
Two oxidation states for chlorine are found in the compound:
(A) $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$
(B) KCl
(C) $KCl{{O}_{3}}$
(D) $C{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Oxidation number is also known as an oxidation state. It is defined as the total number of electrons that an atom either gains or loses, in order to form chemical bonds with another atom.
Complete step by step answer:
We will check the oxidation states in all the given molecules in the question.
i) The molecule $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$ can also be written as Ca(OCl)Cl which contains two chlorine atoms with different oxidation states in the $C{{l}^{-1}}$ ,it is -1 Oxidation State while in $OC{{l}^{-1}}$ ion is in +1 oxidation state. This is proved with the molecular structure of the compound given below.
\[\text{C}{{\text{l}}^{-}}\text{ C}{{\text{a}}^{2+}}\text{ }{{\text{ }}^{-}}\text{OCl}\]
Now, let’s find the oxidation states of the chlorine atom in the given ions.
Oxidation state of O in $OC{{l}^{-}}$ is -2. So, we can write that
\[\begin{align}
& -2\text{ + X = }-1 \\
& \text{X = +1} \\
\end{align}\]
For $C{{l}^{-}}$ ion, we know that in $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$ , Ca is in +2 oxidation state and $OC{{l}^{-}}$ has a formal charge of -1. So, we can write that
\[+2+Y+1=0\]
\[Y=-1\]
Hence, we can say that the oxidation state of chlorine in $C{{l}^{-}}$ is -1.
ii) Oxidation state of Cl in \[\text{KCl}\] can be determined as -1 for Potassium has an Oxidation state of +1. This is demonstrated by the following diagram of \[\text{KCl}\] compound and with equations proving the oxidation state of chlorine to be -1.
\[K-Cl\]
\[\begin{align}
& \text{For KCl,} \\
& +1\text{ + Y = 0 (stable molecule)} \\
& \text{K Cl } \\
& \text{Y = }-1 \\
& \text{ Oxidation number of Cl = }-1 \\
\end{align}\]
