
Two trees \[A\] and \[B\] are on the same side of a river. From a point \[C\] in the river, the distances of the trees \[A\] and \[B\] are 250 m and 300 m respectively. If the angle \[C\] is \[45^\circ \], find the distance between the trees. \[\left( {{\rm{Use }}\sqrt 2 = 1.414} \right)\]
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint:
Here, we need to find the distance between the trees \[A\] and \[B\]. First we draw the diagram based on the given information. We will use the law of cosines and the given information to find the distance between the trees \[A\] and \[B\].
Formula Used: We will use the formula for the law of cosines states that \[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\cos C\], where \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and \[C\] is the angle opposite to the side of length \[c\].
Complete step by step solution:
First, we will draw the diagram as per the given information.
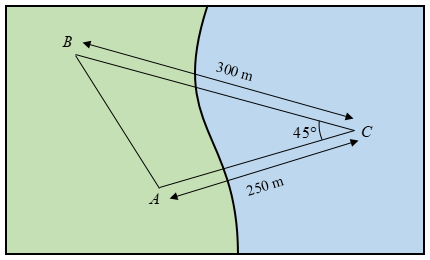
Here, \[C\] is the point in the river. \[BC\] is the distance between the tree \[B\] and point \[C\], and \[AC\] is the distance between the tree \[A\] and the point \[C\].
The distance between the trees \[A\] and \[B\] is \[AB\].
We will use the law of cosines to find the distance between the trees \[A\] and \[B\].
According to the law of cosine, \[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\cos C\], where \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and \[C\] is the angle opposite to the side of the length \[c\].
Substituting \[a = BC\], \[b = AC\], and \[c = AB\] in the law of cosines, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = B{C^2} + A{C^2} - 2\left( {BC} \right)\left( {AC} \right)\cos C\]
Substituting \[BC = 300\]m, \[AC = 250\]m, and \[\angle C = 45^\circ \] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = {\left( {300} \right)^2} + {\left( {250} \right)^2} - 2\left( {300} \right)\left( {250} \right)\cos 45^\circ \]
Applying the exponents on the bases, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 90000 + 62500 - 2\left( {300} \right)\left( {250} \right)\cos 45^\circ \]
We know that the cosine of \[45^\circ \] is \[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\].
Substituting \[\cos 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 90000 + 62500 - 2\left( {300} \right)\left( {250} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)\]
Simplifying the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 90000 + 62500 - \dfrac{{150000}}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
Substituting \[\sqrt 2 = 1.414\] and simplifying, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 90000 + 62500 - \dfrac{{150000}}{{1.414}}\\ \Rightarrow A{B^2} \approx 90000 + 62500 - 106082.03678\end{array}\]
Adding the terms in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} \approx 46417.96322\]
Taking the square roots of both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow AB \approx \sqrt {46417.96322} \approx 215.45\]
\[\therefore \] We get the distance between the trees \[A\] and \[B\] as \[215.45\]m.
Note:
We used the law of cosines to solve the question. In any triangle \[ABC\], we can apply three laws of cosines.
(a) \[{a^2} = {b^2} + {c^2} - 2bc\cos A\], where \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and \[A\] is the angle opposite to the side of length \[a\].
(b) \[{b^2} = {a^2} + {c^2} - 2ac\cos B\], where \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and \[B\] is the angle opposite to the side of length \[b\].
(c) \[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\cos C\], where \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and \[C\] is the angle opposite to the side of length \[c\].
Here, we need to find the distance between the trees \[A\] and \[B\]. First we draw the diagram based on the given information. We will use the law of cosines and the given information to find the distance between the trees \[A\] and \[B\].
Formula Used: We will use the formula for the law of cosines states that \[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\cos C\], where \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and \[C\] is the angle opposite to the side of length \[c\].
Complete step by step solution:
First, we will draw the diagram as per the given information.

Here, \[C\] is the point in the river. \[BC\] is the distance between the tree \[B\] and point \[C\], and \[AC\] is the distance between the tree \[A\] and the point \[C\].
The distance between the trees \[A\] and \[B\] is \[AB\].
We will use the law of cosines to find the distance between the trees \[A\] and \[B\].
According to the law of cosine, \[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\cos C\], where \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and \[C\] is the angle opposite to the side of the length \[c\].
Substituting \[a = BC\], \[b = AC\], and \[c = AB\] in the law of cosines, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = B{C^2} + A{C^2} - 2\left( {BC} \right)\left( {AC} \right)\cos C\]
Substituting \[BC = 300\]m, \[AC = 250\]m, and \[\angle C = 45^\circ \] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = {\left( {300} \right)^2} + {\left( {250} \right)^2} - 2\left( {300} \right)\left( {250} \right)\cos 45^\circ \]
Applying the exponents on the bases, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 90000 + 62500 - 2\left( {300} \right)\left( {250} \right)\cos 45^\circ \]
We know that the cosine of \[45^\circ \] is \[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\].
Substituting \[\cos 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}\] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 90000 + 62500 - 2\left( {300} \right)\left( {250} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)\]
Simplifying the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 90000 + 62500 - \dfrac{{150000}}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
Substituting \[\sqrt 2 = 1.414\] and simplifying, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 90000 + 62500 - \dfrac{{150000}}{{1.414}}\\ \Rightarrow A{B^2} \approx 90000 + 62500 - 106082.03678\end{array}\]
Adding the terms in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} \approx 46417.96322\]
Taking the square roots of both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow AB \approx \sqrt {46417.96322} \approx 215.45\]
\[\therefore \] We get the distance between the trees \[A\] and \[B\] as \[215.45\]m.
Note:
We used the law of cosines to solve the question. In any triangle \[ABC\], we can apply three laws of cosines.
(a) \[{a^2} = {b^2} + {c^2} - 2bc\cos A\], where \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and \[A\] is the angle opposite to the side of length \[a\].
(b) \[{b^2} = {a^2} + {c^2} - 2ac\cos B\], where \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and \[B\] is the angle opposite to the side of length \[b\].
(c) \[{c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\cos C\], where \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and \[C\] is the angle opposite to the side of length \[c\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




