
When two atomic orbitals combine, they form:
A.One molecular orbital
B.Two molecular orbitals
C.Three molecular orbitals
D.Four molecular orbitals
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: Molecular orbital theory uses quantum mechanics to describe the electronic structure of molecules. According to this theory, electrons are treated as entities that move under the influence of the nucleus of the atom, rather than assigning these electrons to individual chemical bonds between atoms. Molecular orbital theory also employs Linear combination of atomic orbital or LCAO for representing the molecular orbitals that are formed by the bonds between the atoms.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
The electrons shared between the two atoms are thus dispersed around the nuclei. The electrons that form the apparent ‘bonds’ are again placed in two different spatial zones. Some of them are placed between the nuclei of the two combining atoms. These electrons are thus placed in the bonding orbital. On the other hand, the remaining set of electrons are placed outside the zone of the nuclei and are placed in the antibonding orbital.
Thus, depending on the number of bonds that are formed, the number of bonding and antibonding orbitals also vary. This is because bonds are formed between hybridized orbitals of the atoms. If ‘n’ number of orbitals are combined, then the number of orbitals formed would also be equal to ‘n’.
The following molecular orbital diagram explains the formation of 2 orbitals, viz. one bonding orbital and one anti bonding orbital, when two ‘1s’ orbitals combine:
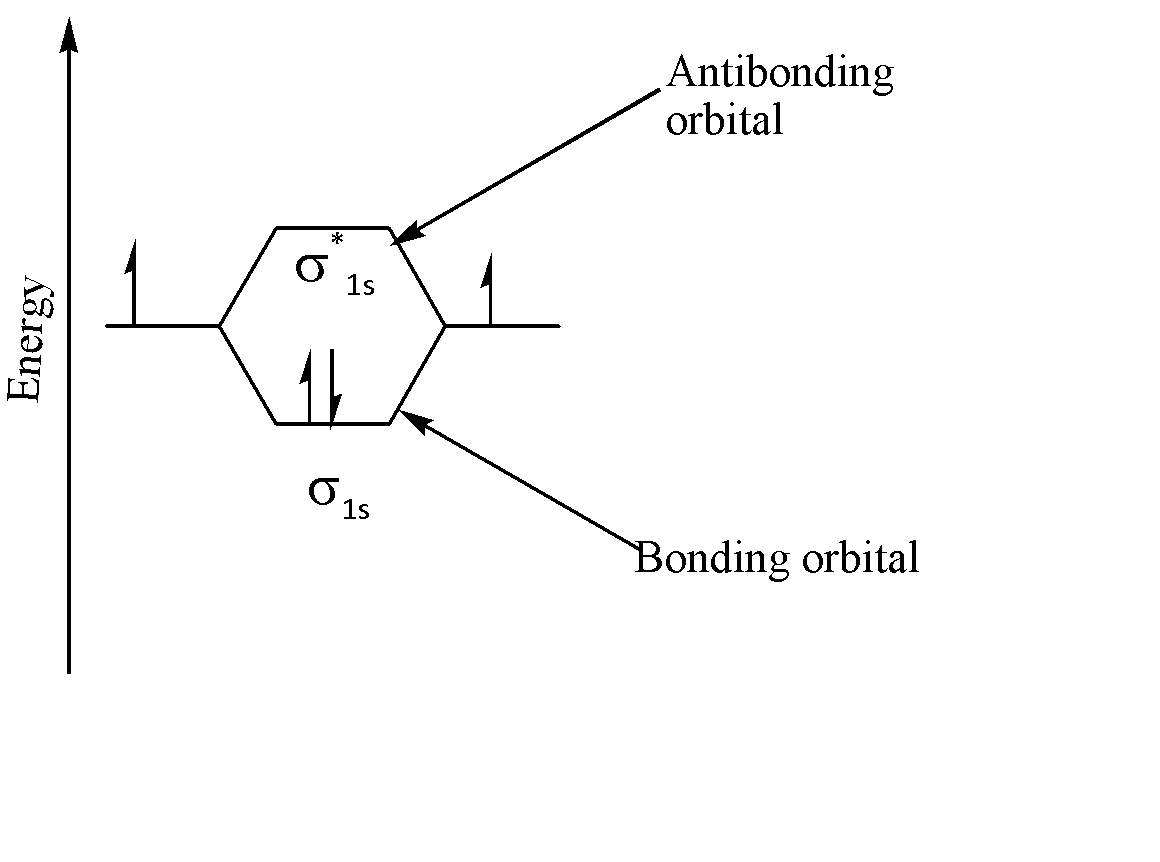
Thus, we can say that if two orbitals are combined, then they form two orbitals as a result.
Hence, Option B is the correct option
Note: Electrons will fill according to the energy levels of the orbitals. They will first fill the lower energy orbitals, and then they will fill the higher energy orbitals. If a bond order of zero is obtained, that means that the molecule is too unstable and so it will not exist.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
The electrons shared between the two atoms are thus dispersed around the nuclei. The electrons that form the apparent ‘bonds’ are again placed in two different spatial zones. Some of them are placed between the nuclei of the two combining atoms. These electrons are thus placed in the bonding orbital. On the other hand, the remaining set of electrons are placed outside the zone of the nuclei and are placed in the antibonding orbital.
Thus, depending on the number of bonds that are formed, the number of bonding and antibonding orbitals also vary. This is because bonds are formed between hybridized orbitals of the atoms. If ‘n’ number of orbitals are combined, then the number of orbitals formed would also be equal to ‘n’.
The following molecular orbital diagram explains the formation of 2 orbitals, viz. one bonding orbital and one anti bonding orbital, when two ‘1s’ orbitals combine:

Thus, we can say that if two orbitals are combined, then they form two orbitals as a result.
Hence, Option B is the correct option
Note: Electrons will fill according to the energy levels of the orbitals. They will first fill the lower energy orbitals, and then they will fill the higher energy orbitals. If a bond order of zero is obtained, that means that the molecule is too unstable and so it will not exist.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