Being an ionic compound, Potassium’s oxidation state is always +1, so in the compound $KCl{{O}_{3}}$, potassium has an oxidation state of +1 while chlorate that is \[\text{Cl}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}^{-}\] has an oxidation state of -1. We know that the oxidation state of oxygen is -2 and 3 oxygen atoms being present in the compound, the total oxidation number of -6 is achieved by oxygen. The following is the molecular structure of the compound inclusive of equations prove the fact that chlorine has an Oxidation state of +5 in \[\text{KCl}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\].
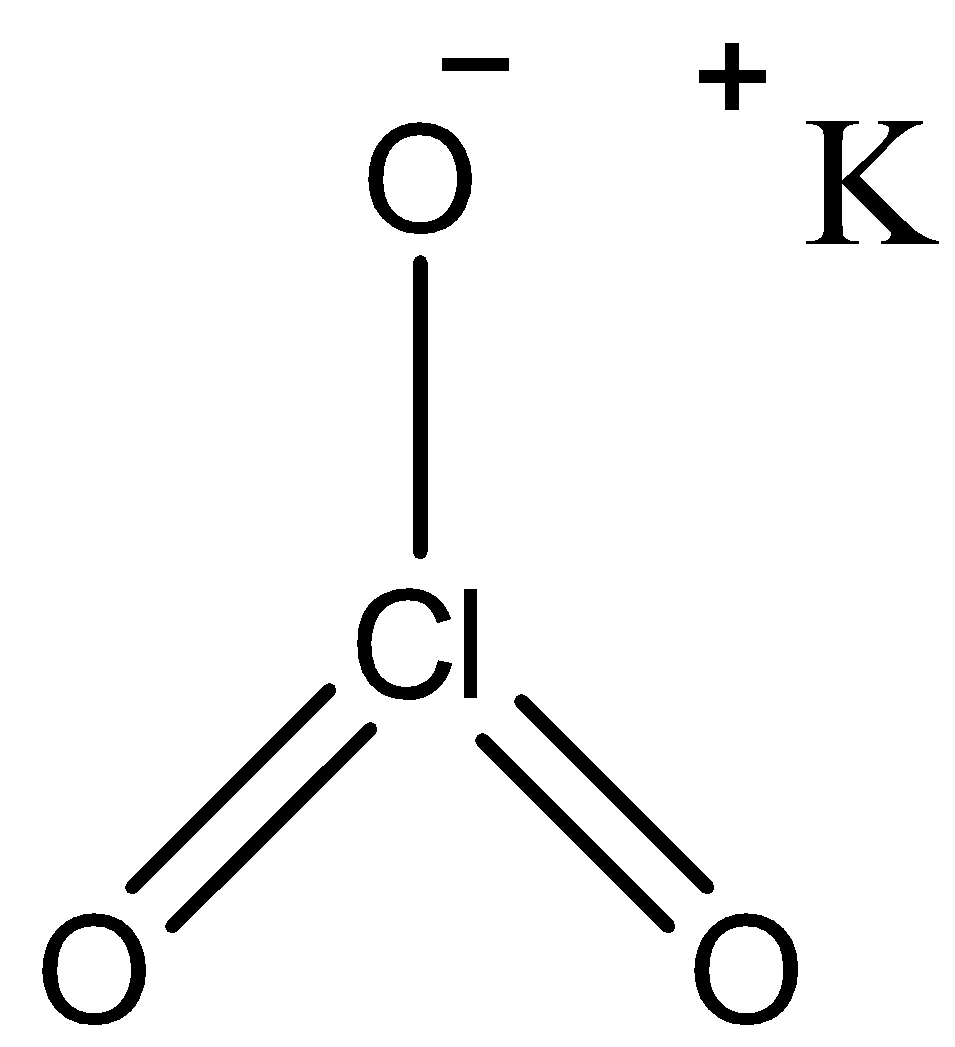
So, for $KCl{{O}_{3}}$, we can write that
\[\begin{align}
& +1\text{ + Y + 3(}-2\text{) = 0 (stable molecule)} \\
& \text{K Cl }{{\text{O}}_{3}} \\
& \text{Y = +}5 \\
\end{align}\]
So, Y= Oxidation state of Cl = +5
iv) In the compound \[\text{C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}\], which is also known as chlorine heptoxide, we know the oxidation number of oxygen is -2 and hence the total oxidation number of oxygen in this compound is -14 which is denoted in the equation given below and thus we can equate the oxidation number of Chlorine. Chlorine having two atoms in the compound has an oxidation number of +7. The molecular structure and the equations proving the oxidation number of Chlorine is given as follows
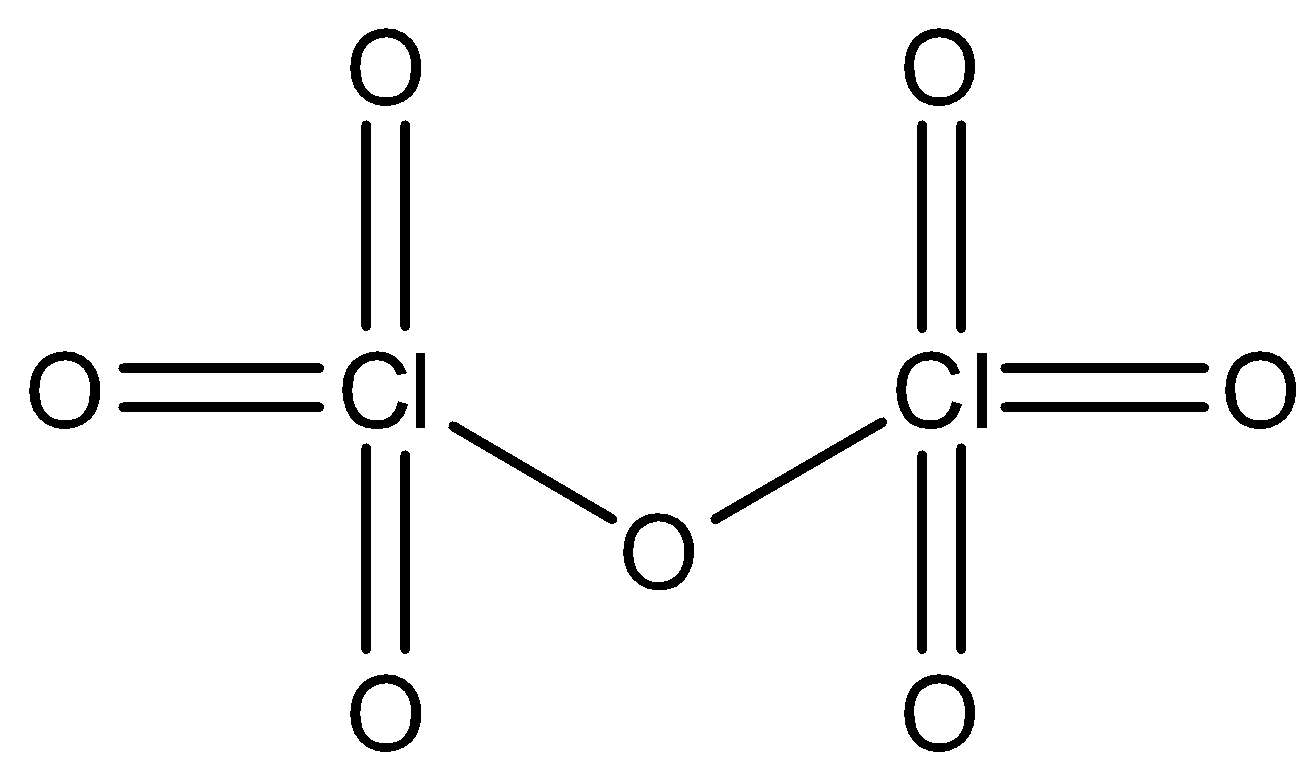
\[\begin{align}
& \text{For C}{{\text{l}}_{2}}{{\text{O}}_{7}}\text{,} \\
& \text{2Y + 7(}-2\text{) = 0 (stable molecule)} \\
& \text{C}{{\text{l}}_{2}}\text{ }{{\text{O}}_{7}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ 2Y = 14} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ Y = 7} \\
& \text{Y = +7} \\
& \text{ Oxidation number of Cl = +7} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence we can see that the compound \[\text{CaOC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] is the only compound given in the options which has two oxidation states of chlorine.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We should know that the oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to the charge of the ion. This can be shown with an example. Like the oxidation number of H is +1. But when it recombines with less electronegative elements, the oxidation state becomes -1. Similarly, the oxidation number of oxygen is usually -2, but it becomes -1, in case of the peroxides.
