
Two parallel sides of an isosceles trapezium are 6 cm and 14 cm respectively. If the length of each non – parallel side is 5 cm, find the area of the trapezium?
Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: Assume ABCD as the trapezium with AB and CD as the longer and smaller parallel sides respectively. Now, construct two perpendiculars from the vertices C and D on the side AB and assume their length as h. Use the Pythagoras theorem given as ${{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}$ in one of the right triangles formed to find the value of height (h). Here, H is the hypotenuse, P is the perpendicular and B is the base. Finally, apply the formula Area of trapezium = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( a+b \right)h$ to get the answer. Here, a and b are the parallel sides of the trapezium.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have been provided with an isosceles trapezium whose parallel sides are of length 6 cm and 14 cm while the lengths of non parallel sides are 5 cm each. We have to find the area of the trapezium.
Now, let us draw a diagram of the given situation.
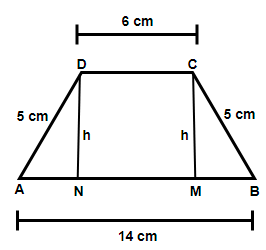
In the above figure we have considered an isosceles trapezium ABCD with AB and CD as the longer and shorter non parallel sides. Also, we have constructed two perpendiculars CM and DN on the sides AB which is considered as the height (h) of the trapezium.
Clearly we can see that NMCD is a rectangle so NM = CD = 6 cm as they are the opposite sides of a rectangle. Also we have AN = BM = 4 cm because AN will be equal to BM (triangle BMC and AND is congruent by RHS congruence criteria) and their sum will be AN + BM = AB – NM = 8 cm.
In right triangle BMC we have, Hypotenuse (H) = BC = 5 cm, Base (B) = BM = 4 cm and Perpendicular (P) = CM = h, so applying the Pythagoras theorem ${{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}$ we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{5}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{4}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=25-16 \\
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{9} \\
& \Rightarrow h=3 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the distance between the parallel sides is 3 cm. Now, we know that the area of a trapezium is given as $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( a+b \right)h$ where a and b are the parallel sides of the trapezium. So substituting the values we get,
$\Rightarrow $ Area of ABCD = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 6+14 \right)\times 3\]
$\Rightarrow $ Area of ABCD = $30c{{m}^{2}}$
Hence, the area of the trapezium is 30 square centimeters.
Note: Remember the properties of rectangle and the four congruence criteria as they are used in problems related to geometry. You must remember the formula of the area of a parallelogram and the Pythagoras theorem to solve the above question. Note that the perpendicular distance between the two parallel lines are always equal. Do not forget to draw the diagram of the given conditions as they will clear all the confusions related to the measurements.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have been provided with an isosceles trapezium whose parallel sides are of length 6 cm and 14 cm while the lengths of non parallel sides are 5 cm each. We have to find the area of the trapezium.
Now, let us draw a diagram of the given situation.

In the above figure we have considered an isosceles trapezium ABCD with AB and CD as the longer and shorter non parallel sides. Also, we have constructed two perpendiculars CM and DN on the sides AB which is considered as the height (h) of the trapezium.
Clearly we can see that NMCD is a rectangle so NM = CD = 6 cm as they are the opposite sides of a rectangle. Also we have AN = BM = 4 cm because AN will be equal to BM (triangle BMC and AND is congruent by RHS congruence criteria) and their sum will be AN + BM = AB – NM = 8 cm.
In right triangle BMC we have, Hypotenuse (H) = BC = 5 cm, Base (B) = BM = 4 cm and Perpendicular (P) = CM = h, so applying the Pythagoras theorem ${{H}^{2}}={{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}$ we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{5}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{4}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=25-16 \\
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{9} \\
& \Rightarrow h=3 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the distance between the parallel sides is 3 cm. Now, we know that the area of a trapezium is given as $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( a+b \right)h$ where a and b are the parallel sides of the trapezium. So substituting the values we get,
$\Rightarrow $ Area of ABCD = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 6+14 \right)\times 3\]
$\Rightarrow $ Area of ABCD = $30c{{m}^{2}}$
Hence, the area of the trapezium is 30 square centimeters.
Note: Remember the properties of rectangle and the four congruence criteria as they are used in problems related to geometry. You must remember the formula of the area of a parallelogram and the Pythagoras theorem to solve the above question. Note that the perpendicular distance between the two parallel lines are always equal. Do not forget to draw the diagram of the given conditions as they will clear all the confusions related to the measurements.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




