefore, the parent cell makes a copy of each chromosome before its mitosis. This occurs during the S phase of interphase.
At the beginning of mitosis, the chromosomes condense and become visible. The nucleolus in the cell disappears. Microtubules projecting from the opposite ends of the cell, attach themselves to the centromeres, and align the chromosomes centrally inside the cell. The microtubules then contract to pull the sister chromatids apart. Sister chromatids at this point are called daughter chromosomes and were initially bound together by cohesin proteins at the centromere. The daughter chromosomes are pulled towards the opposite ends of the cell and they condense maximally in late anaphase. A new nuclear envelope will form around the separated daughter chromosomes, which will later decondense to form interphase nuclei. Next the cell undergoes cytokinesis. In animal cells, during cytokinesis, a cell membrane pinches inward between the two developing nuclei and severs to produce two new cells. In plant cells, however, a cell plate is formed between the two nuclei. Mitosis plays an important role in the production of RBC which assists in wound healing and cell regeneration.
Note:
Red blood cells in our body help to create collagen. They are tough, white fibers that form the foundation for new tissue. The wound is filled in with new tissue, called granulation tissue over which the new skin behind to form.
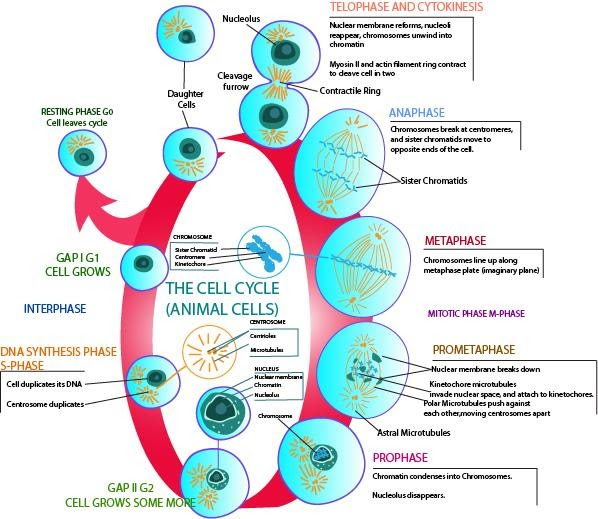
Figure 1: Mitosis
Complete answer:
Mitosis is a cell division process in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. The process has different stages, namely, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes which have been already duplicated, condense and attach to spindle fibers. These fibres pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell which results in two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The rest of the cell then continues to divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of the normal two is a mitotic error which is termed as tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). The mitotic cell division occurs only in eukaryotic cells. Each resultant daughter cell should be genetically identical to the parent cell. Therefore, the parent cell makes a copy of each chromosome before its mitosis. This occurs during the S phase of interphase.
At the beginning of mitosis, the chromosomes condense and become visible. The nucleolus in the cell disappears. Microtubules projecting from the opposite ends of the cell, attach themselves to the centromeres, and align the chromosomes centrally inside the cell. The microtubules then contract to pull the sister chromatids apart. Sister chromatids at this point are called daughter chromosomes and were initially bound together by cohesin proteins at the centromere. The daughter chromosomes are pulled towards the opposite ends of the cell and they condense maximally in late anaphase. A new nuclear envelope will form around the separated daughter chromosomes, which will later decondense to form interphase nuclei. Next the cell undergoes cytokinesis. In animal cells, during cytokinesis, a cell membrane pinches inward between the two developing nuclei and severs to produce two new cells. In plant cells, however, a cell plate is formed between the two nuclei. Mitosis plays an important role in the production of RBC which assists in wound healing and cell regeneration.
Note:
Red blood cells in our body help to create collagen. They are tough, white fibers that form the foundation for new tissue. The wound is filled in with new tissue, called granulation tissue over which the new skin behind to form.

Figure 1: Mitosis
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