Complete step by step answer:
We will check the oxidation states in all the given molecules in the question.
i) The molecule $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$ can also be written as Ca(OCl)Cl which contains two chlorine atoms with different oxidation states in the $C{{l}^{-1}}$ ,it is -1 Oxidation State while in $OC{{l}^{-1}}$ ion is in +1 oxidation state. This is proved with the molecular structure of the compound given below.
\[\text{C}{{\text{l}}^{-}}\text{ C}{{\text{a}}^{2+}}\text{ }{{\text{ }}^{-}}\text{OCl}\]
Now, let’s find the oxidation states of the chlorine atom in the given ions.
Oxidation state of O in $OC{{l}^{-}}$ is -2. So, we can write that
\[\begin{align}
& -2\text{ + X = }-1 \\
& \text{X = +1} \\
\end{align}\]
For $C{{l}^{-}}$ ion, we know that in $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$ , Ca is in +2 oxidation state and $OC{{l}^{-}}$ has a formal charge of -1. So, we can write that
\[+2+Y+1=0\]
\[Y=-1\]
Hence, we can say that the oxidation state of chlorine in $C{{l}^{-}}$ is -1.
ii) Oxidation state of Cl in \[\text{KCl}\] can be determined as -1 for Potassium has an Oxidation state of +1. This is demonstrated by the following diagram of \[\text{KCl}\] compound and with equations proving the oxidation state of chlorine to be -1.
\[K-Cl\]
\[\begin{align}
& \text{For KCl,} \\
& +1\text{ + Y = 0 (stable molecule)} \\
& \text{K Cl } \\
& \text{Y = }-1 \\
& \text{ Oxidation number of Cl = }-1 \\
\end{align}\]
Being an ionic compound, Potassium’s oxidation state is always +1, so in the compound $KCl{{O}_{3}}$, potassium has an oxidation state of +1 while chlorate that is \[\text{Cl}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}^{-}\] has an oxidation state of -1. We know that the oxidation state of oxygen is -2 and 3 oxygen atoms being present in the compound, the total oxidation number of -6 is achieved by oxygen. The following is the molecular structure of the compound inclusive of equations prove the fact that chlorine has an Oxidation state of +5 in \[\text{KCl}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\].

So, for $KCl{{O}_{3}}$, we can write that
\[\begin{align}
& +1\text{ + Y + 3(}-2\text{) = 0 (stable molecule)} \\
& \text{K Cl }{{\text{O}}_{3}} \\
& \text{Y = +}5 \\
\end{align}\]
So, Y= Oxidation state of Cl = +5
iv) In the compound \[\text{C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}\], which is also known as chlorine heptoxide, we know the oxidation number of oxygen is -2 and hence the total oxidation number of oxygen in this compound is -14 which is denoted in the equation given below and thus we can equate the oxidation number of Chlorine. Chlorine having two atoms in the compound has an oxidation number of +7. The molecular structure and the equations proving the oxidation number of Chlorine is given as follows

\[\begin{align}
& \text{For C}{{\text{l}}_{2}}{{\text{O}}_{7}}\text{,} \\
& \text{2Y + 7(}-2\text{) = 0 (stable molecule)} \\
& \text{C}{{\text{l}}_{2}}\text{ }{{\text{O}}_{7}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ 2Y = 14} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ Y = 7} \\
& \text{Y = +7} \\
& \text{ Oxidation number of Cl = +7} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence we can see that the compound \[\text{CaOC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] is the only compound given in the options which has two oxidation states of chlorine.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We should know that the oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to the charge of the ion. This can be shown with an example. Like the oxidation number of H is +1. But when it recombines with less electronegative elements, the oxidation state becomes -1. Similarly, the oxidation number of oxygen is usually -2, but it becomes -1, in case of the peroxides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




