
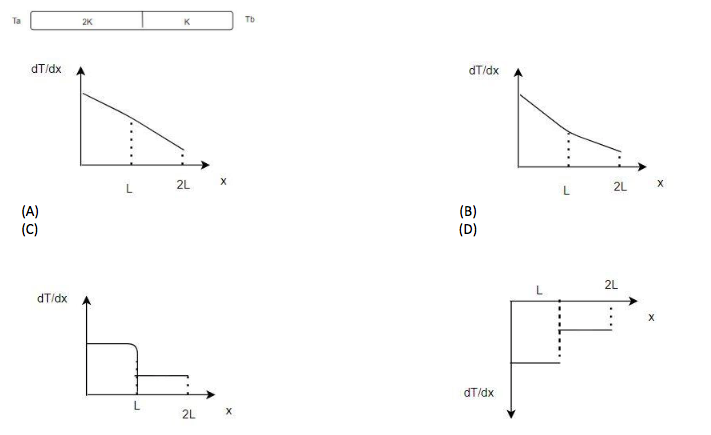
Two rods of same length and cross- sectional area are joined in series. Thermal conductivity of the rods are in the ratio of $2:1$. The ends are maintained at temperature ${\theta _A}$ and ${\theta _B}$ as shown with ${\theta _A} > {\theta _B}$ and sides are thermally insulated. Which of the following graph represents temperature gradient $\left( {\dfrac{{dT}}{{dx}}} \right)$ against $x$ in steady state:

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint:To calculate the temperature gradient of the two rods $A$ and $B$, use the formula of the heat rate flow in the conductor. Substitute the given parameters in the formula and analyze the result obtained to draw the graph of the temperature gradient.
Useful formula:
The thermal current is given by
$dH = \dfrac{{\Delta T}}{{KA}}$
Where $dH$ is the heat rate flow in the conductor, $A$ cross sectional area, $K$ is the thermal conductivity and the $\Delta T$ is the temperature gradient.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that the
The rods have the same length $l$ and the same cross section $A$.
The ratio of the thermal conductivity of the rods, ${T_1}:{T_2} = 2:1$
The temperature of the first rod is maintained greater than the temperature of the second rod.
Since the rods possess the same length and the area the thermal current on the rod will also be the same. By using the formula of thermal current.
$dH = \dfrac{{\Delta T}}{{KA}}$
Substituting the values,
$dH = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{dT}}{{dx}}} \right)}}{{2KA}}$
Since the thermal current in the rods is the same, their temperature gradient is negative.
$\dfrac{{dT}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{ - dH}}{{2KA}}$
Similarly, calculating the temperature gradient for the second rod,
$dH = \dfrac{{\Delta T}}{{KA}}$
$dH = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{dT}}{{dx}}} \right)}}{{KA}}$
Similarly, the temperature gradient has a negative constant value since the thermal current is the same.
$\dfrac{{dT}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{ - dH}}{{KA}}$
Hence both the temperature gradient lies below the x axis.
Thus the option (D) is correct.
Note:The main concept in this problem is the negative sign in the temperature gradient between the rods. Since the thermal current or the heat rate flow in the rods are the same, then it has a constant negative temperature gradient.
Useful formula:
The thermal current is given by
$dH = \dfrac{{\Delta T}}{{KA}}$
Where $dH$ is the heat rate flow in the conductor, $A$ cross sectional area, $K$ is the thermal conductivity and the $\Delta T$ is the temperature gradient.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that the
The rods have the same length $l$ and the same cross section $A$.
The ratio of the thermal conductivity of the rods, ${T_1}:{T_2} = 2:1$
The temperature of the first rod is maintained greater than the temperature of the second rod.
Since the rods possess the same length and the area the thermal current on the rod will also be the same. By using the formula of thermal current.
$dH = \dfrac{{\Delta T}}{{KA}}$
Substituting the values,
$dH = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{dT}}{{dx}}} \right)}}{{2KA}}$
Since the thermal current in the rods is the same, their temperature gradient is negative.
$\dfrac{{dT}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{ - dH}}{{2KA}}$
Similarly, calculating the temperature gradient for the second rod,
$dH = \dfrac{{\Delta T}}{{KA}}$
$dH = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{dT}}{{dx}}} \right)}}{{KA}}$
Similarly, the temperature gradient has a negative constant value since the thermal current is the same.
$\dfrac{{dT}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{ - dH}}{{KA}}$
Hence both the temperature gradient lies below the x axis.
Thus the option (D) is correct.
Note:The main concept in this problem is the negative sign in the temperature gradient between the rods. Since the thermal current or the heat rate flow in the rods are the same, then it has a constant negative temperature gradient.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




